Document
... Water is a __________. 93. The coefficients are missing from the skeleton equation below. Cr (s) + Fe(NO3)2 (aq) Fe(s) + Cr(NO3)3 (aq) The correct order for the missing coefficients is_________. 94. The equation 2 C3H7OH + 9 O2 6 CO2 + 8 H2O is an example of which type of ...
... Water is a __________. 93. The coefficients are missing from the skeleton equation below. Cr (s) + Fe(NO3)2 (aq) Fe(s) + Cr(NO3)3 (aq) The correct order for the missing coefficients is_________. 94. The equation 2 C3H7OH + 9 O2 6 CO2 + 8 H2O is an example of which type of ...
Textbook Unit 4 Review Solutions
... 20. A positron is an antielectron. It is a particle of antimatter that has the mass and spin of the electron but the opposite charge. 21. A pion is an unstable subatomic particle that has a mass roughly 270 times that of an electron. 22. (a) Use the laws of conservation of mass and energy. The mass ...
... 20. A positron is an antielectron. It is a particle of antimatter that has the mass and spin of the electron but the opposite charge. 21. A pion is an unstable subatomic particle that has a mass roughly 270 times that of an electron. 22. (a) Use the laws of conservation of mass and energy. The mass ...
Chapter 8 (Hill/Petrucci/McCreary/Perry Electron Configurations and
... Chapter 8 (Hill/Petrucci/McCreary/Perry Electron Configurations and Atomic Properties This chapter deals with atoms that have more than one electron … we will look at the ways in which electrons are arranged in the rest of the elements and introduce the concept of an orbital energy diagram. These di ...
... Chapter 8 (Hill/Petrucci/McCreary/Perry Electron Configurations and Atomic Properties This chapter deals with atoms that have more than one electron … we will look at the ways in which electrons are arranged in the rest of the elements and introduce the concept of an orbital energy diagram. These di ...
Periodic_Chemical_Properties
... The effective nuclear charge on the valence np electrons of a Halogen is quite large so the nuclear attraction for the added electron is relatively strong. Also, a filled np subshell and a noble gas electron configuration results which is very stable. Silicon I5 >> I4 (b) E = 25,255 kJ·molG1 (Sum of ...
... The effective nuclear charge on the valence np electrons of a Halogen is quite large so the nuclear attraction for the added electron is relatively strong. Also, a filled np subshell and a noble gas electron configuration results which is very stable. Silicon I5 >> I4 (b) E = 25,255 kJ·molG1 (Sum of ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... protons in the nucleus - also indicates the # of electrons if the element is not charged atomic mass – the average mass of all of the isotopes of an element – is a number with a decimal – is always the larger number on the periodic table. mass number (A) - sum of the protons and neutrons in a nucleu ...
... protons in the nucleus - also indicates the # of electrons if the element is not charged atomic mass – the average mass of all of the isotopes of an element – is a number with a decimal – is always the larger number on the periodic table. mass number (A) - sum of the protons and neutrons in a nucleu ...
Electron Arrangement
... When non-metal atoms join! Eg. Water (H2O), ammonia (NH3), Methane (CH4). These have specific shapes because of the covalent bonds. Covalent molecular substances tend to have low melting and boiling points because they only have Van der Waals’ forces holding the molecules together. Van der Waals’ fo ...
... When non-metal atoms join! Eg. Water (H2O), ammonia (NH3), Methane (CH4). These have specific shapes because of the covalent bonds. Covalent molecular substances tend to have low melting and boiling points because they only have Van der Waals’ forces holding the molecules together. Van der Waals’ fo ...
CHEM 1305 - HCC Learning Web
... -------1. What is the term for the value which indicates the number of protons for an atom of a given element? A) Atomic notation? B) Atomic number? C) Atomic mass? D) Mass number? -------2. What is the term for the shorthand description of the arrangement of electrons by sublevels according to incr ...
... -------1. What is the term for the value which indicates the number of protons for an atom of a given element? A) Atomic notation? B) Atomic number? C) Atomic mass? D) Mass number? -------2. What is the term for the shorthand description of the arrangement of electrons by sublevels according to incr ...
Document
... Electric charge: Chapter 21 •Protons have positive charge •Electrons have negative charge •Opposite signs attract •Similar signs repel •Electric field – used to calculate force C 2009 J. Becker ...
... Electric charge: Chapter 21 •Protons have positive charge •Electrons have negative charge •Opposite signs attract •Similar signs repel •Electric field – used to calculate force C 2009 J. Becker ...
biology terms biochemistry
... matter, has a negative charge and exists independently or as the component outside the nucleus of an atom. 38. A ___________________ is an elementary particle having no charge, has a mass slightly greater than that of a proton, and is a constituent of the nuclei of all atoms except those of hydrogen ...
... matter, has a negative charge and exists independently or as the component outside the nucleus of an atom. 38. A ___________________ is an elementary particle having no charge, has a mass slightly greater than that of a proton, and is a constituent of the nuclei of all atoms except those of hydrogen ...
ReviewPackage_ElectricityMagnetism
... In the nucleus of an atom there are protons and neutrons, while electrons surround the nucleus. o Protons are positive: they cannot move. o Electrons are negative: they can move. o Neutrons do not have a charge A positively charged body has more protons than electrons. A negatively charged bod ...
... In the nucleus of an atom there are protons and neutrons, while electrons surround the nucleus. o Protons are positive: they cannot move. o Electrons are negative: they can move. o Neutrons do not have a charge A positively charged body has more protons than electrons. A negatively charged bod ...
AP Chem
... again later and found to contain 1.30 mg of iodine-131. How much time passed between the determinations of the amount of iodine-131 sample? 14-24.Answer the multiple choice questions attached and free response question 25. Read about Japanese nuclear power plant accident. Write facts about the accid ...
... again later and found to contain 1.30 mg of iodine-131. How much time passed between the determinations of the amount of iodine-131 sample? 14-24.Answer the multiple choice questions attached and free response question 25. Read about Japanese nuclear power plant accident. Write facts about the accid ...
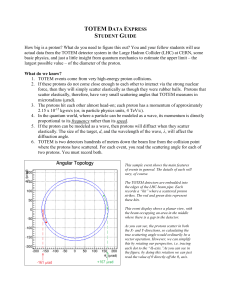
Student Guide - Quarknet
... What do we know? 1. TOTEM events come from very high-energy proton collisions. 2. If these protons do not come close enough to each other to interact via the strong nuclear force, then they will simply scatter elastically as though they were rubber balls. Protons that scatter elastically, therefore, ...
... What do we know? 1. TOTEM events come from very high-energy proton collisions. 2. If these protons do not come close enough to each other to interact via the strong nuclear force, then they will simply scatter elastically as though they were rubber balls. Protons that scatter elastically, therefore, ...
Nuclear Equations - Assignment Point
... known in a nuclear equation, the identity of the missing nucleus (or particle) is easily obtained. – This is illustrated in the next example. ...
... known in a nuclear equation, the identity of the missing nucleus (or particle) is easily obtained. – This is illustrated in the next example. ...
Thomson`s Model of the Atom - ib
... • When some materials are rubbed, they gain the ability to attract or repel other materials. • Such materials are said to have either a positive or a negative electric charge. • Objects with like charges repel, or push apart. • Objects with opposite charges attract, or pull ...
... • When some materials are rubbed, they gain the ability to attract or repel other materials. • Such materials are said to have either a positive or a negative electric charge. • Objects with like charges repel, or push apart. • Objects with opposite charges attract, or pull ...
AP Chemistry Summer Study Guide
... A. Who discovered the electron? Describe the experiment that led to the deduction that electrons are negatively charged. B. Selenium is widely sold as a dietary supplement. It is advertised to “protect” women from breast cancer. Write the nuclear symbol for naturally occurring selenium. It has 34 pr ...
... A. Who discovered the electron? Describe the experiment that led to the deduction that electrons are negatively charged. B. Selenium is widely sold as a dietary supplement. It is advertised to “protect” women from breast cancer. Write the nuclear symbol for naturally occurring selenium. It has 34 pr ...
All you need to know about Additional Science
... What range of pH numbers are acids? What pH number is Neutral? What type of ions make solutions Acidic? What type of ions make solutions Alkaline? What happens to those ions during neutralisation? What type of Salts are made when Sulphuric Acid is used? What type of Salts are made when Hydrochloric ...
... What range of pH numbers are acids? What pH number is Neutral? What type of ions make solutions Acidic? What type of ions make solutions Alkaline? What happens to those ions during neutralisation? What type of Salts are made when Sulphuric Acid is used? What type of Salts are made when Hydrochloric ...
CMC Chapter 5
... Section 5.2 Quantum Theory and the Atom • Compare the Bohr and quantum mechanical models of the atom. • Explain the impact of de Broglie's wave article duality and the Heisenberg uncertainty principle on the current view of electrons in atoms. • Identify the relationships among a hydrogen atom's en ...
... Section 5.2 Quantum Theory and the Atom • Compare the Bohr and quantum mechanical models of the atom. • Explain the impact of de Broglie's wave article duality and the Heisenberg uncertainty principle on the current view of electrons in atoms. • Identify the relationships among a hydrogen atom's en ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.