TPS23753A IEEE 802.3 PoE Interface and Converter Controller With
... maximum average power drawn by the PD during operation. The TPS23753A supports class 0 – 3 power levels. CS The current sense input for the dc/dc converter should be connected to the high side of the switching MOSFET’s current sense resistor. The current-limit threshold, VCSMAX, defines the voltage ...
... maximum average power drawn by the PD during operation. The TPS23753A supports class 0 – 3 power levels. CS The current sense input for the dc/dc converter should be connected to the high side of the switching MOSFET’s current sense resistor. The current-limit threshold, VCSMAX, defines the voltage ...
EXPERIMENT NO
... In common base configuration, the base of the transistor is common to the input and output circuits. Input voltage is applied between emitter and base. Output is taken across collector and base. CB configuration is also called as grounded base configuration. In this set up, an increase in emitter cu ...
... In common base configuration, the base of the transistor is common to the input and output circuits. Input voltage is applied between emitter and base. Output is taken across collector and base. CB configuration is also called as grounded base configuration. In this set up, an increase in emitter cu ...
VSWR, or Voltage Standing Wave Ratio.
... It is important to know that for accurate VSWR measurements of devices, the VSWR should be measured at the input of the device in question (antenna, CDN, etc). Any cable loss, or attenuation, will make the VSWR at the input of the cable appear much better than at the load or termination. The reason ...
... It is important to know that for accurate VSWR measurements of devices, the VSWR should be measured at the input of the device in question (antenna, CDN, etc). Any cable loss, or attenuation, will make the VSWR at the input of the cable appear much better than at the load or termination. The reason ...
I. Introduction
... signal processing. A useful function block for high frequency current mode applications is a current conveyor. The current conveyor is a three terminal device performing many useful analog signal processing functions when the device is connected with other electronic elements in specific circuit con ...
... signal processing. A useful function block for high frequency current mode applications is a current conveyor. The current conveyor is a three terminal device performing many useful analog signal processing functions when the device is connected with other electronic elements in specific circuit con ...
REF01,02,03 - Analog Devices
... With an external buffer and a simple resistor network, the TEMP terminal can be used for temperature sensing and approximation. A TRIM terminal is also provided on the device for fine adjustment of the output voltage. The small footprint, wide supply range, and application versatility make the REF01 ...
... With an external buffer and a simple resistor network, the TEMP terminal can be used for temperature sensing and approximation. A TRIM terminal is also provided on the device for fine adjustment of the output voltage. The small footprint, wide supply range, and application versatility make the REF01 ...
High-Power LED Driver with Integrated High-Side LED General Description Features
... The MAX16834 is a current-mode high-brightness LED (HB LED) driver for boost, boost-buck, SEPIC, and highside buck topologies. In addition to driving an n-channel power MOSFET switch controlled by the switching controller, it also drives an n-channel PWM dimming switch to achieve LED PWM dimming. Th ...
... The MAX16834 is a current-mode high-brightness LED (HB LED) driver for boost, boost-buck, SEPIC, and highside buck topologies. In addition to driving an n-channel power MOSFET switch controlled by the switching controller, it also drives an n-channel PWM dimming switch to achieve LED PWM dimming. Th ...
Building Blocks of Integrated Circuit Amplifiers
... large capacitors are not available very small capacitors are easy to fabricate One objective is to realize as many functions as possible using MOS transistors only. Reduction of device size is of great concern. In this text, focus is placed on CMOS circuit fabrication. ...
... large capacitors are not available very small capacitors are easy to fabricate One objective is to realize as many functions as possible using MOS transistors only. Reduction of device size is of great concern. In this text, focus is placed on CMOS circuit fabrication. ...
AN2983
... Whenever a lighting application, such as street lighting for example, requires an elevated number of LEDs, there are basically two solutions: the first is to connect all the diodes in series in a single "string"; the second is to place several strings in parallel with fewer elements in each one. The ...
... Whenever a lighting application, such as street lighting for example, requires an elevated number of LEDs, there are basically two solutions: the first is to connect all the diodes in series in a single "string"; the second is to place several strings in parallel with fewer elements in each one. The ...
mc34161d.pdf
... The MC34161/MC33161 are universal voltage monitors intended for use in a wide variety of voltage sensing applications. These devices offer the circuit designer an economical solution for positive and negative voltage detection. The circuit consists of two comparator channels each with hysteresis, a ...
... The MC34161/MC33161 are universal voltage monitors intended for use in a wide variety of voltage sensing applications. These devices offer the circuit designer an economical solution for positive and negative voltage detection. The circuit consists of two comparator channels each with hysteresis, a ...
Estimation of Capacitance in CMOS Logic Gates - INESC-ID
... and one output node. The additional difficulty is that we now have internal capacitance modeling. We analyze the equivalent capacitance from superposition of the signals. For example, when calculate the equivalent capacitance to a input node, the inputs and output will be in the ground level. The ca ...
... and one output node. The additional difficulty is that we now have internal capacitance modeling. We analyze the equivalent capacitance from superposition of the signals. For example, when calculate the equivalent capacitance to a input node, the inputs and output will be in the ground level. The ca ...
LOW-NOISE ADSL DUAL DIFFERENTIAL RECEIVER THS6062
... The THS6062 is a high-speed differential receiver designed for ADSL data communication systems. Its very low 1.6 nV/√Hz voltage noise provides the high signal-to-noise ratios necessary for the long transmission lengths of ADSL systems over copper telephone lines. In addition, this receiver operates ...
... The THS6062 is a high-speed differential receiver designed for ADSL data communication systems. Its very low 1.6 nV/√Hz voltage noise provides the high signal-to-noise ratios necessary for the long transmission lengths of ADSL systems over copper telephone lines. In addition, this receiver operates ...
8N3PG10MBKI-161LF - Integrated Device Technology
... the Printed Circuit Board (PCB) within the footprint of the package corresponding to the exposed metal pad or exposed heat slug on the package, as shown in Figure 4. The solderable area on the PCB, as defined by the solder mask, should be at least the same size/shape as the exposed pad/slug area on ...
... the Printed Circuit Board (PCB) within the footprint of the package corresponding to the exposed metal pad or exposed heat slug on the package, as shown in Figure 4. The solderable area on the PCB, as defined by the solder mask, should be at least the same size/shape as the exposed pad/slug area on ...
AAT3604B 数据资料DataSheet下载
... The AAT3604B is a highly integrated device which simplifies system level design for the user with minimal external components required. It contains a step-up (boost) converter, a step-down (buck) converter, an LDO regulator and a single-cell Lithium Ion/Polymer battery charger in a single PMU. The d ...
... The AAT3604B is a highly integrated device which simplifies system level design for the user with minimal external components required. It contains a step-up (boost) converter, a step-down (buck) converter, an LDO regulator and a single-cell Lithium Ion/Polymer battery charger in a single PMU. The d ...
MAX8713 Simplified Multichemistry SMBus Battery Charger General Description
... construction of smart chargers with a minimum number of external components. It uses the Intel System Management Bus (SMBus™) to control the charge voltage and charge current. High efficiency is achieved through the use of a constant off-time step-down topology with synchronous rectification. The MA ...
... construction of smart chargers with a minimum number of external components. It uses the Intel System Management Bus (SMBus™) to control the charge voltage and charge current. High efficiency is achieved through the use of a constant off-time step-down topology with synchronous rectification. The MA ...
THE MclNTOSH C 26 SOLID STATE STEREO PREAMPLIFIER
... in the background when the recordings are played back. This noise is caused by insufficient filtering of the bias oscillator circuits in the tape recorders. A test run should be made for the particular recorders intended for this use. ...
... in the background when the recordings are played back. This noise is caused by insufficient filtering of the bias oscillator circuits in the tape recorders. A test run should be made for the particular recorders intended for this use. ...
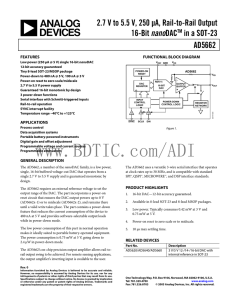
2.7 V to 5.5 V, 250 µA, Rail-to-Rail Output nano AD5662
... and VOUT (ideal) expressed in mV in the linear region of the transfer function. Offset error is measured on the AD5662 with Code 512 loaded in the DAC register. It can be negative or positive. ...
... and VOUT (ideal) expressed in mV in the linear region of the transfer function. Offset error is measured on the AD5662 with Code 512 loaded in the DAC register. It can be negative or positive. ...
Mid-Term Report (March 20)
... result of the absorption of photons, free carriers that support the conduction of current. In other words, a photo detector detects light and transmits a current based on the amount of light detected. The PD used in this design will be of the PIN, or positive-intrinsic-negative, type with a large in ...
... result of the absorption of photons, free carriers that support the conduction of current. In other words, a photo detector detects light and transmits a current based on the amount of light detected. The PD used in this design will be of the PIN, or positive-intrinsic-negative, type with a large in ...
n2” lI/l I3
... 115b, thus providing a relatively constant current flow tional ampli?er 110 in the unity gain mode with the through transistor 1151). This current flow through the differential voltage between leads 116 and 117a equal to inverting input leg provides compensation for the inher zero (i.e. both leads 1 ...
... 115b, thus providing a relatively constant current flow tional ampli?er 110 in the unity gain mode with the through transistor 1151). This current flow through the differential voltage between leads 116 and 117a equal to inverting input leg provides compensation for the inher zero (i.e. both leads 1 ...
BDTIC Application Note No. 017
... Improved stabilization behaviour versus temperature reduced variation in amplifier performance due to the device‘s Beta (current gain) distribution can be achieved by using an active bias circuit. Such a circuit is available as a single device from Infineon - BCR400W. For further information please ...
... Improved stabilization behaviour versus temperature reduced variation in amplifier performance due to the device‘s Beta (current gain) distribution can be achieved by using an active bias circuit. Such a circuit is available as a single device from Infineon - BCR400W. For further information please ...
UNIT-V DAC: Principles – weighted-resistor network, R
... The conversion takes place in two phases: the run-up phase, where the input to the integrator is the voltage to be measured, and the run-down phase, where the input to the integrator is a known reference voltage. During the run-up phase, the switch selects the measured voltage as the input to the in ...
... The conversion takes place in two phases: the run-up phase, where the input to the integrator is the voltage to be measured, and the run-down phase, where the input to the integrator is a known reference voltage. During the run-up phase, the switch selects the measured voltage as the input to the in ...
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that increases the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. In this sense, an amplifier modulates the output of the power supply to make the output signal stronger than the input signal. An amplifier is effectively the opposite of an attenuator: while an amplifier provides gain, an attenuator provides loss.An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit within another device. The ability to amplify is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are extremely widely used in almost all electronic equipment. The types of amplifiers can be categorized in different ways. One is by the frequency of the electronic signal being amplified; audio amplifiers amplify signals in the audio (sound) range of less than 20 kHz, RF amplifiers amplify frequencies in the radio frequency range between 20 kHz and 300 GHz. Another is which quantity, voltage or current is being amplified; amplifiers can be divided into voltage amplifiers, current amplifiers, transconductance amplifiers, and transresistance amplifiers. A further distinction is whether the output is a linear or nonlinear representation of the input. Amplifiers can also be categorized by their physical placement in the signal chain.The first practical electronic device that amplified was the Audion (triode) vacuum tube, invented in 1906 by Lee De Forest, which led to the first amplifiers. The terms ""amplifier"" and ""amplification"" (from the Latin amplificare, 'to enlarge or expand') were first used for this new capability around 1915 when triodes became widespread. For the next 50 years, vacuum tubes were the only devices that could amplify. All amplifiers used them until the 1960s, when transistors appeared. Most amplifiers today use transistors, though tube amplifiers are still produced.