* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Three-Layer Hierarchical Network Design
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
UniPro protocol stack wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
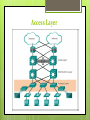
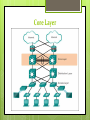
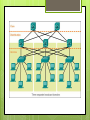
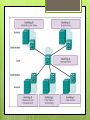
Three-Layer Hierarchical Network Design Cisco Layers Core Layer Distribution Layer Access Layer Why Use This Network Model? This model simplifies the task of building a Reliable Scalable Divide network into functional areas High performance Redundancy Layer design to control congestion Efficient Management and Troubleshooting Easily isolate causes of network trouble Access Layer Provides workgroup/user access to the network Also called the desktop layer because it focuses on connecting client nodes, such as workstations to the network This layer ensure packets are delivered to end users Access Layer The access layer serves a number of functions: Layer 2 switching Packets sent to switch port based on destination MAC address QoS classification and marking and trust boundaries Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) inspection Virtual access control lists (VACLs) Spanning tree Power over Ethernet (PoE) and auxiliary VLANs for VoIP Access Layer Access Layer Equipment Distribution Layer This layer is also called the workgroup layer Combines the data received from the access layer switches before it is transmitted to the core layer for routing to its final destination This layer ensures that packets are properly routed between subnets and VLANs in your enterprise Provides policy-based connectivity and controls the boundary between the access and core layers Distribution Layer Combination of LAN or WAN links. Routing services between LANs and VLANs and between routing domains Redundancy and load balancing. Broadcast domain control Acts as the a dividing point between broadcast domains Distribution Layer Distribution Layer Equipment Cisco 4000, 4500 series router and switch Layer 3 switching Can upgrade without buying new router Activate remotely with a license Upgrade from 200Mbps to 400Mbps for example Usually under 4 ports Core Layer This layer is considered the backbone of the network This layer of the network does not route traffic at the LAN No packet manipulation is done by devices in this layer This layer is concerned with speed and ensures reliable delivery of packets Core Layer Combines the traffic from all the distribution layer devices, so it must be capable of forwarding large amounts of data quickly Providing reliability and fault tolerance Scaling by using faster, but not more, equipment Core Layer Core Layer Equipment Cisco switches such as 7000, 7700, and 12000 7000 7700 4, 9, 10, and 18 slots 550 Gbps bandwidth per slot Up to 192 40 GE ports and 32 100 GE ports Up to $20,000 6, 10, and 18 slots 1.3 Tbps bandwidth per slot Up to 348 40 GE ports and 192 100 GE ports Up to $50,000 12000 2.5 Tbps bandwidth per slot Over $100,000 Catalyst switches such as 6000, 5000, and 4000 6000 Up to 384(10Gbps) ports or 96(40Gbps) ports 7.68 Tbps throughput switching performance Over $30,000 T-1 and E-1 lines Used for voice applications Frame relay connections, ATM networks, Switched Multimegabit Data Service (SMDS)