Unit 5 and 6 revsion - Deans Community High School
... Q14. The burning of fossil fuels is a major source of air pollution. (a) Name the acidic gas formed when air in a car engine is sparked. (b) Name the acidic gas formed when coal with a high sulphur content is burned. (c) Name the toxic gas formed when methane is burned in a limited supply of air. (d ...
... Q14. The burning of fossil fuels is a major source of air pollution. (a) Name the acidic gas formed when air in a car engine is sparked. (b) Name the acidic gas formed when coal with a high sulphur content is burned. (c) Name the toxic gas formed when methane is burned in a limited supply of air. (d ...
Pyrolysis
... c Steam to carbon molar ratio of the feed. d Time on stream. e Carbon conversion. f Catalyst was pre-reduced in H at 500°C. ...
... c Steam to carbon molar ratio of the feed. d Time on stream. e Carbon conversion. f Catalyst was pre-reduced in H at 500°C. ...
Activation of Carbon Chlorine Bonds Using Palladium (II) Catalysts
... in various industrial equipment, including transformers, capacitors, and hydraulic systems. However, PCBs also have many adverse health affects, including carcinogenic properties. In order to safely dispose of these chemicals, the inert carbon chlorine bond must be activated. ...
... in various industrial equipment, including transformers, capacitors, and hydraulic systems. However, PCBs also have many adverse health affects, including carcinogenic properties. In order to safely dispose of these chemicals, the inert carbon chlorine bond must be activated. ...
formula - eduBuzz.org
... number of hydrogen atoms in an alkane molecule? • What is a homologous series, and why are the alkanes an example of one? • What is the general formula for the alkanes? • Why are the products of combustion the same for every alkane? ...
... number of hydrogen atoms in an alkane molecule? • What is a homologous series, and why are the alkanes an example of one? • What is the general formula for the alkanes? • Why are the products of combustion the same for every alkane? ...
C14_-_Organic_Chemistry
... alkanes and alkenes (not cistrans), containing up to four carbon atoms per molecule. ...
... alkanes and alkenes (not cistrans), containing up to four carbon atoms per molecule. ...
Introduction
... is specially appealing from the ecological standpoint due to its ability to eliminate pollutants as oppose to classical oxidation that results in turning the pollution from one form into another. The process is operated at mild conditions (0.1-0.5 MPa, T≤100 ºC), and therefore with low energy requir ...
... is specially appealing from the ecological standpoint due to its ability to eliminate pollutants as oppose to classical oxidation that results in turning the pollution from one form into another. The process is operated at mild conditions (0.1-0.5 MPa, T≤100 ºC), and therefore with low energy requir ...
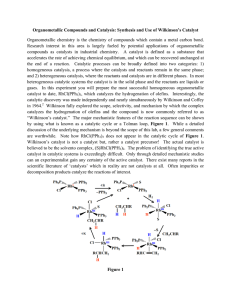
Organometallic Compounds and Catalysis: Synthesis
... Research interest in this area is largely fueled by potential applications of organometallic compounds as catalysts in industrial chemistry. A catalyst is defined as a substance that accelerates the rate of achieving chemical equilibrium, and which can be recovered unchanged at the end of a reaction ...
... Research interest in this area is largely fueled by potential applications of organometallic compounds as catalysts in industrial chemistry. A catalyst is defined as a substance that accelerates the rate of achieving chemical equilibrium, and which can be recovered unchanged at the end of a reaction ...
File
... different chemical compounds – it is not much use straight out of the ground (there are too many substances in it, all with different boiling points). As such it needs to be refined… ...
... different chemical compounds – it is not much use straight out of the ground (there are too many substances in it, all with different boiling points). As such it needs to be refined… ...
Unit_Chemistry_1a_Oil
... compounds. A mixture consists of two or more elements or compounds not chemically combined together. The chemical properties of each substance in the mixture are unchanged. It is possible to separate the substances in a mixture by physical methods including distillation. ...
... compounds. A mixture consists of two or more elements or compounds not chemically combined together. The chemical properties of each substance in the mixture are unchanged. It is possible to separate the substances in a mixture by physical methods including distillation. ...
Fluid catalytic cracking

Fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) is one of the most important conversion processes used in petroleum refineries. It is widely used to convert the high-boiling, high-molecular weight hydrocarbon fractions of petroleum crude oils to more valuable gasoline, olefinic gases, and other products. Cracking of petroleum hydrocarbons was originally done by thermal cracking, which has been almost completely replaced by catalytic cracking because it produces more gasoline with a higher octane rating. It also produces byproduct gases that are more olefinic, and hence more valuable, than those produced by thermal cracking.The feedstock to an FCC is usually that portion of the crude oil that has an initial boiling point of 340 °C or higher at atmospheric pressure and an average molecular weight ranging from about 200 to 600 or higher. This portion of crude oil is often referred to as heavy gas oil or vacuum gas oil (HVGO). The FCC process vaporizes and breaks the long-chain molecules of the high-boiling hydrocarbon liquids into much shorter molecules by contacting the feedstock, at high temperature and moderate pressure, with a fluidized powdered catalyst.