ioSelect DC to Frequency Isolating Signal Conditioner
... If, for example, the input represents a flow in gallons per hour, then the time integral of this flow signal (total count) will represent total gallons. The input of the UP475 can supply voltage for a 2-wire current loop, up to 20 V dc. There are two output choices, an npn open collector or a reed r ...
... If, for example, the input represents a flow in gallons per hour, then the time integral of this flow signal (total count) will represent total gallons. The input of the UP475 can supply voltage for a 2-wire current loop, up to 20 V dc. There are two output choices, an npn open collector or a reed r ...
[PDF]
... and a reference source. The column drivers are especially important to achieving high-speed driving, high resolution and low-power dissipation. Class A and class B amplifier combine their configuration in class AB amplifier in which small collector current will flow when there is no input signal but ...
... and a reference source. The column drivers are especially important to achieving high-speed driving, high resolution and low-power dissipation. Class A and class B amplifier combine their configuration in class AB amplifier in which small collector current will flow when there is no input signal but ...
Users Manual
... allows the user gain-up and re-slope the amp’s tone stack allowing much more midrange to flow through the circuit; thereby gaining up the entire amp naturally and not inducing false preamp gain that creates fizz and buzz. The end result is the effect of having two amps in one. Speed & Intensity: The ...
... allows the user gain-up and re-slope the amp’s tone stack allowing much more midrange to flow through the circuit; thereby gaining up the entire amp naturally and not inducing false preamp gain that creates fizz and buzz. The end result is the effect of having two amps in one. Speed & Intensity: The ...
A v
... • Power the op-amp and apply a voltage • Works as an amplifier, but: • No flexibility (A~105-6) • Exact gain is unreliable (depends on chip, frequency and temp) • Saturates at very low input voltages (Max vout=power supply voltage) • To operate as an amp, v+-v-
... • Power the op-amp and apply a voltage • Works as an amplifier, but: • No flexibility (A~105-6) • Exact gain is unreliable (depends on chip, frequency and temp) • Saturates at very low input voltages (Max vout=power supply voltage) • To operate as an amp, v+-v-
DMT 231 / 3 Lecture V Frequency Response of BJT
... less voltage gain (then they have at higher freq): Figure 1 More signal voltage is dropped across C1 & C3 (higher reactances : reduce voltage gain) Reactance of C2 becomes significant & the emitter is no longer at ac ground. ...
... less voltage gain (then they have at higher freq): Figure 1 More signal voltage is dropped across C1 & C3 (higher reactances : reduce voltage gain) Reactance of C2 becomes significant & the emitter is no longer at ac ground. ...
Document
... the four types, only class A amplifier does not have high distortion output. However, it has a draw back of low efficiency. Therefore, it is usually used on small signal amplifier. Class AB can also work on analogue signals but at least two transistors will be used to build an amplifier to achieve ...
... the four types, only class A amplifier does not have high distortion output. However, it has a draw back of low efficiency. Therefore, it is usually used on small signal amplifier. Class AB can also work on analogue signals but at least two transistors will be used to build an amplifier to achieve ...
MAX9715 2.8W, Low-EMI, Stereo, Filterless Class D Audio Amplifier General Description
... dielectrics, such as tantalum or aluminum electrolytic. Capacitors with high-voltage coefficients, such as ceramics, may result in increased distortion at low frequencies. The inability of small diaphragm speakers to reproduce low frequencies can be exploited to improve click-andpop performance. Set ...
... dielectrics, such as tantalum or aluminum electrolytic. Capacitors with high-voltage coefficients, such as ceramics, may result in increased distortion at low frequencies. The inability of small diaphragm speakers to reproduce low frequencies can be exploited to improve click-andpop performance. Set ...
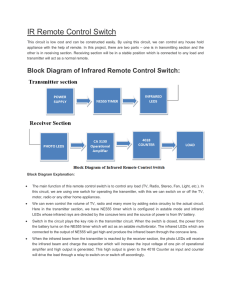
Block Diagram of Infrared Remote Control Switch
... CA3130: CA3130 is a BiCMOS operational amplifier, which has very high input impedance, very low input current and high speed performance. It had very low input swing i.e. below 0.5V; the operating supply voltage is of around 5V to 16V. It will permit the output swing also. Maximum differential volta ...
... CA3130: CA3130 is a BiCMOS operational amplifier, which has very high input impedance, very low input current and high speed performance. It had very low input swing i.e. below 0.5V; the operating supply voltage is of around 5V to 16V. It will permit the output swing also. Maximum differential volta ...
M/s CMR Design
... (b) In Schottky TTL circuits, the transistors are not allowed to go into saturation. (c) A TTL gate has a passive pull up. (d) The input transistor in a TTL gate operates in inverse active mode when input is low. 20. Select the wrong statement (s). (a) A Pseudo-NMOS AND gate contains only one pull u ...
... (b) In Schottky TTL circuits, the transistors are not allowed to go into saturation. (c) A TTL gate has a passive pull up. (d) The input transistor in a TTL gate operates in inverse active mode when input is low. 20. Select the wrong statement (s). (a) A Pseudo-NMOS AND gate contains only one pull u ...
Giga-tronics white paper - RF/Microwave instrumentation amplifiers
... required to optimize any one parameter over another and performance compromises are usually necessary for an amplifier that may be used in a general purpose testing application. Broadband amplifiers, covering a decade or more in bandwidth are difficult to achieve, especially at higher power levels. ...
... required to optimize any one parameter over another and performance compromises are usually necessary for an amplifier that may be used in a general purpose testing application. Broadband amplifiers, covering a decade or more in bandwidth are difficult to achieve, especially at higher power levels. ...
click here
... amplifier is undoubtedly compromised by the modest Q of the input inductor. The SMT trimmer capacitor is also subject. But 1.5 dB will be more than adequate for 50 MHz applications. There should be no difficulty in obtaining similar results at HF and at 144 MHz. ...
... amplifier is undoubtedly compromised by the modest Q of the input inductor. The SMT trimmer capacitor is also subject. But 1.5 dB will be more than adequate for 50 MHz applications. There should be no difficulty in obtaining similar results at HF and at 144 MHz. ...
SC451 - Semtech
... Geyserville-III core voltage specification. It provides direct “deeper sleep” mode and boot voltage support. Automatic “power-save” is present to prevent negative current flow in the low-side FET during light loading conditions, saving even more power. The high side driver initially turns on with a ...
... Geyserville-III core voltage specification. It provides direct “deeper sleep” mode and boot voltage support. Automatic “power-save” is present to prevent negative current flow in the low-side FET during light loading conditions, saving even more power. The high side driver initially turns on with a ...
Chapter 6 - An
... The common-collector (CC) amplifier is usually referred to as an emitter-follower (EF). The input is applied to the base through a coupling capacitor, and the output is at the emitter (no phase change between input and output). The voltage gain of a CC amplifier is approximately 1, and its main ad ...
... The common-collector (CC) amplifier is usually referred to as an emitter-follower (EF). The input is applied to the base through a coupling capacitor, and the output is at the emitter (no phase change between input and output). The voltage gain of a CC amplifier is approximately 1, and its main ad ...
Lab02_PartA - Weber State University
... Note that the biggest source of variations from your simulation results will be due to the variation in β. Q1: What is the maximum gain that you can achieve without distorting the output signal? Q2: Increase the input voltage amplitude until you start seeing distortion in the output voltage. Can you ...
... Note that the biggest source of variations from your simulation results will be due to the variation in β. Q1: What is the maximum gain that you can achieve without distorting the output signal? Q2: Increase the input voltage amplitude until you start seeing distortion in the output voltage. Can you ...
Ami Pro - EUMC-DEF.SAM
... biased, the oscillation frequency approaches the critical frequency of the artificial transmission line fc , while it reaches its minimum when the rightmost device is the only active one. Besides four discrete frequencies, each belonging to one active transistor, this oscillator is capable of genera ...
... biased, the oscillation frequency approaches the critical frequency of the artificial transmission line fc , while it reaches its minimum when the rightmost device is the only active one. Besides four discrete frequencies, each belonging to one active transistor, this oscillator is capable of genera ...
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that increases the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. In this sense, an amplifier modulates the output of the power supply to make the output signal stronger than the input signal. An amplifier is effectively the opposite of an attenuator: while an amplifier provides gain, an attenuator provides loss.An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit within another device. The ability to amplify is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are extremely widely used in almost all electronic equipment. The types of amplifiers can be categorized in different ways. One is by the frequency of the electronic signal being amplified; audio amplifiers amplify signals in the audio (sound) range of less than 20 kHz, RF amplifiers amplify frequencies in the radio frequency range between 20 kHz and 300 GHz. Another is which quantity, voltage or current is being amplified; amplifiers can be divided into voltage amplifiers, current amplifiers, transconductance amplifiers, and transresistance amplifiers. A further distinction is whether the output is a linear or nonlinear representation of the input. Amplifiers can also be categorized by their physical placement in the signal chain.The first practical electronic device that amplified was the Audion (triode) vacuum tube, invented in 1906 by Lee De Forest, which led to the first amplifiers. The terms ""amplifier"" and ""amplification"" (from the Latin amplificare, 'to enlarge or expand') were first used for this new capability around 1915 when triodes became widespread. For the next 50 years, vacuum tubes were the only devices that could amplify. All amplifiers used them until the 1960s, when transistors appeared. Most amplifiers today use transistors, though tube amplifiers are still produced.

![[PDF]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008779537_1-466d226fe03fdd75dfb861180f8c75c2-300x300.png)