Developing the International Marketing Plan
... must identify and understand the target market • Determine if there is or is not a global market ...
... must identify and understand the target market • Determine if there is or is not a global market ...
Full Text - International Journal of Business and Social Science
... service enterprises may have a monopoly in a particular service, such as water or power supply and it may fix a price for it, but the service being a public utility, it may set a price lower than its cost of production so that the welfare of the community is not adversely affected. The general princ ...
... service enterprises may have a monopoly in a particular service, such as water or power supply and it may fix a price for it, but the service being a public utility, it may set a price lower than its cost of production so that the welfare of the community is not adversely affected. The general princ ...
Chapter 1 PowerPoint - Rogers Heritage High School
... Travelers want a clean room and someone to keep it clean. (10) Customers want quality food and someone to prepare and serve it well. (11) ...
... Travelers want a clean room and someone to keep it clean. (10) Customers want quality food and someone to prepare and serve it well. (11) ...
Business marketing
... the key areas of uncertainty as to trends or events that have the potential to impact strategy? Internal Analysis Understanding a business in depth is the goal of internal analysis. This analysis is based resources and capabilities of the firm. Resources A good starting point to identify company res ...
... the key areas of uncertainty as to trends or events that have the potential to impact strategy? Internal Analysis Understanding a business in depth is the goal of internal analysis. This analysis is based resources and capabilities of the firm. Resources A good starting point to identify company res ...
MARKETING
... UTILITY, VALUE AND SATISFACTION Utility is “The quality of being practical use”. Value means a numerical quantity measured or the quality (positive or negative) that renders something desirable. Satisfaction is “State of being gratified” In marketing there are number of product options for a human n ...
... UTILITY, VALUE AND SATISFACTION Utility is “The quality of being practical use”. Value means a numerical quantity measured or the quality (positive or negative) that renders something desirable. Satisfaction is “State of being gratified” In marketing there are number of product options for a human n ...
New product development
... Same as butt-on, but arranging the new item at the top of a season. Example: Polaroid used this strategy often, putting new replacement items out during the Christmas season. Another version of butt-on, but arranged by a sequence of market segments. Mercedes introduced its C series country by countr ...
... Same as butt-on, but arranging the new item at the top of a season. Example: Polaroid used this strategy often, putting new replacement items out during the Christmas season. Another version of butt-on, but arranged by a sequence of market segments. Mercedes introduced its C series country by countr ...
The Market System and the Circular Flow
... Characteristics of the Market System • Freedom of enterprise and choice – free to obtain and use resources to produce their choice of goods/services and sell them – enable owners to employ or dispose of their property and money as they see fit. • Allows individuals to designate who receives their p ...
... Characteristics of the Market System • Freedom of enterprise and choice – free to obtain and use resources to produce their choice of goods/services and sell them – enable owners to employ or dispose of their property and money as they see fit. • Allows individuals to designate who receives their p ...
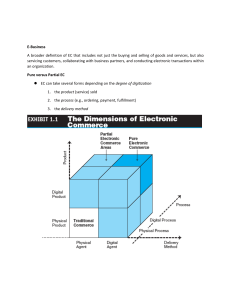
Course\EC\EC by KMV SY BBA ITM
... Technology that enables networked peer computers to share data and processing with each other directly; can be used in C2C, B2B, and B2C e-commerce. For example, in P2P application (Viber, WeChat, etc.), people can exchange music, photo, and other digitized goods electronically. ...
... Technology that enables networked peer computers to share data and processing with each other directly; can be used in C2C, B2B, and B2C e-commerce. For example, in P2P application (Viber, WeChat, etc.), people can exchange music, photo, and other digitized goods electronically. ...
Nonlinear Pricing In Oligopoly: An Application to the US Mobile
... model. In particular, a single-product …rm that introduces a second, higher quality good, should decrease its price for the low quality good. Accordingly, Cohen …nds a negative e¤ect on price associated with being the lowest quality in the product line. He also estimates that 55-65% of the variation ...
... model. In particular, a single-product …rm that introduces a second, higher quality good, should decrease its price for the low quality good. Accordingly, Cohen …nds a negative e¤ect on price associated with being the lowest quality in the product line. He also estimates that 55-65% of the variation ...
Topic 19 Customer focus and the marketing mix
... Why a business does needs customers to survive? (D) Explain how knowing who and how many customers might be interested in buying products from the business is important (C). Understand that a business will have to consider its price, the product itself how to make customers aware of the product (pro ...
... Why a business does needs customers to survive? (D) Explain how knowing who and how many customers might be interested in buying products from the business is important (C). Understand that a business will have to consider its price, the product itself how to make customers aware of the product (pro ...
promotion, public relation, personal sale are the most cardinal
... international companies. Background image must give the consumer the very first expectations from future use of the product. Color should not be mixed and uniformed in tone; clarity and contrast attract attention more effectively. In addition, the presence of contact information for more gen will gi ...
... international companies. Background image must give the consumer the very first expectations from future use of the product. Color should not be mixed and uniformed in tone; clarity and contrast attract attention more effectively. In addition, the presence of contact information for more gen will gi ...
Sant presentation 022014
... sales cycles. That is, we believe that if we can convince the customer that our solution is the best choice, we might have to worry less about losing to the lowest bidder. A value proposition, Dr. Sant said, is a promise to deliver specific results that the client desires, backed up by evidence that ...
... sales cycles. That is, we believe that if we can convince the customer that our solution is the best choice, we might have to worry less about losing to the lowest bidder. A value proposition, Dr. Sant said, is a promise to deliver specific results that the client desires, backed up by evidence that ...
Micro Glossary File
... marginal rate of substitution: - the amount of one good a consumer is willing to give up to get one more unit of another good and still maintain the same level of satisfaction. marginal revenue product: - the increase in a firm's total revenue that results from the use of one more unit of input. mar ...
... marginal rate of substitution: - the amount of one good a consumer is willing to give up to get one more unit of another good and still maintain the same level of satisfaction. marginal revenue product: - the increase in a firm's total revenue that results from the use of one more unit of input. mar ...
MARKETING WEEK 1: CONSUMER VALUE • Marketing is about
... Customer satisfaction is the extent to which a product’s perceived performance matches expectations. ...
... Customer satisfaction is the extent to which a product’s perceived performance matches expectations. ...
Product and Price Decisions
... • A product is a necessity • There is no substitutes • Price increases is not significant relative to the customer’s income • There are time restraints ...
... • A product is a necessity • There is no substitutes • Price increases is not significant relative to the customer’s income • There are time restraints ...
MARKETING PRINCIPLES
... Marketing managers work closely with top management and the various company departments. All company departments will have some impact on the success of marketing plans. -Housekeeping is responsible for delivering clean rooms sold by the sales department, -The accounting department has to measure re ...
... Marketing managers work closely with top management and the various company departments. All company departments will have some impact on the success of marketing plans. -Housekeeping is responsible for delivering clean rooms sold by the sales department, -The accounting department has to measure re ...
Marketing is Selling
... such as Google or Yahoo, which are used by consumers for locating local businesses ◦ These often link to a company’s Web site, thereby communicating more information ...
... such as Google or Yahoo, which are used by consumers for locating local businesses ◦ These often link to a company’s Web site, thereby communicating more information ...
New product - Seattle Central College
... Maximize profits while defending market share May modify product ...
... Maximize profits while defending market share May modify product ...
Value - Acacia Avenue
... In addition to this type of consumer confusion around the link between price and value, we have also seen generational differences. In our work, we continue to hear people from the Boomer and GenX cohorts talking about brands as ‘adding value’. They have been successfully trained by marketers to tre ...
... In addition to this type of consumer confusion around the link between price and value, we have also seen generational differences. In our work, we continue to hear people from the Boomer and GenX cohorts talking about brands as ‘adding value’. They have been successfully trained by marketers to tre ...
3.02 Part A Notes
... competing goods and services in the marketplace. Competitors in the marketplace – The ideal situation are when consumers perceive a business’s products to be superior to its competitors’ products or services. A great deal of marketing efforts is used in competitive positioning. ...
... competing goods and services in the marketplace. Competitors in the marketplace – The ideal situation are when consumers perceive a business’s products to be superior to its competitors’ products or services. A great deal of marketing efforts is used in competitive positioning. ...
Pricing-Product
... • FOB (free on board) pricing means that the goods are delivered to the carrier and the title and responsibility passes to the customer. • Uniformed delivery pricing means the company charges the same price plus freight to all customers, regardless of location. ...
... • FOB (free on board) pricing means that the goods are delivered to the carrier and the title and responsibility passes to the customer. • Uniformed delivery pricing means the company charges the same price plus freight to all customers, regardless of location. ...
SEM II 4.04 notes only-not fib
... information about competitors' products and marketing activities in order to determine their strengths and weaknesses in order to help them to determine what they need to do to be more competitive. MARKETING: An organizational function and a set of processes for creating, communicating, and deliveri ...
... information about competitors' products and marketing activities in order to determine their strengths and weaknesses in order to help them to determine what they need to do to be more competitive. MARKETING: An organizational function and a set of processes for creating, communicating, and deliveri ...
Service parts pricing

Service Parts Pricing refers to the aspect of Service Lifecycle Management that deals with setting prices for service parts in the after-sales market. Like other streams of Pricing, Service Parts Pricing is a scientific pursuit aimed at aligning service part prices internally to be logical and consistent, and at the same time aligning them externally with the market. This is done with the overarching aim of extracting the maximum possible price from service parts and thus maximize the profit margins. Pricing analysts have to be cognizant of possible repercussions of pricing their parts too high or too low in the after-sales market; they constantly have to strive to get the prices just right towards achieving maximum margins and maximum possible volumes.The after-sales market consists of service part and after-sales service. These areas often account for a low share in total sales, but for a relatively high share in total profits. It is important to understand that the after-sales supply chain is very different from the manufacturing supply chain, and hence rules that apply to pricing manufacturing parts do not hold good for pricing service parts. Service Parts Pricing requires a different outlook and approach.Service networks deal with a considerably higher number of SKUs and a heterogeneous product portfolio, are more complex, have a sporadic nature of demand AND have minimal response times and strict SLAs. Companies have traditionally been content with outsourcing the after-sales side of their business and have encouraged third-party parts and service providers in the market. The result has been a bevy of these operators in the market with strict price competition and low margins.Increasingly, however, companies are realizing the importance of the after-sales market and its impact on customer retention and loyalty. Increasingly, also, companies have realized that they can extract higher profit margins from the after-sales services market due to the intangible nature of services. Companies are investing in their after-sales service networks to deliver high levels of customer service and in return command higher prices for their parts and services. Customers are being sold the concept of total cost of ownership (TCO) and are being made to realize that buying from OEMs comes packaged with better distribution channels, shorter response times, better knowledge on products, and ultimately higher product uptime.The challenge for companies is to provide reliable service levels in an environment of uncertainty. Unlike factories, businesses can’t produce services in advance of demand. They can manufacture them only when an unpredictable event, such as a product failure, triggers a need. The challenge for Service Parts Pricing is to put a value to this customer need. Parts that are critical, for example, can command higher prices. So can parts that only the OEM provides in the market. Parts that are readily available in the market cannot, and must not, be priced to high. Another problem with after-sales market is that demand cannot be stimulated with price discounts, customers do not stock up service parts just because they are on discount. On the up-side, the fact that most service parts are inelastic means pricing analysts can raise prices without the adverse effects that manufacturing or retail networks witness.These and other characteristics of the after-sales market give Service Parts Pricing a life of its own. Companies are realizing that they can use the lever of service part pricing to increase profitability and don't have to take prices as market determined. Understanding customer needs and expectations, along with the company's internal strengths and weaknesses, goes a long way in designing an effective service part pricing strategy.