Synchrotron - schoolphysics
... The Proton Synchrotron at CERN in Geneva has an orbit diameter of 172m, deflecting magnets of 1.4T and accelerates protons to 28 GeV. Each proton pulse contains about 1011 protons and during the acceleration the protons travel some 80 000 km (50 000 miles)! Protons from the synchrotron are shot into ...
... The Proton Synchrotron at CERN in Geneva has an orbit diameter of 172m, deflecting magnets of 1.4T and accelerates protons to 28 GeV. Each proton pulse contains about 1011 protons and during the acceleration the protons travel some 80 000 km (50 000 miles)! Protons from the synchrotron are shot into ...
prompt_double_jpsi
... reconstructed event number of color-singlet model would be great less than that of Wuhan, color-octet. ...
... reconstructed event number of color-singlet model would be great less than that of Wuhan, color-octet. ...
Computational aspects The role of the gel
... energy of soft gel-like particles from a fluid interface is calculated. The role of the particle softness on the desorption energy is studied. Contrary to the common belief about the desorption energy of soft particles, it is shown that the higher softness of the particle does not affect the maximum ...
... energy of soft gel-like particles from a fluid interface is calculated. The role of the particle softness on the desorption energy is studied. Contrary to the common belief about the desorption energy of soft particles, it is shown that the higher softness of the particle does not affect the maximum ...
1-12
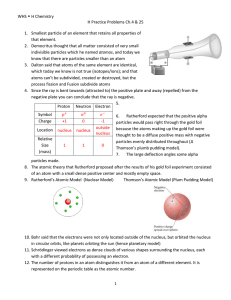
... Rutherford expected that the positive alpha particles would pass right through the gold foil because the atoms making up the gold foil were thought to be a diffuse positive mass with negative particles evenly distributed throughout (JJ Thomson’s plumb pudding model). ...
... Rutherford expected that the positive alpha particles would pass right through the gold foil because the atoms making up the gold foil were thought to be a diffuse positive mass with negative particles evenly distributed throughout (JJ Thomson’s plumb pudding model). ...
PP_Cosm_2b
... Physicists went on mountain tops for experiments! 1937: New particle discovered: negative charge, ~ 200 me Very longe range in matter !? Not Yukawa’s “pion” ! ...
... Physicists went on mountain tops for experiments! 1937: New particle discovered: negative charge, ~ 200 me Very longe range in matter !? Not Yukawa’s “pion” ! ...
Compact Muon Solenoid

The Compact Muon Solenoid (CMS) experiment is one of two large general-purpose particle physics detectors built on the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN in Switzerland and France. The goal of CMS experiment is to investigate a wide range of physics, including the search for the Higgs boson, extra dimensions, and particles that could make up dark matter.CMS is 21.6 metres long, 15 metres in diameter, and weighs about 14,000 tonnes. Approximately 3,800 people, representing 199 scientific institutes and 43 countries, form the CMS collaboration who built and now operate the detector. It is located in an underground cavern at Cessy in France, just across the border from Geneva. In July 2012, along with ATLAS, CMS tentatively discovered the Higgs Boson.