Electric Field - Uplift Education
... Bring a charged object near a conducting surface, electrons will move in conductor even though no physical contact: electrons in conductor are repelled from the charged object – since some are free to move, they will! ...
... Bring a charged object near a conducting surface, electrons will move in conductor even though no physical contact: electrons in conductor are repelled from the charged object – since some are free to move, they will! ...
Bonding
... The mixing of two or more atomic orbitals of similar energies on the same atom to produce new orbitals of equal energies Hybrid orbitals - equal energy produced by the combination of two or more orbitals on the same atom ...
... The mixing of two or more atomic orbitals of similar energies on the same atom to produce new orbitals of equal energies Hybrid orbitals - equal energy produced by the combination of two or more orbitals on the same atom ...
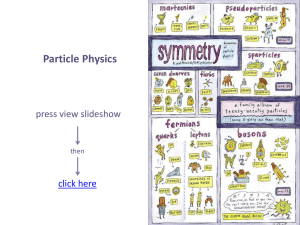
Standard Model
... was developed throughout the mid to late 20th century, is a theory concerning the electromagnetic, weak, and strong nuclear interactions, which mediate the dynamics of the known subatomic particles. Since then, discoveries of the bottom quark (1977), the top quark (1995) and the tau neutrino (2000) ...
... was developed throughout the mid to late 20th century, is a theory concerning the electromagnetic, weak, and strong nuclear interactions, which mediate the dynamics of the known subatomic particles. Since then, discoveries of the bottom quark (1977), the top quark (1995) and the tau neutrino (2000) ...
File
... Chemical reactions change the way atoms are grouped but atoms themselves do not change Looks like a billiard ball (solid, uniform, sphere) o J.J. Thomson: Thought atoms might be made up of smaller particles Proved that negatively charged electrons were part of an atom Viewed atom as a “rai ...
... Chemical reactions change the way atoms are grouped but atoms themselves do not change Looks like a billiard ball (solid, uniform, sphere) o J.J. Thomson: Thought atoms might be made up of smaller particles Proved that negatively charged electrons were part of an atom Viewed atom as a “rai ...
31 - University of South Alabama
... Give a reason why the Thomson plum-pudding model does not agree with experimental observations. ...
... Give a reason why the Thomson plum-pudding model does not agree with experimental observations. ...
What is electricity?
... your jumper like a magnet, because your jumper gains an opposite electric charge. So your jumper and the balloon attract one another like the opposite ends of two magnets. Have you ever walked across a nylon rug or carpet and felt a slight tingling sensation? Then touched something metal, like a doo ...
... your jumper like a magnet, because your jumper gains an opposite electric charge. So your jumper and the balloon attract one another like the opposite ends of two magnets. Have you ever walked across a nylon rug or carpet and felt a slight tingling sensation? Then touched something metal, like a doo ...
Electric Field - Uplift Meridian
... Bring a charged object near a conducting surface, electrons will move in conductor even though no physical contact: electrons in conductor are repelled from the charged object – since some are free to move, they will! ...
... Bring a charged object near a conducting surface, electrons will move in conductor even though no physical contact: electrons in conductor are repelled from the charged object – since some are free to move, they will! ...
4. bonding - New Hartford Central Schools
... atoms in a compound is always zero. 4. When each element has the same oxidation number, these numbers are dropped and the formula is correct as written in step 1. ...
... atoms in a compound is always zero. 4. When each element has the same oxidation number, these numbers are dropped and the formula is correct as written in step 1. ...
Historical influence to MRI
... and magnetic fields, which do not cause ionization and therefore do not have associated potentially harmful effects of ...
... and magnetic fields, which do not cause ionization and therefore do not have associated potentially harmful effects of ...
B2.IV Nuclear and Particle Physics
... where mp ≈ 938.3 MeV/c2 and mn ≈ 939.6 MeV are the masses of the proton and neutron respectively. In nuclear physics it is convenient to measure energies in units of MeV and masses in units of MeV/c2 . Using these units makes it easy for us to convert from mass to mass-energy and vice versa. By assu ...
... where mp ≈ 938.3 MeV/c2 and mn ≈ 939.6 MeV are the masses of the proton and neutron respectively. In nuclear physics it is convenient to measure energies in units of MeV and masses in units of MeV/c2 . Using these units makes it easy for us to convert from mass to mass-energy and vice versa. By assu ...
Power Point over chemistry
... retaining heat is important to our climate. It means that our climate stays much more stable than it would if there were less water on Earth. TAKS Need to Know ...
... retaining heat is important to our climate. It means that our climate stays much more stable than it would if there were less water on Earth. TAKS Need to Know ...
Summer Resources - mvhs
... diamond (Cx), quartz(SiO2)x, silicon carbide(SiC)x. Such solids are essentially giant molecules. The subscript x in these formulas indicates that the component with in the parentheses extends indefinitely. The network solids are hard and brittle (Why?). They have rather high mps. ...
... diamond (Cx), quartz(SiO2)x, silicon carbide(SiC)x. Such solids are essentially giant molecules. The subscript x in these formulas indicates that the component with in the parentheses extends indefinitely. The network solids are hard and brittle (Why?). They have rather high mps. ...
The neutron Hypothesis - The Ohio State University
... The mass of a proton, p, is an important fundamental constant. A logical quantum rationale for the origin of its mass is unknown. Understanding the origin of the mass of a proton is therefore very important in a unified physics model. It is question that has not been asked since there seems to be no ...
... The mass of a proton, p, is an important fundamental constant. A logical quantum rationale for the origin of its mass is unknown. Understanding the origin of the mass of a proton is therefore very important in a unified physics model. It is question that has not been asked since there seems to be no ...
Chapter 2 power point
... Figure 2.5 Millikan’s oil-drop experiment for measuring an electron’s charge. ...
... Figure 2.5 Millikan’s oil-drop experiment for measuring an electron’s charge. ...
Laser in protons out
... The plasma dynamics is described via one-fluid two-temperature Lagrangian "hydrodynamics" codes. Contains a detailed model of the laser-plasma interaction. Laser absorption is calculated by numerical solution of Maxwell’s equations for laser radiation. A simplified model of atomic physics is includ ...
... The plasma dynamics is described via one-fluid two-temperature Lagrangian "hydrodynamics" codes. Contains a detailed model of the laser-plasma interaction. Laser absorption is calculated by numerical solution of Maxwell’s equations for laser radiation. A simplified model of atomic physics is includ ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.