Lab 7
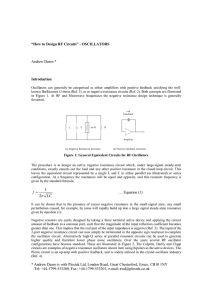
... R1 with C2 forms a low pass filter. If the difference in the voltage between the negative input terminal on the op amp and Vo is relatively constant, C1 acts like an open circuit and all of the current through R2 and C1 will flow through R1. If the difference in the voltage between the negative inpu ...
... R1 with C2 forms a low pass filter. If the difference in the voltage between the negative input terminal on the op amp and Vo is relatively constant, C1 acts like an open circuit and all of the current through R2 and C1 will flow through R1. If the difference in the voltage between the negative inpu ...
Differentiator
... If the difference in the voltage between the negative input terminal on the op amp and Vo is relatively constant, C1 acts like an open circuit and all of the current through R2 and C1 will flow through R1. If the difference in the voltage between the negative input terminal on the op amp and Vo vari ...
... If the difference in the voltage between the negative input terminal on the op amp and Vo is relatively constant, C1 acts like an open circuit and all of the current through R2 and C1 will flow through R1. If the difference in the voltage between the negative input terminal on the op amp and Vo vari ...
Lab-15-datasheet-new
... 6. Looking at the amplitude of the heartbeat waveforms from your results above, and the gain of the circuit at 1Hz that you calculated or measured, what do you expect the amplitude is of the voltage coming off the voltage divider? 7. In your own words, how does this circuit show a person’s heartbeat ...
... 6. Looking at the amplitude of the heartbeat waveforms from your results above, and the gain of the circuit at 1Hz that you calculated or measured, what do you expect the amplitude is of the voltage coming off the voltage divider? 7. In your own words, how does this circuit show a person’s heartbeat ...
Application Note
... an analog-to-digital converter (A/D) for data acquisition begins with characterizing the application. Generally, it will fall into one of two broad categories – signals made up of pulses or those signals that are sinusoidal or contain sinusoidal frequency components. When dealing with pulses, an eng ...
... an analog-to-digital converter (A/D) for data acquisition begins with characterizing the application. Generally, it will fall into one of two broad categories – signals made up of pulses or those signals that are sinusoidal or contain sinusoidal frequency components. When dealing with pulses, an eng ...
Fiber Optic Communications
... simply turning it on and off—pulses. – Small signal modulation or pulse code modulation is more practical for communications. – Limited response time – Large wavelength chirp – High bias currents ...
... simply turning it on and off—pulses. – Small signal modulation or pulse code modulation is more practical for communications. – Limited response time – Large wavelength chirp – High bias currents ...
HYUNDAI Placement Paper 2011
... time, we observe the following sequence of entry into and exit from the interrupt service routine: ...
... time, we observe the following sequence of entry into and exit from the interrupt service routine: ...
AN1229
... close as possible to Rp of 5.38 Ω. From the circuit schematic given in Figure 6 , we can see that the input matching network is based on a two section balun (1:1 balun in cascade with a 9:1 balun transformer) which transforms the unbalanced 50 Ω to a balanced 5.56 Ω (2 x 2.78 Ω / 9:1 ratio). The fir ...
... close as possible to Rp of 5.38 Ω. From the circuit schematic given in Figure 6 , we can see that the input matching network is based on a two section balun (1:1 balun in cascade with a 9:1 balun transformer) which transforms the unbalanced 50 Ω to a balanced 5.56 Ω (2 x 2.78 Ω / 9:1 ratio). The fir ...
dU/dt output Filters for 3
... The filter case has hot points when working: do not mount it near to inflammable objects. Leave free space around it for air circulation and mount it ...
... The filter case has hot points when working: do not mount it near to inflammable objects. Leave free space around it for air circulation and mount it ...
Meijer'I,
... is measuring the full frequency spectrum Fl up to 500 MHz using a sweeptime of 500 ms. Secondly, a frequency spectrum F2 is measured using a sweeptime of 5 seconds. As a result, both spectra will show the continuous noise signals present, however, if there is any PD activity, more pulses will be cap ...
... is measuring the full frequency spectrum Fl up to 500 MHz using a sweeptime of 500 ms. Secondly, a frequency spectrum F2 is measured using a sweeptime of 5 seconds. As a result, both spectra will show the continuous noise signals present, however, if there is any PD activity, more pulses will be cap ...
Analog and Digital Signals
... • Digital signal are commonly referred to as square waves or clock signals. • Their minimum value must be 0 volts, and their maximum value must be 5 volts. • They can be periodic (repeating) or non-periodic. • The time the signal is high (tH) can vary anywhere from 1% of the period to 99% of the per ...
... • Digital signal are commonly referred to as square waves or clock signals. • Their minimum value must be 0 volts, and their maximum value must be 5 volts. • They can be periodic (repeating) or non-periodic. • The time the signal is high (tH) can vary anywhere from 1% of the period to 99% of the per ...
6 The Time Dimension I
... spectrum decreases with increasing frequency. This means that in general the higher frequency components contribute much less to the overall signal profile than the lower frequency components. However, they do influence small local changes taking place in a short time span. When a signal is a contin ...
... spectrum decreases with increasing frequency. This means that in general the higher frequency components contribute much less to the overall signal profile than the lower frequency components. However, they do influence small local changes taking place in a short time span. When a signal is a contin ...
Preliminary Work
... a. For the low pass part of the filter the capacitor needs to drop the output voltage to zero when the frequency is high. At high frequency the capacitor behaves as a short so it should be in parallel with the output resistance. b. For the high pass part of the filter the capacitor needs to drop the ...
... a. For the low pass part of the filter the capacitor needs to drop the output voltage to zero when the frequency is high. At high frequency the capacitor behaves as a short so it should be in parallel with the output resistance. b. For the high pass part of the filter the capacitor needs to drop the ...
SGA3586Z 数据资料DataSheet下载
... The information in this publication is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by RF Micro Devices, Inc. ("RFMD") for its use, nor for any infringement of patents, or other rights of third parties, resulting from its use. No license is granted by implication or ot ...
... The information in this publication is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by RF Micro Devices, Inc. ("RFMD") for its use, nor for any infringement of patents, or other rights of third parties, resulting from its use. No license is granted by implication or ot ...
SGA3563Z 数据资料DataSheet下载
... infringement of patents, or other rights of third parties, resulting from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of RFMD. RFMD reserves the right to change component circuitry, recommended application circuitry and specifications at any time with ...
... infringement of patents, or other rights of third parties, resulting from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of RFMD. RFMD reserves the right to change component circuitry, recommended application circuitry and specifications at any time with ...
TGA4826-SM 数据资料DataSheet下载
... The TGA4826-SM is a high power wideband amplifier that typically provides 22 dB small signal gain. The TGA4826-SM is an excellent choice for applications requiring high drive combined with high linearity. The TGA4826-SM can be used as a gain block when Vdbypass is used, or alternatively, can deliver ...
... The TGA4826-SM is a high power wideband amplifier that typically provides 22 dB small signal gain. The TGA4826-SM is an excellent choice for applications requiring high drive combined with high linearity. The TGA4826-SM can be used as a gain block when Vdbypass is used, or alternatively, can deliver ...
Damped Second Order System
... • Lock Range: DWL, once in lock state and protuberated by abrupt changes or variation at input frequencies, we define the range of input frequencies within it the loop will remain locked. If the abrupt frequency changes over interval time step t is smaller than the natural frequency , the pll remain ...
... • Lock Range: DWL, once in lock state and protuberated by abrupt changes or variation at input frequencies, we define the range of input frequencies within it the loop will remain locked. If the abrupt frequency changes over interval time step t is smaller than the natural frequency , the pll remain ...
Heterodyne
Heterodyning is a radio signal processing technique invented in 1901 by Canadian inventor-engineer Reginald Fessenden, in which new frequencies are created by combining or mixing two frequencies. Heterodyning is used to shift one frequency range into another, new one, and is also involved in the processes of modulation and demodulation. The two frequencies are combined in a nonlinear signal-processing device such as a vacuum tube, transistor, or diode, usually called a mixer. In the most common application, two signals at frequencies f1 and f2 are mixed, creating two new signals, one at the sum f1 + f2 of the two frequencies, and the other at the difference f1 − f2. These new frequencies are called heterodynes. Typically only one of the new frequencies is desired, and the other signal is filtered out of the output of the mixer. Heterodynes are related to the phenomenon of ""beats"" in acoustics.A major application of the heterodyne process is in the superheterodyne radio receiver circuit, which is used in virtually all modern radio receivers.