Chapter 11: Heat 1. The energy that flows from a high temperature
... 55. __________ is a pattern which has got one more atom at the centre of a simple cube. (simple cube, face centred cube, body centred cube, none of these) 56. The electrons, which can wander in the solid, are known as __________. ...
... 55. __________ is a pattern which has got one more atom at the centre of a simple cube. (simple cube, face centred cube, body centred cube, none of these) 56. The electrons, which can wander in the solid, are known as __________. ...
β - Institute of Particle and Nuclear Physics
... • In conventional NMR a relatively small nuclear polarization is generated by applying a large magnetic field after which it is tilted with a small RF magnetic field. An inductive pickup coil is used to detect the resulting precession of the nuclear magnetization. Typically one needs about 1018 nucl ...
... • In conventional NMR a relatively small nuclear polarization is generated by applying a large magnetic field after which it is tilted with a small RF magnetic field. An inductive pickup coil is used to detect the resulting precession of the nuclear magnetization. Typically one needs about 1018 nucl ...
Unit 1 Notes (general chem review)
... Matter – anything that has mass and occupies space 3 phases – solid, liquid, gas; defined in terms of particle spacing solid – the particles are very closely spaced – well aligned liquid – the particles are fairly close, but not well aligned gas – the particles are very spread out – large ...
... Matter – anything that has mass and occupies space 3 phases – solid, liquid, gas; defined in terms of particle spacing solid – the particles are very closely spaced – well aligned liquid – the particles are fairly close, but not well aligned gas – the particles are very spread out – large ...
Final Exam Review whole thing
... Different types of atoms make up different elements An element is a pure substance made up of only one type of atoms Elements are listed on the ...
... Different types of atoms make up different elements An element is a pure substance made up of only one type of atoms Elements are listed on the ...
Exam 3 Key
... For each of the following, write the word, words, or number in each blank that best completes each sentence. (2 points each) 1. The condition of an atom that has at least one of its electrons in orbitals that do not represent the lowest possible potential energy is called a(n) excited state. 2. A(n ...
... For each of the following, write the word, words, or number in each blank that best completes each sentence. (2 points each) 1. The condition of an atom that has at least one of its electrons in orbitals that do not represent the lowest possible potential energy is called a(n) excited state. 2. A(n ...
Glossary
... nuclear change are natural radioactivity, nuclear fission, and nuclear fusion. Compare chemical change, physical change. ...
... nuclear change are natural radioactivity, nuclear fission, and nuclear fusion. Compare chemical change, physical change. ...
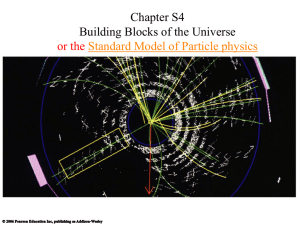
More on the Standard Model
... Only one fermion can be an any state, which explains most of chemistry…the electrons fill up the energy levels with only one per state. This is the Pauli exclusion principle. But can’t I put two electrons per state? Yes, but their spins are in different directions, so they are not really in the same ...
... Only one fermion can be an any state, which explains most of chemistry…the electrons fill up the energy levels with only one per state. This is the Pauli exclusion principle. But can’t I put two electrons per state? Yes, but their spins are in different directions, so they are not really in the same ...
irm_ch11
... 11.42 Alpha and beta are stopped; gamma goes through. 11.43 Alpha particle velocities are on the order of 0.1 the speed of light; beta particle velocities are up to 0.9 the speed of light; gamma rays have a velocity equal to the speed of light. 11.44 An alpha produces 40,000 ion pairs, and a beta pr ...
... 11.42 Alpha and beta are stopped; gamma goes through. 11.43 Alpha particle velocities are on the order of 0.1 the speed of light; beta particle velocities are up to 0.9 the speed of light; gamma rays have a velocity equal to the speed of light. 11.44 An alpha produces 40,000 ion pairs, and a beta pr ...
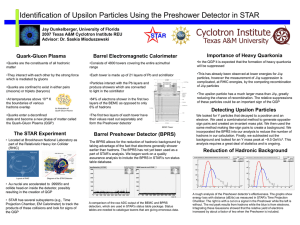
mc2007_ATLAS_Neil
... Muons are the only charged particles which can pass through the calorimeters. The muon system therefore acts like the inner tracker but outside the calorimeters to measure the muon properties ...
... Muons are the only charged particles which can pass through the calorimeters. The muon system therefore acts like the inner tracker but outside the calorimeters to measure the muon properties ...
Grade 11 Chemistry Exam Review
... The reaction of solutions of ammonium phosphate and barium nitrate gives a precipitate of barium phosphate. The equation that best represents this statement is a) 2(NH4)3PO4(s) + 3Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(aq) + 6NH4NO3(s). b) 2(NH4)3PO4(aq) + 3Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(s) + 6NH4NO3(aq). c) 2(NH4)3PO4 ...
... The reaction of solutions of ammonium phosphate and barium nitrate gives a precipitate of barium phosphate. The equation that best represents this statement is a) 2(NH4)3PO4(s) + 3Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(aq) + 6NH4NO3(s). b) 2(NH4)3PO4(aq) + 3Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(s) + 6NH4NO3(aq). c) 2(NH4)3PO4 ...
Mock Final Exam
... c. During a chemical reaction atoms are changed into different atoms. d. Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine. e. Atoms of an element are not changed into different atoms by chemical reactions. 2.2: Molecules & formulas 12. What Law defines or describes a molecule? State tha ...
... c. During a chemical reaction atoms are changed into different atoms. d. Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine. e. Atoms of an element are not changed into different atoms by chemical reactions. 2.2: Molecules & formulas 12. What Law defines or describes a molecule? State tha ...
THSNMR
... instruments. We take an NMR of that standard and measure its absorbance frequency. We then measure the frequency of our sample and subtract its frequency from that of the standard. We then then divide by the frequency of the standard. This gives a number called the “chemical shift,” also called , w ...
... instruments. We take an NMR of that standard and measure its absorbance frequency. We then measure the frequency of our sample and subtract its frequency from that of the standard. We then then divide by the frequency of the standard. This gives a number called the “chemical shift,” also called , w ...
AtomMoleculeNaming_G1
... Because of different mass among isotopes, atomic mass is the weighted average among all isotopes. • Average mass = ATOMIC WEIGHT • Atomic mass = S abundance mass number =abundance1 x #mass1 + abundance2 x #mass2 + … ...
... Because of different mass among isotopes, atomic mass is the weighted average among all isotopes. • Average mass = ATOMIC WEIGHT • Atomic mass = S abundance mass number =abundance1 x #mass1 + abundance2 x #mass2 + … ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.