SEMESTER_2_Chapter_4KEY
... Establishment of adjacencies with neighboring routers using the EIGRP hello protocol. Support for VLSM and manual route summarization. These allow EIGRP to create hierarchically structured large networks. Although routes are propagated in a distance vector manner, the metric is based on minimum band ...
... Establishment of adjacencies with neighboring routers using the EIGRP hello protocol. Support for VLSM and manual route summarization. These allow EIGRP to create hierarchically structured large networks. Although routes are propagated in a distance vector manner, the metric is based on minimum band ...
Material (PDF 48KB)
... 6. In Multicast Distribution trees, explain Source Based and Core Based Distribution Tree. 7. In IPv4 there is special multicast address space. Actually these are not just traditional addresses, but they are multicast group identifiers. What addresses have been reserved for multicast routing? Explai ...
... 6. In Multicast Distribution trees, explain Source Based and Core Based Distribution Tree. 7. In IPv4 there is special multicast address space. Actually these are not just traditional addresses, but they are multicast group identifiers. What addresses have been reserved for multicast routing? Explai ...
pptx - Cambridge Computer Lab
... • understand principles behind network layer services: – network layer service models – forwarding versus routing (versus switching) – how a router works – routing (path selection) – IPv6 ...
... • understand principles behind network layer services: – network layer service models – forwarding versus routing (versus switching) – how a router works – routing (path selection) – IPv6 ...
Optical Networks: The Platform for the Next Generation
... COntention Resolution by Delay lines (CORD) Asynchronous Transfer Mode Optical Switching (ATMOS) Multi-token packet switched ring ...
... COntention Resolution by Delay lines (CORD) Asynchronous Transfer Mode Optical Switching (ATMOS) Multi-token packet switched ring ...
tm8106-ois
... • OIS – continuous adaptation of the wavelength topology by distributed decision making – Suitable, scalable and allows traffic variations for short time scales (seconds to minutes) ...
... • OIS – continuous adaptation of the wavelength topology by distributed decision making – Suitable, scalable and allows traffic variations for short time scales (seconds to minutes) ...
Introduction to IP Routing
... metric is flooded to all routers Each link up/down status change is incrementally flooded Each router re-computes the routing table in parallel using the common link state database OSPF is the main protocol in use today ...
... metric is flooded to all routers Each link up/down status change is incrementally flooded Each router re-computes the routing table in parallel using the common link state database OSPF is the main protocol in use today ...
Introduction to IP Routing
... metric is flooded to all routers Each link up/down status change is incrementally flooded Each router re-computes the routing table in parallel using the common link state database OSPF is the main protocol in use today ...
... metric is flooded to all routers Each link up/down status change is incrementally flooded Each router re-computes the routing table in parallel using the common link state database OSPF is the main protocol in use today ...
Network Layer - SI-35-02
... port and segment. • Routers take packets from LAN devices (e.g. workstations) and, based on Layer 3 information, forward them through the network. • In fact, routing is sometimes referred to as Layer 3 switching ...
... port and segment. • Routers take packets from LAN devices (e.g. workstations) and, based on Layer 3 information, forward them through the network. • In fact, routing is sometimes referred to as Layer 3 switching ...
Chap 11 Routing
... Network and host addressing Path selection and packet switching Routed versus routing protocol Network-layer protocol operations Multiprotocol routing ...
... Network and host addressing Path selection and packet switching Routed versus routing protocol Network-layer protocol operations Multiprotocol routing ...
Document
... routed, who routes through its net. intra-AS: single admin, so no policy decisions needed ...
... routed, who routes through its net. intra-AS: single admin, so no policy decisions needed ...
Three-Layer Hierarchical Network Design
... Upgrade from 200Mbps to 400Mbps for example Usually under 4 ports ...
... Upgrade from 200Mbps to 400Mbps for example Usually under 4 ports ...
I/O Router Placement and Fine-Grained Routing
... present in each row of Spider II. Each group is further divided into 4 sub-groups that service two rows of Titan. Each sub-group consists of 3 router modules. Algorithm 1 describes how a client chooses the optimal router module for a given group. The client-to-group pairing is decided using a fixed ...
... present in each row of Spider II. Each group is further divided into 4 sub-groups that service two rows of Titan. Each sub-group consists of 3 router modules. Algorithm 1 describes how a client chooses the optimal router module for a given group. The client-to-group pairing is decided using a fixed ...
Connection-oriented internetworking
... • Examples: MPLS switch with PoS link and GbE link. For the PoS link, LSP encoding should be SONET while switching type: PSC-1 and for the GbE link, LSP encoding should be Ethernet and switching type: PSC-1. Vijay says that MPLS specs don’t allow this sort of LSP to be set up. Both switching and LSP ...
... • Examples: MPLS switch with PoS link and GbE link. For the PoS link, LSP encoding should be SONET while switching type: PSC-1 and for the GbE link, LSP encoding should be Ethernet and switching type: PSC-1. Vijay says that MPLS specs don’t allow this sort of LSP to be set up. Both switching and LSP ...
Lecture 13
... A routing table maintained at each node, indicating the best known distance and next hop to get there Calculate w(u,v), is the cost associated with edge uv Calculate d(u), the distance of node u from a root node For each uv, find minimum d(u,v) Repeat n-1 times for n-nodes ...
... A routing table maintained at each node, indicating the best known distance and next hop to get there Calculate w(u,v), is the cost associated with edge uv Calculate d(u), the distance of node u from a root node For each uv, find minimum d(u,v) Repeat n-1 times for n-nodes ...
8) Network layer-3
... d) IP uses only an error detection mechanism (Chechsum) and discards the packet if it is corrupted. e) IP does its best to deliver a packet to its destination, but with no guarantees. Needs to rely on TCP layer for reliable ...
... d) IP uses only an error detection mechanism (Chechsum) and discards the packet if it is corrupted. e) IP does its best to deliver a packet to its destination, but with no guarantees. Needs to rely on TCP layer for reliable ...
No Slide Title
... • Node failures within a service layer can only be dealt with by the actions of peer-level network elements. • Some networking operating contexts need IP restoration other than physical layer restoration. ...
... • Node failures within a service layer can only be dealt with by the actions of peer-level network elements. • Some networking operating contexts need IP restoration other than physical layer restoration. ...
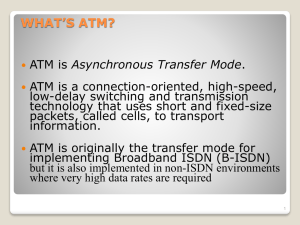
ATM
... VC transport: cells carried on VC from source to destination ◦ call setup, teardown for each call before data can flow ◦ each packet carries VC identifier (not destination ID) ◦ every switch on source-dest path maintain “state” for each passing connection ◦ link,switch resources (bandwidth, buffers) ...
... VC transport: cells carried on VC from source to destination ◦ call setup, teardown for each call before data can flow ◦ each packet carries VC identifier (not destination ID) ◦ every switch on source-dest path maintain “state” for each passing connection ◦ link,switch resources (bandwidth, buffers) ...
EIGRP
... through Three as a loop-free path (a feasible successor). When the path through Router One becomes unavailable, Router Two examines its topology table and, finding a feasible successor, begins using the path through Three immediately. ...
... through Three as a loop-free path (a feasible successor). When the path through Router One becomes unavailable, Router Two examines its topology table and, finding a feasible successor, begins using the path through Three immediately. ...
Virtual Router - UCF CS - University of Central Florida
... • Using Virtual Routers: Virtual routers are stationary → links are robust → fewer reroute S → less overhead ! ...
... • Using Virtual Routers: Virtual routers are stationary → links are robust → fewer reroute S → less overhead ! ...
A Hybrid QoS Routing Strategy for Suburban Ad
... may be covered with higher transmission energy Interference may increase as connectivity increases Overall network throughput may decrease ...
... may be covered with higher transmission energy Interference may increase as connectivity increases Overall network throughput may decrease ...
Basic Scheme: Inter-domain Mobility
... • a large number of BGP updates • handles only when moves across ASes (autonomous systems) [2] A. Dul, Global IP Network Mobility using Border Gateway Protocol, Mar. 2006. [Online] ...
... • a large number of BGP updates • handles only when moves across ASes (autonomous systems) [2] A. Dul, Global IP Network Mobility using Border Gateway Protocol, Mar. 2006. [Online] ...