Fundamentals of Linear Electronics Integrated & Discrete
... to maintain a pure sine wave. If the gain is left too high, the sinewave amplitude will increase until it hits the rails and is clipped. • The cure is to include a means for the circuit to lower its gain a bit once it starts oscillating. This is a type of negative feedback based on amplitude. ...
... to maintain a pure sine wave. If the gain is left too high, the sinewave amplitude will increase until it hits the rails and is clipped. • The cure is to include a means for the circuit to lower its gain a bit once it starts oscillating. This is a type of negative feedback based on amplitude. ...
Power VS Frequency - Pulse Electronics
... in higher Rac due to the fact that currents will be induced in the ‘extra’ copper. Furthermore, the conductor height (width of foil or diameter of wire) from a proximity standpoint which is considered to be the conductor height times the number of layers, in high frequency designs conductor size and ...
... in higher Rac due to the fact that currents will be induced in the ‘extra’ copper. Furthermore, the conductor height (width of foil or diameter of wire) from a proximity standpoint which is considered to be the conductor height times the number of layers, in high frequency designs conductor size and ...
Implementation of Doppler Radar
... internal oscillator used to produce the signal frequency transmitted as the source. The received signal is then mixed with this set signal, which produces an output that is a sinusoid containing the frequency difference between the output and receiver signals. In most systems, these values need to b ...
... internal oscillator used to produce the signal frequency transmitted as the source. The received signal is then mixed with this set signal, which produces an output that is a sinusoid containing the frequency difference between the output and receiver signals. In most systems, these values need to b ...
Week 2 - Cochise College
... – Digital circuits are cheaper, more accurate, more reliable, have fewer transmission errors and are easier to maintain than analog circuits ...
... – Digital circuits are cheaper, more accurate, more reliable, have fewer transmission errors and are easier to maintain than analog circuits ...
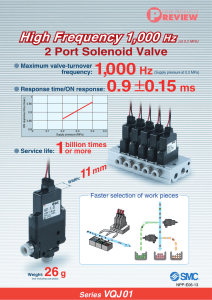
High Frequency 1,000 Hz High Frequency 1,000 Hz (at 0.2 MPa)
... Note 1) Do not exceed 30 seconds of continuous use when using products with 24 VDC and an operating frequency of 400 Hz or more. After using products continuously, the de-energizing time must be longer than the energizing time. Input signal waveform ...
... Note 1) Do not exceed 30 seconds of continuous use when using products with 24 VDC and an operating frequency of 400 Hz or more. After using products continuously, the de-energizing time must be longer than the energizing time. Input signal waveform ...
PPT - Senior Design
... • With the filter in-line generate a sine wave of known amplitude. • Find amplitude of filtered sine wave • Divide this amplitude by the amplitude of the unfiltered sine wave • Convert to decibels – 20 log10(filtered / unfiltered) ...
... • With the filter in-line generate a sine wave of known amplitude. • Find amplitude of filtered sine wave • Divide this amplitude by the amplitude of the unfiltered sine wave • Convert to decibels – 20 log10(filtered / unfiltered) ...
ppt
... cos2*pi*5t + (1/3)cos2*pi*15t + (1/5)cos2*pi*25t + (1/7)cos2*pi*35t) In this example the 15 and 35 Hz signals have suffered a phase shift (which can be caused as a result of different propagation speeds) with respect to the 5 and 25 Hz signals. The pulse shape changes significantly. ...
... cos2*pi*5t + (1/3)cos2*pi*15t + (1/5)cos2*pi*25t + (1/7)cos2*pi*35t) In this example the 15 and 35 Hz signals have suffered a phase shift (which can be caused as a result of different propagation speeds) with respect to the 5 and 25 Hz signals. The pulse shape changes significantly. ...
SGC-2486Z
... Sirenza Microdevices’ SGC-2486Z is a high performance SiGe HBT MMIC amplifier utilizing a Darlington configuration with a patented active bias network. The active bias network provides stable current over temperature and process Beta variations. Designed to run directly from a 3V supply, the SGC-248 ...
... Sirenza Microdevices’ SGC-2486Z is a high performance SiGe HBT MMIC amplifier utilizing a Darlington configuration with a patented active bias network. The active bias network provides stable current over temperature and process Beta variations. Designed to run directly from a 3V supply, the SGC-248 ...
4520.RF Basics and Getting Started 2012
... – Shorter range than a sub 1 GHz solution (same output power) – Many possible interferers are present in the band ...
... – Shorter range than a sub 1 GHz solution (same output power) – Many possible interferers are present in the band ...
DN276 - LTC1564: A Digitally Tuned Antialiasing / Reconstruction Filter Simplifies High Performance DSP Design
... Introduction Typically an analog antialiasing filter is used to band-limit wideband signals at the input of an analog-to-digital converter. In addition, as the converter’s sampling rate changes, an antialiasing filter’s passband should increase or decrease accordingly. A frequency-tunable analog fil ...
... Introduction Typically an analog antialiasing filter is used to band-limit wideband signals at the input of an analog-to-digital converter. In addition, as the converter’s sampling rate changes, an antialiasing filter’s passband should increase or decrease accordingly. A frequency-tunable analog fil ...
FIBER-OPTIC COMMUNICATION LINKS –ACTIVE AND PASSIVE
... GDP growth , moreover, the real demand consistently exceeds the predicted one . The rapid development of telecommunication technology and the use of optical transmission techniques also have affects on equipment of Closed Circuit Television (CCTV). The most important advantages of fiber – optic comm ...
... GDP growth , moreover, the real demand consistently exceeds the predicted one . The rapid development of telecommunication technology and the use of optical transmission techniques also have affects on equipment of Closed Circuit Television (CCTV). The most important advantages of fiber – optic comm ...
Capacitor Self
... In the interest of time, the receiver is build for you. This will let you concentrate on measuring the performance of the receiver and on listening to FM music. The phototransistor has a 1 KΩ load and therefore a cutoff frequency of around 10 KHz. The phototransistor therefore acts as a low pass fil ...
... In the interest of time, the receiver is build for you. This will let you concentrate on measuring the performance of the receiver and on listening to FM music. The phototransistor has a 1 KΩ load and therefore a cutoff frequency of around 10 KHz. The phototransistor therefore acts as a low pass fil ...
TU5PFP030
... signal in the system, and the amplitude modulation of the system is achieved by adjusting the external connection resistor’s value of the chip. The output frequency is tuneable from 98.5 to 99.5 MHz. The principles and experimental results of the signal synthesizer will be presented. The driver ampl ...
... signal in the system, and the amplitude modulation of the system is achieved by adjusting the external connection resistor’s value of the chip. The output frequency is tuneable from 98.5 to 99.5 MHz. The principles and experimental results of the signal synthesizer will be presented. The driver ampl ...
HWS400 - Hexawave
... The HWS400 is a GaAs MMIC SPDT terminated (non-reflective) switch in a low cost QFN12L (3x3 mm) plastic package and can be used in both 50 ohm and 75 ohm systems. The HWS400 features low insertion loss and high isolation with very low DC ...
... The HWS400 is a GaAs MMIC SPDT terminated (non-reflective) switch in a low cost QFN12L (3x3 mm) plastic package and can be used in both 50 ohm and 75 ohm systems. The HWS400 features low insertion loss and high isolation with very low DC ...
Questions Pools Element 9
... 67. 9A67 | A red LED on the control panel has failed. You find a spare which has the same electrical characteristics, but is marked 1.06micrometers. A. This cannot be used as it is not visible. B. This can be used but is the wrong color. C. This is not an LED. D. It can be used with a filter. ...
... 67. 9A67 | A red LED on the control panel has failed. You find a spare which has the same electrical characteristics, but is marked 1.06micrometers. A. This cannot be used as it is not visible. B. This can be used but is the wrong color. C. This is not an LED. D. It can be used with a filter. ...
Heterodyne
Heterodyning is a radio signal processing technique invented in 1901 by Canadian inventor-engineer Reginald Fessenden, in which new frequencies are created by combining or mixing two frequencies. Heterodyning is used to shift one frequency range into another, new one, and is also involved in the processes of modulation and demodulation. The two frequencies are combined in a nonlinear signal-processing device such as a vacuum tube, transistor, or diode, usually called a mixer. In the most common application, two signals at frequencies f1 and f2 are mixed, creating two new signals, one at the sum f1 + f2 of the two frequencies, and the other at the difference f1 − f2. These new frequencies are called heterodynes. Typically only one of the new frequencies is desired, and the other signal is filtered out of the output of the mixer. Heterodynes are related to the phenomenon of ""beats"" in acoustics.A major application of the heterodyne process is in the superheterodyne radio receiver circuit, which is used in virtually all modern radio receivers.