Lesson 2 slides RBD comments
... segment (RBD: I’m going to be obnoxious and ask, “Why does the user need to know about market segmentation—isn’t it enough to point out that different markets have different prices and requirements?—market segmentation sounds a bit like business school jargon….) ...
... segment (RBD: I’m going to be obnoxious and ask, “Why does the user need to know about market segmentation—isn’t it enough to point out that different markets have different prices and requirements?—market segmentation sounds a bit like business school jargon….) ...
Chapter 02 Study Guide
... C > B the action is rejected. (In this case, the item is not purchased.) Thus where supply equals demand, the purchasing stops and equilibrium is reached. The sum of the net benefits of each participant in the market is maximized at this point, and therefore equilibrium is the standard against which ...
... C > B the action is rejected. (In this case, the item is not purchased.) Thus where supply equals demand, the purchasing stops and equilibrium is reached. The sum of the net benefits of each participant in the market is maximized at this point, and therefore equilibrium is the standard against which ...
Module on the basics of Competition policy and law
... circle. They compete on non-price competition (facilities like cricket match score, stock market quotation etc.) among themselves and take competitors’ possible reactions into account while deciding their strategy. Need for regulation As competition results in lower profits, firms have an incentive ...
... circle. They compete on non-price competition (facilities like cricket match score, stock market quotation etc.) among themselves and take competitors’ possible reactions into account while deciding their strategy. Need for regulation As competition results in lower profits, firms have an incentive ...
ECO 212 – Macroeconomics
... 13. Refer to the above diagram. If society is currently producing the combination of bicycles and computers shown by point D, the production of 2 more units of bicycles: A. cannot be achieved because resources are fully employed. B. will cost 1 unit of computers. C. will cost 2 units of computers. ...
... 13. Refer to the above diagram. If society is currently producing the combination of bicycles and computers shown by point D, the production of 2 more units of bicycles: A. cannot be achieved because resources are fully employed. B. will cost 1 unit of computers. C. will cost 2 units of computers. ...
Price Elasticity of Demand - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... • Supply is more elastic than in market period P ...
... • Supply is more elastic than in market period P ...
Study Guide Sample Chapter 3
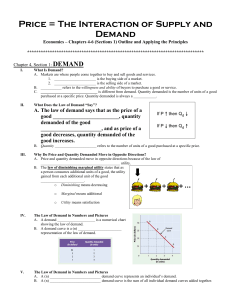
... 8. The ____________________ of demand states that when the price of a good rises, and everything else remains the same, the quantity of the good demanded will ____________________. 9. The ____________________ shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded, holding const ...
... 8. The ____________________ of demand states that when the price of a good rises, and everything else remains the same, the quantity of the good demanded will ____________________. 9. The ____________________ shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded, holding const ...
abhijit bhowmick
... Steering initiatives towards achievement of organisational goals & vision with chief responsibilities pertaining to Strategy Planning, International Marketing, Business Development, Distribution, Technocommercial Functions, Product Management across Europe, Africa & the Middle East. Managing a team ...
... Steering initiatives towards achievement of organisational goals & vision with chief responsibilities pertaining to Strategy Planning, International Marketing, Business Development, Distribution, Technocommercial Functions, Product Management across Europe, Africa & the Middle East. Managing a team ...
Module 6
... understand. Focus all communication. • Different positioning strategies include: attribute, benefit, use/application, user, competitor, product category, and quality/price positioning. ...
... understand. Focus all communication. • Different positioning strategies include: attribute, benefit, use/application, user, competitor, product category, and quality/price positioning. ...
Markets Manual
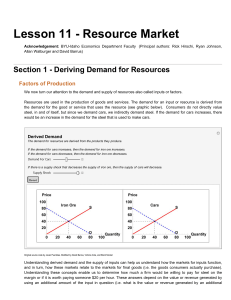
... Suppliers—those prepared (if conditions are right) to sell a given product in this market—are assumed to be business firms. The suppliers, wheat farmers in this module, are assumed to be motivated by only one thing: profit. Ignoring all sorts of potential complexities, profit is defined as the total ...
... Suppliers—those prepared (if conditions are right) to sell a given product in this market—are assumed to be business firms. The suppliers, wheat farmers in this module, are assumed to be motivated by only one thing: profit. Ignoring all sorts of potential complexities, profit is defined as the total ...
... Throughout history, prices have usually been determined between the sellers and buyers in price negotiations (bargains). Traditionally, consumer decisions and purchase decision making processes largely depend on price. However, non–price factors, e.g. product features, place of origin, communication ...
Document
... and keep the sale price equal or near the average for the market. If successful companies may lower the price of a product if they have a significant production cost advantage over the competition. In doing so, it can further increase it’s Market Share. – Cost focus: Business seek a lower-cost advan ...
... and keep the sale price equal or near the average for the market. If successful companies may lower the price of a product if they have a significant production cost advantage over the competition. In doing so, it can further increase it’s Market Share. – Cost focus: Business seek a lower-cost advan ...
Market Disturbances
... Suppliers—those prepared (if conditions are right) to sell a given product in this market—are assumed to be business firms. The suppliers, wheat farmers in this module, are assumed to be motivated by only one thing: profit. Ignoring all sorts of potential complexities, profit is defined as the tota ...
... Suppliers—those prepared (if conditions are right) to sell a given product in this market—are assumed to be business firms. The suppliers, wheat farmers in this module, are assumed to be motivated by only one thing: profit. Ignoring all sorts of potential complexities, profit is defined as the tota ...
Designing & Managing Services
... detergent to liquid detergent. Such innovations tend to be easily and readily accepted by the market and they quickly move through the PLC. ...
... detergent to liquid detergent. Such innovations tend to be easily and readily accepted by the market and they quickly move through the PLC. ...