Data Communication
... Consumers don’t buy products; they buy benefits Functional benefits: relating to the practical purpose a product ...
... Consumers don’t buy products; they buy benefits Functional benefits: relating to the practical purpose a product ...
4.04 Practice Exam
... Product mix is the particular assortment of goods and services that a business offers to meet the needs of its market(s) and to achieve its goals. Often, the target market's needs and wants change, so the business must be willing to change its product mix, so it can remain competitive in the marketp ...
... Product mix is the particular assortment of goods and services that a business offers to meet the needs of its market(s) and to achieve its goals. Often, the target market's needs and wants change, so the business must be willing to change its product mix, so it can remain competitive in the marketp ...
Chapter 12
... Marketing Orientation – approach requiring organizations to gather information about customer needs, share information across firm, use information to build long-term relationships with customers. ...
... Marketing Orientation – approach requiring organizations to gather information about customer needs, share information across firm, use information to build long-term relationships with customers. ...
Marketing - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... • The size and diversity of the consumer market forces marketers to decide which groups they want to serve. • Market Segmentation -- Divides the total market ...
... • The size and diversity of the consumer market forces marketers to decide which groups they want to serve. • Market Segmentation -- Divides the total market ...
Segmentation and positioning
... makes the most sense. Products that can vary in design, such as cameras and automobiles, are more suited to differentiation or concentration. The product’s life-cycle stage also must be considered. When a firm introduces a new product, it may be practical to launch only one version, initially. Marke ...
... makes the most sense. Products that can vary in design, such as cameras and automobiles, are more suited to differentiation or concentration. The product’s life-cycle stage also must be considered. When a firm introduces a new product, it may be practical to launch only one version, initially. Marke ...
Market Segmentation
... Develop Product Positioning Positioning can be achieved through any one of these strategies Superiority to competitive products on one or more product attributes Positioned by use or application Positioned in terms of particular types of users Positioned relative to a product class Posi ...
... Develop Product Positioning Positioning can be achieved through any one of these strategies Superiority to competitive products on one or more product attributes Positioned by use or application Positioned in terms of particular types of users Positioned relative to a product class Posi ...
• Chapter 5 The Free Enterprise System • Chapter 6 Legal and
... ways. The concept of profit is the driving force in our free enterprise system. It encourages people to develop new products and services in the hope of making a profit. Without profit, few new products would be introduced. Profit remains high when sales are high and costs are kept low. This encoura ...
... ways. The concept of profit is the driving force in our free enterprise system. It encourages people to develop new products and services in the hope of making a profit. Without profit, few new products would be introduced. Profit remains high when sales are high and costs are kept low. This encoura ...
+ of operating cost and profit centres
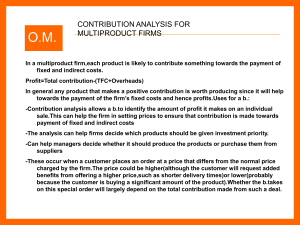
... In a multiproduct firm,each product is likely to contribute something towards the payment of fixed and indirect costs. Profit=Total contribution-(TFC+Overheads) In general any product that makes a positive contribution is worth producing since it will help towards the payment of the firm’s fixed cos ...
... In a multiproduct firm,each product is likely to contribute something towards the payment of fixed and indirect costs. Profit=Total contribution-(TFC+Overheads) In general any product that makes a positive contribution is worth producing since it will help towards the payment of the firm’s fixed cos ...
Marketing Activity of the International New Ventures. Results
... exceeded their competitors with respect to efficiency of supply (see also Table 1)9. A similar result was obtained for the same question in the 2013 study, when 65% of companies admitted they exceeded their competitors with respect to efficiency of supply. However, when asked an open question about ...
... exceeded their competitors with respect to efficiency of supply (see also Table 1)9. A similar result was obtained for the same question in the 2013 study, when 65% of companies admitted they exceeded their competitors with respect to efficiency of supply. However, when asked an open question about ...
MP_CHAPTER 1
... Intranets – connecting with others in the company, and Extranets – connecting with strategic partners, suppliers, and dealers. ...
... Intranets – connecting with others in the company, and Extranets – connecting with strategic partners, suppliers, and dealers. ...
View/Open
... in each of four food retailer categories were surveyed. Those four retailer types were: (1) locallyowned, family-operated grocery stores, (2) produce markets carrying fruits and vegetables, primarily, (3) butcher shops selling meat, eggs and dairy products, and (4) convenience stores marketing food ...
... in each of four food retailer categories were surveyed. Those four retailer types were: (1) locallyowned, family-operated grocery stores, (2) produce markets carrying fruits and vegetables, primarily, (3) butcher shops selling meat, eggs and dairy products, and (4) convenience stores marketing food ...
e-con 159 transcript - Consortium for Educational
... Micro marketing is not just selling stuffs but it is also looking at what the customers want. How do we enhance the satisfaction? At the macro level we have to look into the factors at the international and at the national level, looking at how everybody in the country can have access to the things ...
... Micro marketing is not just selling stuffs but it is also looking at what the customers want. How do we enhance the satisfaction? At the macro level we have to look into the factors at the international and at the national level, looking at how everybody in the country can have access to the things ...
Lecturer Notes
... rivals. Consideration should also be given to the various sources of information available to firms that enable them to gauge competitors’ strengths and weaknesses. Competing successfully depends not only on an ability to identify customer wants and needs but also upon an ability to be able to satis ...
... rivals. Consideration should also be given to the various sources of information available to firms that enable them to gauge competitors’ strengths and weaknesses. Competing successfully depends not only on an ability to identify customer wants and needs but also upon an ability to be able to satis ...
finalterm examination
... options is not a part of supply chain management? Planning► Implementing► Controlling► the physical flow of goods, services, and information Gathering customer’s ideas for new► products Question No: 48 ( Marks: 1 ) - Please choose one Being a marketing manager, you ha ...
... options is not a part of supply chain management? Planning► Implementing► Controlling► the physical flow of goods, services, and information Gathering customer’s ideas for new► products Question No: 48 ( Marks: 1 ) - Please choose one Being a marketing manager, you ha ...
Chapter 12 Monopoly I. Market Power A. Market power and
... b) Monopoly firms can charge different buyers different prices for the same good or service. Giving a lower price on advance purchase airline tickets is an example of this form of price discrimination. C. Profiting by Price Discriminating Figure 12.8 and Figure 12.9 show the same market with a sing ...
... b) Monopoly firms can charge different buyers different prices for the same good or service. Giving a lower price on advance purchase airline tickets is an example of this form of price discrimination. C. Profiting by Price Discriminating Figure 12.8 and Figure 12.9 show the same market with a sing ...
Marketing Dynamics
... enhance relationships with customers and other partners, at a profit, so that the objectives of the parties involved are met. This is achieved by mutual exchange and fulfilment of promises’ (Gronroos, 1997) ...
... enhance relationships with customers and other partners, at a profit, so that the objectives of the parties involved are met. This is achieved by mutual exchange and fulfilment of promises’ (Gronroos, 1997) ...
A Marketing Strategy Analysis of a New Product Launch
... that the companies sell, lease or supply to others. It also includes the wholesale and retail companies which are purchasing goods for resale or lease with a profit. It is possible to subdivide institutional markets into the industrial, commercial and government markets. Target markets thus do not c ...
... that the companies sell, lease or supply to others. It also includes the wholesale and retail companies which are purchasing goods for resale or lease with a profit. It is possible to subdivide institutional markets into the industrial, commercial and government markets. Target markets thus do not c ...
MBA 860 - Adv. Mkt. Strategy
... When portfolio models were first introduced, marketers did what the grid position indicated rather than using them as a tool to help visualize company’s mix of SBUs, interrelationships, relative strengths, etc. ...
... When portfolio models were first introduced, marketers did what the grid position indicated rather than using them as a tool to help visualize company’s mix of SBUs, interrelationships, relative strengths, etc. ...
Marketing - Harris Academy
... Brand is perceived to be of high quality, which can mean premium prices can be charged. Makes it easier to launch new products onto the market as there is already a brand family of products. Brand names can be expensive to build up as it takes time to achieve their reputation. Bad publicity can affe ...
... Brand is perceived to be of high quality, which can mean premium prices can be charged. Makes it easier to launch new products onto the market as there is already a brand family of products. Brand names can be expensive to build up as it takes time to achieve their reputation. Bad publicity can affe ...
Sports and Entertainment Marketing
... Tactic is the way a product or service is _______________ in the minds of customers from other competing products or services and strategies are the _________ by which tactics are implemented 9. BEATING THE COMPETITION “Winning the game” in business means ____________ market share over competitors a ...
... Tactic is the way a product or service is _______________ in the minds of customers from other competing products or services and strategies are the _________ by which tactics are implemented 9. BEATING THE COMPETITION “Winning the game” in business means ____________ market share over competitors a ...
JOB DESCRIPTION
... (Products include: events, entertainment, hours of opening, interpretation and exhibitions, pricing deals, joint ventures with transport companies and other attractions, retail and catering opportunities or anything else which might impact on visitor numbers and profit.) ...
... (Products include: events, entertainment, hours of opening, interpretation and exhibitions, pricing deals, joint ventures with transport companies and other attractions, retail and catering opportunities or anything else which might impact on visitor numbers and profit.) ...
Slide 1
... Sam's Bakery (SB) is located in XXX, New York. SB produces a variety of cookies, Polish delicacies, white rolls and rye bread. SB sells their products at their production location, at a storefront location and wholesales to several areas markets. SB sells bread from $3.00 to $6.00, cookies from $0.7 ...
... Sam's Bakery (SB) is located in XXX, New York. SB produces a variety of cookies, Polish delicacies, white rolls and rye bread. SB sells their products at their production location, at a storefront location and wholesales to several areas markets. SB sells bread from $3.00 to $6.00, cookies from $0.7 ...
Competitive Strategy
... company resources in the search for a competitive advantage in the marketplace. The steps are well known: analyze where your customers, competitors and company are today; determine where you want them to be tomorrow; develop a plan for getting there; and then implement it. It all sounds so simple. B ...
... company resources in the search for a competitive advantage in the marketplace. The steps are well known: analyze where your customers, competitors and company are today; determine where you want them to be tomorrow; develop a plan for getting there; and then implement it. It all sounds so simple. B ...
Service parts pricing

Service Parts Pricing refers to the aspect of Service Lifecycle Management that deals with setting prices for service parts in the after-sales market. Like other streams of Pricing, Service Parts Pricing is a scientific pursuit aimed at aligning service part prices internally to be logical and consistent, and at the same time aligning them externally with the market. This is done with the overarching aim of extracting the maximum possible price from service parts and thus maximize the profit margins. Pricing analysts have to be cognizant of possible repercussions of pricing their parts too high or too low in the after-sales market; they constantly have to strive to get the prices just right towards achieving maximum margins and maximum possible volumes.The after-sales market consists of service part and after-sales service. These areas often account for a low share in total sales, but for a relatively high share in total profits. It is important to understand that the after-sales supply chain is very different from the manufacturing supply chain, and hence rules that apply to pricing manufacturing parts do not hold good for pricing service parts. Service Parts Pricing requires a different outlook and approach.Service networks deal with a considerably higher number of SKUs and a heterogeneous product portfolio, are more complex, have a sporadic nature of demand AND have minimal response times and strict SLAs. Companies have traditionally been content with outsourcing the after-sales side of their business and have encouraged third-party parts and service providers in the market. The result has been a bevy of these operators in the market with strict price competition and low margins.Increasingly, however, companies are realizing the importance of the after-sales market and its impact on customer retention and loyalty. Increasingly, also, companies have realized that they can extract higher profit margins from the after-sales services market due to the intangible nature of services. Companies are investing in their after-sales service networks to deliver high levels of customer service and in return command higher prices for their parts and services. Customers are being sold the concept of total cost of ownership (TCO) and are being made to realize that buying from OEMs comes packaged with better distribution channels, shorter response times, better knowledge on products, and ultimately higher product uptime.The challenge for companies is to provide reliable service levels in an environment of uncertainty. Unlike factories, businesses can’t produce services in advance of demand. They can manufacture them only when an unpredictable event, such as a product failure, triggers a need. The challenge for Service Parts Pricing is to put a value to this customer need. Parts that are critical, for example, can command higher prices. So can parts that only the OEM provides in the market. Parts that are readily available in the market cannot, and must not, be priced to high. Another problem with after-sales market is that demand cannot be stimulated with price discounts, customers do not stock up service parts just because they are on discount. On the up-side, the fact that most service parts are inelastic means pricing analysts can raise prices without the adverse effects that manufacturing or retail networks witness.These and other characteristics of the after-sales market give Service Parts Pricing a life of its own. Companies are realizing that they can use the lever of service part pricing to increase profitability and don't have to take prices as market determined. Understanding customer needs and expectations, along with the company's internal strengths and weaknesses, goes a long way in designing an effective service part pricing strategy.