MAX9155 Low-Jitter, Low-Noise LVDS Repeater in an SC70 Package General Description
... Note 1: All devices are 100% tested at TA = +25°C. Limits over temperature are guaranteed by design and characterization. Note 2: Current into a pin is defined as positive. Current out of a pin is defined as negative. All voltages are referenced to ground except VTH, VTL, VOD, and ∆VOD. Note 3: Guar ...
... Note 1: All devices are 100% tested at TA = +25°C. Limits over temperature are guaranteed by design and characterization. Note 2: Current into a pin is defined as positive. Current out of a pin is defined as negative. All voltages are referenced to ground except VTH, VTL, VOD, and ∆VOD. Note 3: Guar ...
a High Speed, Low Noise Quad Operational Amplifier OP471
... From Figures 4 and 5, it can be seen that to reduce total noise, source resistance must be kept to a minimum. In applications with a high source resistance, the OP400, with lower current noise than the OP471, will provide lower total noise. ...
... From Figures 4 and 5, it can be seen that to reduce total noise, source resistance must be kept to a minimum. In applications with a high source resistance, the OP400, with lower current noise than the OP471, will provide lower total noise. ...
4 Biomedical Measurements and Transducers Full
... In addition, most transducers have a large manufacturing variation in the sensitivity of the diaphragm and consequently there is a large variation in the span sensitivity from one transducer to the next. This means that the parameter S has a large variation so that the full-scale output voltage from ...
... In addition, most transducers have a large manufacturing variation in the sensitivity of the diaphragm and consequently there is a large variation in the span sensitivity from one transducer to the next. This means that the parameter S has a large variation so that the full-scale output voltage from ...
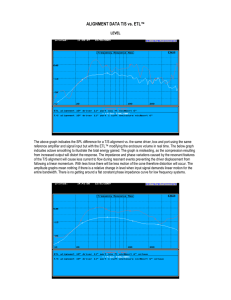
ALIGNMENT DATA T/S vs
... The phase is constant throughout this period with a phase shift less than 5 throughout its bandwidth to 125Hz. The impedance phase does not cross the zero marker throughout a 125 Hz bandwidth with a single zero crossing occurring at driver resonance vs. 4 crossings for the T/L alignment. Driver ou ...
... The phase is constant throughout this period with a phase shift less than 5 throughout its bandwidth to 125Hz. The impedance phase does not cross the zero marker throughout a 125 Hz bandwidth with a single zero crossing occurring at driver resonance vs. 4 crossings for the T/L alignment. Driver ou ...
AD584 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... together to the positive supply (in this case, ground). The AD584 common pin is connected through a resistor to the negative supply. The output is now taken from the common pin instead of VOUT. With 1 mA flowing through the AD584 in this mode, a typical unit will show a 2 mV increase in output level ...
... together to the positive supply (in this case, ground). The AD584 common pin is connected through a resistor to the negative supply. The output is now taken from the common pin instead of VOUT. With 1 mA flowing through the AD584 in this mode, a typical unit will show a 2 mV increase in output level ...
AD8228 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... Low voltage offset, low offset drift, low gain drift, high gain accuracy, and high CMRR make this part an excellent choice in applications that demand the best dc performance possible, such as bridge signal conditioning. ...
... Low voltage offset, low offset drift, low gain drift, high gain accuracy, and high CMRR make this part an excellent choice in applications that demand the best dc performance possible, such as bridge signal conditioning. ...
MAX8526/MAX8527/MAX8528 1.425V to 3.6V Input, 2A, 0.2V Dropout LDO Regulators General Description
... 2A of output current with as little as 200mV of headroom from input to output. The PMOS output stage can be driven from input voltages down to +1.425V without sacrificing stability or transient performance. Since this regulator has a PMOS output device, supply current is not a significant function o ...
... 2A of output current with as little as 200mV of headroom from input to output. The PMOS output stage can be driven from input voltages down to +1.425V without sacrificing stability or transient performance. Since this regulator has a PMOS output device, supply current is not a significant function o ...
ISL6840, ISL6841, ISL6842, ISL6843, ISL6844, ISL6845 Datasheet
... For applications where the maximum duty cycle is less than 50%, slope compensation may be used to improve noise immunity, particularly at lighter loads. The amount of slope compensation required for noise immunity is determined empirically, but is generally about 10% of the full scale current feedba ...
... For applications where the maximum duty cycle is less than 50%, slope compensation may be used to improve noise immunity, particularly at lighter loads. The amount of slope compensation required for noise immunity is determined empirically, but is generally about 10% of the full scale current feedba ...
FEATURES DESCRIPTION D
... OPA820 to operate on a single +5V supply with > 2VPP output swing. While not a rail-to-rail (RR) output, this swing will support most emerging analog-to-digital converter (ADC) input ranges with lower power and noise than typical RR output op amps. Exceptionally low dG/dP (0.01%/0.03°) supports low- ...
... OPA820 to operate on a single +5V supply with > 2VPP output swing. While not a rail-to-rail (RR) output, this swing will support most emerging analog-to-digital converter (ADC) input ranges with lower power and noise than typical RR output op amps. Exceptionally low dG/dP (0.01%/0.03°) supports low- ...
AD8065
... Despite the low cost, the amplifiers provide excellent overall performance. The differential gain and phase errors of 0.02% and 0.02°, respectively, along with 0.1 dB flatness out to 7 MHz, make these amplifiers ideal for video applications. Additionally, they offer a high slew rate of 180 V/μs, exc ...
... Despite the low cost, the amplifiers provide excellent overall performance. The differential gain and phase errors of 0.02% and 0.02°, respectively, along with 0.1 dB flatness out to 7 MHz, make these amplifiers ideal for video applications. Additionally, they offer a high slew rate of 180 V/μs, exc ...
AD8251 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... programmable gains that has GΩ input impedance, low output noise, and low distortion, making it suitable for interfacing with sensors and driving high sample rate analog-to-digital converters (ADCs). It has a high bandwidth of 10 MHz, low THD of −110 dB, and fast settling time of 785 ns (maximum) to ...
... programmable gains that has GΩ input impedance, low output noise, and low distortion, making it suitable for interfacing with sensors and driving high sample rate analog-to-digital converters (ADCs). It has a high bandwidth of 10 MHz, low THD of −110 dB, and fast settling time of 785 ns (maximum) to ...
EE 230: Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 12
... resolution time for a photo diode receiver and an APD receiver with mean gain G=100 and an excess noise factor F=2 ...
... resolution time for a photo diode receiver and an APD receiver with mean gain G=100 and an excess noise factor F=2 ...
CONTACTLESS DIAGNOSTICS OF THIN FILM LAYERS Vaclav Papez Stanislava Papezova
... and its gain is set in order that the voltage on the output of the amplitude detector answers to the reference voltage. current is led into the amplitude detector through the frequency dependent element with a transmission characteristic, where the transfer magnitude is comparable to the frequency. ...
... and its gain is set in order that the voltage on the output of the amplitude detector answers to the reference voltage. current is led into the amplitude detector through the frequency dependent element with a transmission characteristic, where the transfer magnitude is comparable to the frequency. ...
Low-Noise, Regulated, Negative Charge-Pump Power Supplies for GaAsFET Bias _______________General Description ____________________________Features
... Use capacitors with low effective series resistance (ESR) to maintain a low dropout voltage (VIN - |VOUT|). The overall dropout voltage is a function of the charge pump’s output resistance and the voltage drop across the linear regulator (N-channel pass transistor). At the 100kHz switching frequency ...
... Use capacitors with low effective series resistance (ESR) to maintain a low dropout voltage (VIN - |VOUT|). The overall dropout voltage is a function of the charge pump’s output resistance and the voltage drop across the linear regulator (N-channel pass transistor). At the 100kHz switching frequency ...
ADP3301 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... above 165°C, the output current is reduced until die temperature has dropped to a safe level. Output current is restored when the die temperature is reduced. Current and thermal limit protections are intended to protect the device against accidental overload conditions. For normal operation, device ...
... above 165°C, the output current is reduced until die temperature has dropped to a safe level. Output current is restored when the die temperature is reduced. Current and thermal limit protections are intended to protect the device against accidental overload conditions. For normal operation, device ...
MULTIFUNCTION VERY LOW DROP VOLTAGE REGULATOR
... internal voltage is present at Pin 3 (VZ). This voltage should not be used as an output because the output capability is very small (≤10µA). This output may be used as an option when a better transient behaviour for supply voltages less than 8V is required (see also application note). In this case a ...
... internal voltage is present at Pin 3 (VZ). This voltage should not be used as an output because the output capability is very small (≤10µA). This output may be used as an option when a better transient behaviour for supply voltages less than 8V is required (see also application note). In this case a ...
Triple Differential Driver With Sync-On-Common-Mode AD8134
... The AD8134 is a major advancement beyond using discrete op amps for driving differential RGB signals over twisted pair cable. The AD8134 is a triple, low cost differential or singleended input to differential output driver, and each amplifier has a fixed gain of 2 to compensate for the attenuation o ...
... The AD8134 is a major advancement beyond using discrete op amps for driving differential RGB signals over twisted pair cable. The AD8134 is a triple, low cost differential or singleended input to differential output driver, and each amplifier has a fixed gain of 2 to compensate for the attenuation o ...
MAX8516/MAX8517/MAX8518 1.425V to 3.6V Input, 1A, 0.2V Dropout LDO Regulators General Description
... from input to output. The PMOS output stage can be driven from input voltages down to +1.425V without sacrificing stability or transient performance. Since these regulators have a PMOS output device, supply current is not a significant function of load or input headroom. ...
... from input to output. The PMOS output stage can be driven from input voltages down to +1.425V without sacrificing stability or transient performance. Since these regulators have a PMOS output device, supply current is not a significant function of load or input headroom. ...
Capacitor Self
... over a couple hundred feet with inexpensive plastic lenses (the type that you used for bugboxes when you were a kid). Notice that the experiment above only required 9 V and therefore, can be built using two 9 V batteries. The input to the LED could be a tape/CD player, or simply a small electric mic ...
... over a couple hundred feet with inexpensive plastic lenses (the type that you used for bugboxes when you were a kid). Notice that the experiment above only required 9 V and therefore, can be built using two 9 V batteries. The input to the LED could be a tape/CD player, or simply a small electric mic ...
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that increases the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. In this sense, an amplifier modulates the output of the power supply to make the output signal stronger than the input signal. An amplifier is effectively the opposite of an attenuator: while an amplifier provides gain, an attenuator provides loss.An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit within another device. The ability to amplify is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are extremely widely used in almost all electronic equipment. The types of amplifiers can be categorized in different ways. One is by the frequency of the electronic signal being amplified; audio amplifiers amplify signals in the audio (sound) range of less than 20 kHz, RF amplifiers amplify frequencies in the radio frequency range between 20 kHz and 300 GHz. Another is which quantity, voltage or current is being amplified; amplifiers can be divided into voltage amplifiers, current amplifiers, transconductance amplifiers, and transresistance amplifiers. A further distinction is whether the output is a linear or nonlinear representation of the input. Amplifiers can also be categorized by their physical placement in the signal chain.The first practical electronic device that amplified was the Audion (triode) vacuum tube, invented in 1906 by Lee De Forest, which led to the first amplifiers. The terms ""amplifier"" and ""amplification"" (from the Latin amplificare, 'to enlarge or expand') were first used for this new capability around 1915 when triodes became widespread. For the next 50 years, vacuum tubes were the only devices that could amplify. All amplifiers used them until the 1960s, when transistors appeared. Most amplifiers today use transistors, though tube amplifiers are still produced.