Final Review Session
... why sky is blue and sunsets red, why clouds are white, why water is green-blue Ch 31: Light Quanta, intro to quantum mechanics, historic debate on is light a wave or particle, Planck’s constant, quantization, E=hf for photon, light brightness depends on N, photoelectric effect, Young’s double-slit e ...
... why sky is blue and sunsets red, why clouds are white, why water is green-blue Ch 31: Light Quanta, intro to quantum mechanics, historic debate on is light a wave or particle, Planck’s constant, quantization, E=hf for photon, light brightness depends on N, photoelectric effect, Young’s double-slit e ...
IONIC bond
... Elements are arranged by their atomic number on the Periodic Table The horizontal rows are called Periods & tell the number of energy levels Vertical groups are called Families & tell the outermost number of electrons ...
... Elements are arranged by their atomic number on the Periodic Table The horizontal rows are called Periods & tell the number of energy levels Vertical groups are called Families & tell the outermost number of electrons ...
Molecular Geometry Why?
... is based on the premise that electrons around a central atom repel each other. Electron domains are areas of high electron density such as bonds (single, double or triple) and lone-pairs of electrons. In simple terms VSEPR means that all electron bonding domains and electron nonbonding domains aroun ...
... is based on the premise that electrons around a central atom repel each other. Electron domains are areas of high electron density such as bonds (single, double or triple) and lone-pairs of electrons. In simple terms VSEPR means that all electron bonding domains and electron nonbonding domains aroun ...
the Mythical Man-Month Frederick P. Brooks, Jr., 1975
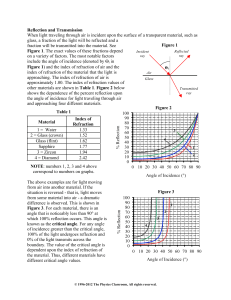
... from one medium to another. It is due to light travelling at different speeds in the two media. It is called refraction of light. As a result, the ray keeps the same direction as before but is laterally ...
... from one medium to another. It is due to light travelling at different speeds in the two media. It is called refraction of light. As a result, the ray keeps the same direction as before but is laterally ...
Laser Communication Systems.pdf
... A population inversion is achieved when the majority of atoms have reached this metastable state. Lasing action occurs when an electron spontaneously returns to its ground state and produces a photon. If the energy from this photon is of the precise wavelength, it will stimulate the production of an ...
... A population inversion is achieved when the majority of atoms have reached this metastable state. Lasing action occurs when an electron spontaneously returns to its ground state and produces a photon. If the energy from this photon is of the precise wavelength, it will stimulate the production of an ...
8 Seeing the Heavens: Telescopes and Detectors
... 2. As the particles created in the original collision collide with other nuclei in the atmosphere, they produce additional particles and high-energy photons. 3. In the lower atmosphere, the cascade of particles slows sufficiently that most of the interaction with the atmosphere produces UV light thr ...
... 2. As the particles created in the original collision collide with other nuclei in the atmosphere, they produce additional particles and high-energy photons. 3. In the lower atmosphere, the cascade of particles slows sufficiently that most of the interaction with the atmosphere produces UV light thr ...
Photoionization of Carbon-60 - UW-Madison Astronomy
... This behavior was not observed in a previous C60 experiment [3]. For this reason, we are now closely investigating the cross section of the C60 between the energies of 85-240eV. We are also trying to determine if this behavior is a result of using a Si3N4 filter or if this could be due to temperatur ...
... This behavior was not observed in a previous C60 experiment [3]. For this reason, we are now closely investigating the cross section of the C60 between the energies of 85-240eV. We are also trying to determine if this behavior is a result of using a Si3N4 filter or if this could be due to temperatur ...























