II. Masses of Atoms
... • A MOLECULE OF CARBON MONOXIDE, CO, HAS ONE ATOM OF OXYGEN WHILE A MOLECULE OF CARBON DIOXIDE, CO2, HAS TWO. IN A SAMPLE OF CO CONTAINING 1 G OF CARBON, 1.33 G OF OXYGEN WILL COMBINE WITH THE CARBON TO FORM THE MOLECULE. WHAT IS THE MASS OF OXYGEN IN A SAMPLE OF CO2 CONTAINING 1 G OF ...
... • A MOLECULE OF CARBON MONOXIDE, CO, HAS ONE ATOM OF OXYGEN WHILE A MOLECULE OF CARBON DIOXIDE, CO2, HAS TWO. IN A SAMPLE OF CO CONTAINING 1 G OF CARBON, 1.33 G OF OXYGEN WILL COMBINE WITH THE CARBON TO FORM THE MOLECULE. WHAT IS THE MASS OF OXYGEN IN A SAMPLE OF CO2 CONTAINING 1 G OF ...
Electron Configuration I Radiant Energy A. study of atomic structure
... IV A New Approach to the Atom A. quantum-mechanical model 1. quantized 2. wavelike 3. can not know exact location B. probability and orbital 1. areas of greatest probability (electron density) described as a cloud 2. orbitals - certain regions where electrons with given energy are likely to be found ...
... IV A New Approach to the Atom A. quantum-mechanical model 1. quantized 2. wavelike 3. can not know exact location B. probability and orbital 1. areas of greatest probability (electron density) described as a cloud 2. orbitals - certain regions where electrons with given energy are likely to be found ...
Bonding homework
... Particles formed from covalent bonding of atoms are called ions. _____________ Molecules are neutral. _____________________ When an atom gains or loses electrons, the charged particle is called a molecule. ________ An atom is chemically unstable when its outer energy level contains all the electrons ...
... Particles formed from covalent bonding of atoms are called ions. _____________ Molecules are neutral. _____________________ When an atom gains or loses electrons, the charged particle is called a molecule. ________ An atom is chemically unstable when its outer energy level contains all the electrons ...
Chemistry - StudyTime NZ
... 2 electrons and 8 electrons. Adding these together, we get a total number of ( 2 + 8 + 2 = 12 electrons) and an electron configura>on of 2, 8, 2. ...
... 2 electrons and 8 electrons. Adding these together, we get a total number of ( 2 + 8 + 2 = 12 electrons) and an electron configura>on of 2, 8, 2. ...
Chemistry 11 – Course Outcomes
... electron configuration notation Distinguish between s and p orbitals Distinguish between orbit and orbital State the: Aufbau principle, Hund’s rule, and Pauli Exclusion principle Define: ionization energy, atomic size (radius) and electron affinity State and explain trends in the periodic table for ...
... electron configuration notation Distinguish between s and p orbitals Distinguish between orbit and orbital State the: Aufbau principle, Hund’s rule, and Pauli Exclusion principle Define: ionization energy, atomic size (radius) and electron affinity State and explain trends in the periodic table for ...
PHY583 - Test 3 - 20.6.12 - with solution
... A type of hadron made up of a quark and an antiquark. All have spin 0 or 1, Their masses between that of the electron & proton. All mesons are known to decay finally into electrons, positrons, neutrinos & photons. Eg. Pion and Kaon ...
... A type of hadron made up of a quark and an antiquark. All have spin 0 or 1, Their masses between that of the electron & proton. All mesons are known to decay finally into electrons, positrons, neutrinos & photons. Eg. Pion and Kaon ...
Nucleus Chapter 1
... The smallest unit of length with which most of us are familiar, is the millimetre (a thousandth of a metre), but for many objects which are only visible through a microscope, length scales are more sensibly expressed in terms of microns. A micron is a millionth of a metre, or a thousandth of a milli ...
... The smallest unit of length with which most of us are familiar, is the millimetre (a thousandth of a metre), but for many objects which are only visible through a microscope, length scales are more sensibly expressed in terms of microns. A micron is a millionth of a metre, or a thousandth of a milli ...
nuclear decays, radioactivity, and reactions
... A is sum of protons and neutrons, Z is number of protons also called atomic number, the principle number that defines the place of an element in the periodic table, X is called parent nucleus for example and Y is called daughter nucleus ...
... A is sum of protons and neutrons, Z is number of protons also called atomic number, the principle number that defines the place of an element in the periodic table, X is called parent nucleus for example and Y is called daughter nucleus ...
ppt - Physics
... The physical quantity responsible of physical and chemical changes in an irradiated material is the energy absorbed from the radiation field. Dosimetry provides a way to determine the amount of energy that has been absorbed by the irradiated material from the radiation. The dose D, is the amount of ...
... The physical quantity responsible of physical and chemical changes in an irradiated material is the energy absorbed from the radiation field. Dosimetry provides a way to determine the amount of energy that has been absorbed by the irradiated material from the radiation. The dose D, is the amount of ...
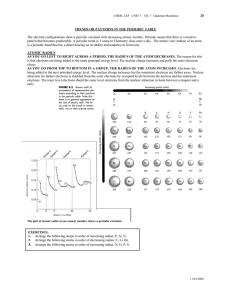
TRENDS OR PATTERNS IN THE PERIODIC TABLE
... Metals are characterized by low ionization energy (very little energy needed to remove the electron). Metals want to lose electrons easily so they must have very low ionization energy. It is easy to pull an electron away from a metal. Nonmetals have high ionization energies (smaller radius – electro ...
... Metals are characterized by low ionization energy (very little energy needed to remove the electron). Metals want to lose electrons easily so they must have very low ionization energy. It is easy to pull an electron away from a metal. Nonmetals have high ionization energies (smaller radius – electro ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.