Owner’s Manual Sigma Series AMP5 Five-Channel Amplifier
... 14. Refer all servicing to qualified service personnel. Servicing is required when the apparatus has been damaged in any way, such as power-supply cord or plug is damaged, liquid has been spilled or objects have fallen into the apparatus, the apparatus has been exposed to rain or moisture, does no ...
... 14. Refer all servicing to qualified service personnel. Servicing is required when the apparatus has been damaged in any way, such as power-supply cord or plug is damaged, liquid has been spilled or objects have fallen into the apparatus, the apparatus has been exposed to rain or moisture, does no ...
差分放大器系列AD8321 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... of 0 dB to –53.4 dB, which is preceded by a low noise, fixed gain buffer and followed by a low distortion high power ampli fier. The AD8321 accepts a differential or single-ended input signal. The output is specified for driving a 75 W load, such as coaxial cable, although the AD8321 is capable of ...
... of 0 dB to –53.4 dB, which is preceded by a low noise, fixed gain buffer and followed by a low distortion high power ampli fier. The AD8321 accepts a differential or single-ended input signal. The output is specified for driving a 75 W load, such as coaxial cable, although the AD8321 is capable of ...
4.5V 至18V 输入、5.5A 同步降压转换器(Rev. A)
... an internal compensation circuit for pseudo-fixed frequency and low external component count configuration with both low ESR and ceramic output capacitors. It is stable even with virtually no ripple at the output. At the beginning of each cycle, the high-side MOSFET is turned on. This MOSFET is turn ...
... an internal compensation circuit for pseudo-fixed frequency and low external component count configuration with both low ESR and ceramic output capacitors. It is stable even with virtually no ripple at the output. At the beginning of each cycle, the high-side MOSFET is turned on. This MOSFET is turn ...
AppNote Triac Coupler
... The dV/dTcr parameter refers to the situation where the output dV/dT is so fast that it actually triggers the TRIAC eventhough the input trigger voltage is held at zero. Such situations can arise either because the voltage and frequency of the output waveform are extremely high, or more commonly bec ...
... The dV/dTcr parameter refers to the situation where the output dV/dT is so fast that it actually triggers the TRIAC eventhough the input trigger voltage is held at zero. Such situations can arise either because the voltage and frequency of the output waveform are extremely high, or more commonly bec ...
A variable step-down conversion ratio switched capacitor DC–DC
... Vref with a low temperature coefficient can be easily obtained by optimizing temperature-independent circuit parameters r1 /r2 , N. The op-amp with an nMOS differential pair and pMOS followers includes an R–C compensation network for achieving a sufficient stability margin, which allows the input common- ...
... Vref with a low temperature coefficient can be easily obtained by optimizing temperature-independent circuit parameters r1 /r2 , N. The op-amp with an nMOS differential pair and pMOS followers includes an R–C compensation network for achieving a sufficient stability margin, which allows the input common- ...
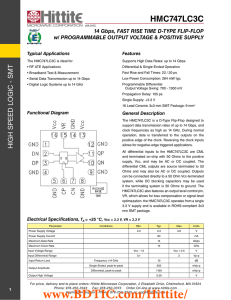
NB4N507A 3.3V/5V, 50 MHz to 200 MHz PECL Clock Synthesizer
... NOTE: Device will meet the specifications after thermal equilibrium has been established when mounted in a test socket or printed circuit board with maintained transverse airflow greater than 500 lfpm. Electrical parameters are guaranteed only over the declared operating temperature range. Functiona ...
... NOTE: Device will meet the specifications after thermal equilibrium has been established when mounted in a test socket or printed circuit board with maintained transverse airflow greater than 500 lfpm. Electrical parameters are guaranteed only over the declared operating temperature range. Functiona ...
MAX8758 Step-Up Regulator with Switch Control and Operational Amplifier for TFT LCD
... The step-up DC-DC regulator provides the regulated supply voltage for the panel source driver ICs. The converter is a high-frequency (640kHz/1.2MHz), current-mode regulator with an integrated 14V n-channel power MOSFET. The high-switching frequency allows the use of ultra-small inductors and ceramic ...
... The step-up DC-DC regulator provides the regulated supply voltage for the panel source driver ICs. The converter is a high-frequency (640kHz/1.2MHz), current-mode regulator with an integrated 14V n-channel power MOSFET. The high-switching frequency allows the use of ultra-small inductors and ceramic ...
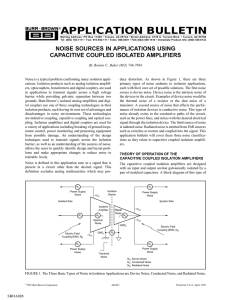
noise sources in applications using capacitive coupled isolated
... DEVICE NOISE AND CAPACITIVE COUPLED ISOLATION AMPLIFIERS Device noise is generated by the devices in the circuit. Examples of device noise generators would be a discrete resistor, which generates thermal noise, or an operational amplifier, which would generate 1/f noise, etc. Specifically, with Burr ...
... DEVICE NOISE AND CAPACITIVE COUPLED ISOLATION AMPLIFIERS Device noise is generated by the devices in the circuit. Examples of device noise generators would be a discrete resistor, which generates thermal noise, or an operational amplifier, which would generate 1/f noise, etc. Specifically, with Burr ...
2.5 V/3.0 V High Precision Reference AD780
... (Q6 and Q7) that differ in emitter area by 12×. The difference in their Vbes produces a PTAT current in R5. This, in turn, produces a PTAT voltage across R4 that, when combined with the Vbe of Q7, produces a voltage (Vbg) that does not vary with temperature. Precision laser trimming of the resistors ...
... (Q6 and Q7) that differ in emitter area by 12×. The difference in their Vbes produces a PTAT current in R5. This, in turn, produces a PTAT voltage across R4 that, when combined with the Vbe of Q7, produces a voltage (Vbg) that does not vary with temperature. Precision laser trimming of the resistors ...
Design of high-speed, low-power frequency dividers and phase
... dissipation, low supply voltage, and highly automated synthesis. In high-speed applications, however, the relatively low transconductance of MOSFET’s often imposes severe speedpower trade-offs, thereby limiting their advantage over silicon bipolar and III-V devices. These trade-offs are nonetheless ...
... dissipation, low supply voltage, and highly automated synthesis. In high-speed applications, however, the relatively low transconductance of MOSFET’s often imposes severe speedpower trade-offs, thereby limiting their advantage over silicon bipolar and III-V devices. These trade-offs are nonetheless ...
Instructions for Use Owner`s Reference
... differ only by how many channels are housed within the amplifier. A Showcase 5 includes five amplifier channels, a Showcase 6 includes six amplifier channels, and a Showcase 7 includes seven amplifier channels. The Showcase 5 and Showcase 6 may be upgraded with additional channels, up to seven. The ...
... differ only by how many channels are housed within the amplifier. A Showcase 5 includes five amplifier channels, a Showcase 6 includes six amplifier channels, and a Showcase 7 includes seven amplifier channels. The Showcase 5 and Showcase 6 may be upgraded with additional channels, up to seven. The ...
VISHAY SI786 datasheet
... 300-kHz or 200-kHz internal oscillator, or an external sync signal. Amount of output current is limited by external components, but can deliver greater than 6 A on either supply. As well as these two main Buck controllers, additional loads can be driven from two micropower linear regulators, one 5 V ...
... 300-kHz or 200-kHz internal oscillator, or an external sync signal. Amount of output current is limited by external components, but can deliver greater than 6 A on either supply. As well as these two main Buck controllers, additional loads can be driven from two micropower linear regulators, one 5 V ...
LDT-10 Laboratory Transmitter
... Downhole measurements can be made using the configuration shown in Figure 3. The current output should be used with the negative terminal attached to the downhole electrode. Select the current desired, up to 10 milliamps, being careful not to saturate. Current is monitored using the CURRENT MONITOR ...
... Downhole measurements can be made using the configuration shown in Figure 3. The current output should be used with the negative terminal attached to the downhole electrode. Select the current desired, up to 10 milliamps, being careful not to saturate. Current is monitored using the CURRENT MONITOR ...
An Ultra-Low-Power Pulse Oximeter Implemented with an Energy-Efficient Transimpedance Amplifier
... The idea behind the operation of pulse oximeters is that hemoglobin changes color from dark red to bright red when oxygenated and reduces its absorption of red light. Hence, if we shine red LED light at 660 nm through one side of a patient’s finger and measure the transmitted light on the other side ...
... The idea behind the operation of pulse oximeters is that hemoglobin changes color from dark red to bright red when oxygenated and reduces its absorption of red light. Hence, if we shine red LED light at 660 nm through one side of a patient’s finger and measure the transmitted light on the other side ...
MAX1875/MAX1876 Dual 180° Out-of-Phase PWM Step- Down Controllers with POR General Description
... sub-1V to 18V and supports loads of 10A or higher. Input voltage ripple and total RMS input ripple current are reduced by synchronized 180° out-of-phase operation. The switching frequency is adjustable from 100kHz to 600kHz with an external resistor. Alternatively, the controller can be synchronized ...
... sub-1V to 18V and supports loads of 10A or higher. Input voltage ripple and total RMS input ripple current are reduced by synchronized 180° out-of-phase operation. The switching frequency is adjustable from 100kHz to 600kHz with an external resistor. Alternatively, the controller can be synchronized ...
OPA251 Single-Supply, POWER OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
... supply voltage while the OPA251 series is optimized for high power supplies. Both can operate from either single (+2.7V to +36V) or dual supplies (±1.35V to ±18V). The input common-mode voltage range extends 200mV below the negative supply—ideal for single-supply applications. They are unity-gain st ...
... supply voltage while the OPA251 series is optimized for high power supplies. Both can operate from either single (+2.7V to +36V) or dual supplies (±1.35V to ±18V). The input common-mode voltage range extends 200mV below the negative supply—ideal for single-supply applications. They are unity-gain st ...
Transistor TIP120 - Mechanical Engineering
... collector characteristic has three important regions: the cutoff region, the active linear region, the saturation region. The cutoff region is the region in which the collector and base currents are oppose each other. The voltages generally cancel each other out because the collector current tends t ...
... collector characteristic has three important regions: the cutoff region, the active linear region, the saturation region. The cutoff region is the region in which the collector and base currents are oppose each other. The voltages generally cancel each other out because the collector current tends t ...
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that increases the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. In this sense, an amplifier modulates the output of the power supply to make the output signal stronger than the input signal. An amplifier is effectively the opposite of an attenuator: while an amplifier provides gain, an attenuator provides loss.An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit within another device. The ability to amplify is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are extremely widely used in almost all electronic equipment. The types of amplifiers can be categorized in different ways. One is by the frequency of the electronic signal being amplified; audio amplifiers amplify signals in the audio (sound) range of less than 20 kHz, RF amplifiers amplify frequencies in the radio frequency range between 20 kHz and 300 GHz. Another is which quantity, voltage or current is being amplified; amplifiers can be divided into voltage amplifiers, current amplifiers, transconductance amplifiers, and transresistance amplifiers. A further distinction is whether the output is a linear or nonlinear representation of the input. Amplifiers can also be categorized by their physical placement in the signal chain.The first practical electronic device that amplified was the Audion (triode) vacuum tube, invented in 1906 by Lee De Forest, which led to the first amplifiers. The terms ""amplifier"" and ""amplification"" (from the Latin amplificare, 'to enlarge or expand') were first used for this new capability around 1915 when triodes became widespread. For the next 50 years, vacuum tubes were the only devices that could amplify. All amplifiers used them until the 1960s, when transistors appeared. Most amplifiers today use transistors, though tube amplifiers are still produced.