chapt02_lecture from text
... • Key to the chemical behavior of an atom lies in the number and arrangement of its electrons in their orbitals • Bohr model – electrons in discrete orbits • Modern physics defines orbital as area around a nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found • No orbital can contain more than two el ...
... • Key to the chemical behavior of an atom lies in the number and arrangement of its electrons in their orbitals • Bohr model – electrons in discrete orbits • Modern physics defines orbital as area around a nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found • No orbital can contain more than two el ...
A New Physical Model for the Atomic Mass
... neutral atoms by adding the Z number electron masses to the mass of X(A,Z) nuclei. However, the liquid drop model does not give answers for many important questions related to the structure and forces inside the nuclei. The long-standing goal of nuclear physics has been to understand how the structu ...
... neutral atoms by adding the Z number electron masses to the mass of X(A,Z) nuclei. However, the liquid drop model does not give answers for many important questions related to the structure and forces inside the nuclei. The long-standing goal of nuclear physics has been to understand how the structu ...
The chemical elements are fundamental building materials of matter
... • 1.A: All matter is made of atoms. There are a limited number of types of atoms: these are the elements. • 1.B: The atoms of each element have unique structures arising from interactions between electrons and nuclei. • 1.C: Elements display periodicity in their properties when the elements are orga ...
... • 1.A: All matter is made of atoms. There are a limited number of types of atoms: these are the elements. • 1.B: The atoms of each element have unique structures arising from interactions between electrons and nuclei. • 1.C: Elements display periodicity in their properties when the elements are orga ...
Phys 282 EXP 8
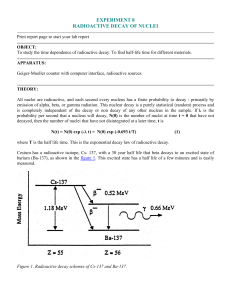
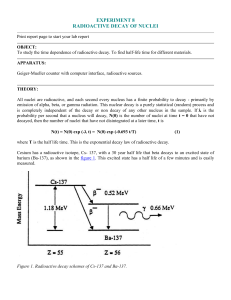
... To study the time dependence of radioactive decay. To find half-life time for different materials. APPARATUS: Geiger-Mueller counter with computer interface, radioactive sources. ...
... To study the time dependence of radioactive decay. To find half-life time for different materials. APPARATUS: Geiger-Mueller counter with computer interface, radioactive sources. ...
1.3 Notes
... 1. Two universal forces in nature are __________________________ and ________________________. 2. They are universal because each force acts the same _____________________ in the universe. 3. __________________________ act between two or more masses. 4. ___________________________ act between two or ...
... 1. Two universal forces in nature are __________________________ and ________________________. 2. They are universal because each force acts the same _____________________ in the universe. 3. __________________________ act between two or more masses. 4. ___________________________ act between two or ...
NMR notes v4.1
... an area of low electron density, the Blocal term in eq. 8 is small. This leads to a higher resonance frequency as seen by eq. 10. When a nucleus is an area of low electron density, the nucleus is said to be deshielded from the applied magnetic field. In order to standardize and simplify the reported ...
... an area of low electron density, the Blocal term in eq. 8 is small. This leads to a higher resonance frequency as seen by eq. 10. When a nucleus is an area of low electron density, the nucleus is said to be deshielded from the applied magnetic field. In order to standardize and simplify the reported ...
CHEMISTRY FALL FINAL PRACTICE 2016
... a. Get the atomic number _________ b. Identify the element __________________ c. Find the mass number of the most common isotope of an element _________ d. Get how many neutrons the most common isotope has _________ e. How many valence electrons an element has _________ f. What is its charge/oxidati ...
... a. Get the atomic number _________ b. Identify the element __________________ c. Find the mass number of the most common isotope of an element _________ d. Get how many neutrons the most common isotope has _________ e. How many valence electrons an element has _________ f. What is its charge/oxidati ...
Chem Regents 2015 A Few Things
... In BOTH types of cell the same types of reaction occur at the same electrode: ANode — OXidation ...
... In BOTH types of cell the same types of reaction occur at the same electrode: ANode — OXidation ...
The Periodic Table OL Page 1 of 2 G. Galvin Name: Periodic Table
... No. of neutrons in an atom = Mass Number (A) – Atomic Number (Z) Defn: Isotopes are atoms of the same element (i.e. they have the same atomic number) which have different mass numbers due to the different number of neutrons in the nucleus. Defn: Relative atomic mass (Ar) is the average of the mass ...
... No. of neutrons in an atom = Mass Number (A) – Atomic Number (Z) Defn: Isotopes are atoms of the same element (i.e. they have the same atomic number) which have different mass numbers due to the different number of neutrons in the nucleus. Defn: Relative atomic mass (Ar) is the average of the mass ...
1.6--NOTES--Detecting Radiation Nuclear Rxtns
... SPS3. Students will distinguish the characteristics and components of radioactivity. a. Differentiate among alpha and beta particles and gamma radiation. b. Differentiate between fission and fusion. c. Explain the process half-life as related to radioactive decay. d. Describe nuclear energy, its pra ...
... SPS3. Students will distinguish the characteristics and components of radioactivity. a. Differentiate among alpha and beta particles and gamma radiation. b. Differentiate between fission and fusion. c. Explain the process half-life as related to radioactive decay. d. Describe nuclear energy, its pra ...
Chem 101A Exam 4 Concepts Chapter 7 – Modern Atomic Theory
... Chem 101A Exam 4 Concepts Chapter 7 – Modern Atomic Theory Use formulas that relate energy of photon, frequency, wavelength, speed of light, and the Rydberg Equation Notable scientists and their contributions: Rutherford, Bohr, Planc, de Broglie, Heisenberg, Schrödinger. The four Quantum ...
... Chem 101A Exam 4 Concepts Chapter 7 – Modern Atomic Theory Use formulas that relate energy of photon, frequency, wavelength, speed of light, and the Rydberg Equation Notable scientists and their contributions: Rutherford, Bohr, Planc, de Broglie, Heisenberg, Schrödinger. The four Quantum ...
CHM_101_TUTORIAL_QUESTIONS_1
... power.The order of penetration power of different sub-shells - s > p > d > f.Therefore, Ionization energy is Directly proportional to Penetration Power. 4. Stability: In stable configuration we require more energy to release the electron as compared to non stable configuration.Therefore, Ionization ...
... power.The order of penetration power of different sub-shells - s > p > d > f.Therefore, Ionization energy is Directly proportional to Penetration Power. 4. Stability: In stable configuration we require more energy to release the electron as compared to non stable configuration.Therefore, Ionization ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.