DIP-PFC APPLICATION NOTE MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORPORATION POWER SEMICONDUCTOR
... DIP-PFC is manufactured by using the transfer mold technology, which realizes smaller size, lower cost and improved productivity. Furthermore, By mounting a DIP-PFC on the same control board with DIP-IPM, minimum wiring and share of one heat sink can be easily realized. (3) Lower Power Loss DIP-PFC ...
... DIP-PFC is manufactured by using the transfer mold technology, which realizes smaller size, lower cost and improved productivity. Furthermore, By mounting a DIP-PFC on the same control board with DIP-IPM, minimum wiring and share of one heat sink can be easily realized. (3) Lower Power Loss DIP-PFC ...
LTC6410-6
... IF amplifier with configurable input impedance designed for use in applications from DC to 1.4GHz. The LTC6410-6 has 6dB of voltage gain. The LTC6410-6 is an excellent choice for interfacing active mixers to SAW filters. It features an active input termination that allows a customized input impedance f ...
... IF amplifier with configurable input impedance designed for use in applications from DC to 1.4GHz. The LTC6410-6 has 6dB of voltage gain. The LTC6410-6 is an excellent choice for interfacing active mixers to SAW filters. It features an active input termination that allows a customized input impedance f ...
Q01413601365
... size component or logic circuit are needed. Steady state performance is equivalent to today’s sophisticated SR buck converter, and practically very little power loss-due to transient operation. Output ripple can be designed to be small as a large steady state output inductor can be used. Input filte ...
... size component or logic circuit are needed. Steady state performance is equivalent to today’s sophisticated SR buck converter, and practically very little power loss-due to transient operation. Output ripple can be designed to be small as a large steady state output inductor can be used. Input filte ...
KSR-Level sensor KSR-Schwimmer-Magnetschalter KSR Control
... The analogue output and displayed values are programmable. Thus the device can be used to measure the contents of vessels with linear or non-linear shapes (e.g. cylindrical). Tracker 223 and Tracker 224 convert the resistance signal into a voltage or current signal. This signal can be used for furth ...
... The analogue output and displayed values are programmable. Thus the device can be used to measure the contents of vessels with linear or non-linear shapes (e.g. cylindrical). Tracker 223 and Tracker 224 convert the resistance signal into a voltage or current signal. This signal can be used for furth ...
HMC440QS16G 数据资料DataSheet下载
... For applications which can not tolerate a momentary undefined division ratio, which normally occurs while changing the data bits (A0-A4) at random, synchronous programming can be used. Data is loaded into the counter on every rising edge of the clock which occurs while the output (OUT) is “HIGH”. Th ...
... For applications which can not tolerate a momentary undefined division ratio, which normally occurs while changing the data bits (A0-A4) at random, synchronous programming can be used. Data is loaded into the counter on every rising edge of the clock which occurs while the output (OUT) is “HIGH”. Th ...
PDF: 410KB
... DIP-PFC is manufactured by using the transfer mold technology, which realizes smaller size, lower cost and improved productivity. Furthermore, By mounting a DIP-PFC on the same control board with DIP-IPM, minimum wiring and share of one heat sink can be easily realized. (3) Lower Power Loss DIP-PFC ...
... DIP-PFC is manufactured by using the transfer mold technology, which realizes smaller size, lower cost and improved productivity. Furthermore, By mounting a DIP-PFC on the same control board with DIP-IPM, minimum wiring and share of one heat sink can be easily realized. (3) Lower Power Loss DIP-PFC ...
erii5 555 timer monostable operation
... charging through the resistor R1 and the 555 output is driven HIGH. ...
... charging through the resistor R1 and the 555 output is driven HIGH. ...
ME 104: Fall 2001 - UCSB College of Engineering
... 5. If the DC bias VDC in your circuit is between 125 to 175 mV, you do not need to adjust VDC so you can skip the next three steps and proceed directly to Experiment #2. 6. If the DC bias VDC in your circuit is outside of the range 125-175 mV, proceed as follows. Place the ruler flat on your table. ...
... 5. If the DC bias VDC in your circuit is between 125 to 175 mV, you do not need to adjust VDC so you can skip the next three steps and proceed directly to Experiment #2. 6. If the DC bias VDC in your circuit is outside of the range 125-175 mV, proceed as follows. Place the ruler flat on your table. ...
LM555 - Texas Instruments
... Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design impleme ...
... Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design impleme ...
比较器系列ADCMP600 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... The ADCMP600/ADCMP601/ADCMP602 comparators are very high speed devices. Despite the low noise output stage, it is essential to use proper high speed design techniques to achieve the specified performance. Because comparators are uncompensated amplifiers, feedback in any phase relationship is likely ...
... The ADCMP600/ADCMP601/ADCMP602 comparators are very high speed devices. Despite the low noise output stage, it is essential to use proper high speed design techniques to achieve the specified performance. Because comparators are uncompensated amplifiers, feedback in any phase relationship is likely ...
AN140 - Basic Concepts of Linear Regulator and Switching Mode
... there is little EMI problem. Some special LDOs, such as Linear Technology’s LT1761 LDO family, have as low as 20μVRMS noise voltage on the output. It is almost impossible for an SMPS to achieve this low noise level. An SMPS usually has mV of output ripple even with very low ESR capacitors. 3. Fast ...
... there is little EMI problem. Some special LDOs, such as Linear Technology’s LT1761 LDO family, have as low as 20μVRMS noise voltage on the output. It is almost impossible for an SMPS to achieve this low noise level. An SMPS usually has mV of output ripple even with very low ESR capacitors. 3. Fast ...
Analog Dialogue Volume 47, Number 2, 2013
... a photodiode or other current-output sensor often include a transimpedance amplifier (TIA) and a programmable-gain stage to maximize dynamic range. This article shows the benefits and challenges of implementing a single-stage programmable-gain TIA to minimize noise while maintaining high bandwidth a ...
... a photodiode or other current-output sensor often include a transimpedance amplifier (TIA) and a programmable-gain stage to maximize dynamic range. This article shows the benefits and challenges of implementing a single-stage programmable-gain TIA to minimize noise while maintaining high bandwidth a ...
CS-304 - ITM GOI
... Bandwidth : The range of the frequency over with the gain is equal to or greater than 70.7% of the maximum gain is known as bandwidth from the figure it is clear that f1 – f2 is bandwidth f1 is the lower cutoff frequency and f2 is the higher cutoff frequency. The frequency f1 and f2 is also called 3 ...
... Bandwidth : The range of the frequency over with the gain is equal to or greater than 70.7% of the maximum gain is known as bandwidth from the figure it is clear that f1 – f2 is bandwidth f1 is the lower cutoff frequency and f2 is the higher cutoff frequency. The frequency f1 and f2 is also called 3 ...
High Efficiency, Fast Transient Synchronous Step
... The NB638 is a fully integrated high frequency synchronous rectified step-down switch mode converter. It offers a very compact solution to achieve 6A continuous output current over a wide input supply range with excellent load and line regulation. The NB638 operates at high efficiency over a wide ou ...
... The NB638 is a fully integrated high frequency synchronous rectified step-down switch mode converter. It offers a very compact solution to achieve 6A continuous output current over a wide input supply range with excellent load and line regulation. The NB638 operates at high efficiency over a wide ou ...
LM1084 - Texas Instruments
... constant current then flows through R2. The resulting voltage drop across R2 adds to the reference voltage to sets the desired output voltage. The current IADJ from the adjustment terminal introduces an output error. But because it is small (120 uA max), it becomes negligible when R1 is in the 100 Ω ...
... constant current then flows through R2. The resulting voltage drop across R2 adds to the reference voltage to sets the desired output voltage. The current IADJ from the adjustment terminal introduces an output error. But because it is small (120 uA max), it becomes negligible when R1 is in the 100 Ω ...
LABORATORY WORK BOOK For The Course EL
... Department of Electronic Engineering N.E.D. University of Engineering & Technology, Karachi –75270, Pakistan ...
... Department of Electronic Engineering N.E.D. University of Engineering & Technology, Karachi –75270, Pakistan ...
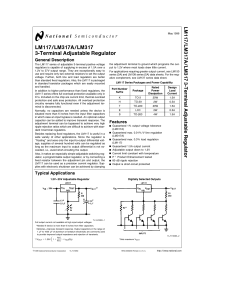
LM117/LM317A/LM317 3-Terminal Adjustable Regulator
... to the absence of input bypassing when adjustment or output capacitors are used but the above values will eliminate the possibility of problems. The adjustment terminal can be bypassed to ground on the LM117 to improve ripple rejection. This bypass capacitor prevents ripple from being amplified as t ...
... to the absence of input bypassing when adjustment or output capacitors are used but the above values will eliminate the possibility of problems. The adjustment terminal can be bypassed to ground on the LM117 to improve ripple rejection. This bypass capacitor prevents ripple from being amplified as t ...
AD7401A 数据手册DataSheet下载
... (±320 mV full scale). The analog input is continuously sampled by the analog modulator, eliminating the need for external sample-and-hold circuitry. The input information is contained in the output stream as a density of ones with a data rate up to 20 MHz. The original information can be reconstruct ...
... (±320 mV full scale). The analog input is continuously sampled by the analog modulator, eliminating the need for external sample-and-hold circuitry. The input information is contained in the output stream as a density of ones with a data rate up to 20 MHz. The original information can be reconstruct ...
Precision Logarithmic and Log Ratio Amplifier
... NOTES: (1) Log Conformity Error is the peak deviation from the best-fit-straight line of VO versus LOG (I1/I2) curve expressed as a percent of peak-to-peak fullscale output. K, scale factor, equals 0.5V output per decade of input current. (2) Scale factor of core log function is trimmed to 0.5V outp ...
... NOTES: (1) Log Conformity Error is the peak deviation from the best-fit-straight line of VO versus LOG (I1/I2) curve expressed as a percent of peak-to-peak fullscale output. K, scale factor, equals 0.5V output per decade of input current. (2) Scale factor of core log function is trimmed to 0.5V outp ...
ICS854S01I Datasheet - Integrated Device Technology
... Propagation delay: 600ps (maximum) Part-to-part skew: 350ps (maximum) Full 3.3V supply mode -40°C to 85°C ambient operating temperature Available in lead-free (RoHS 6) package ...
... Propagation delay: 600ps (maximum) Part-to-part skew: 350ps (maximum) Full 3.3V supply mode -40°C to 85°C ambient operating temperature Available in lead-free (RoHS 6) package ...
Elec301
... air to flow into the tyre and not out, the diode (ideally) allows current to flow one way only. In practice there is a very small current in the reverse direction, but for our purposes we can approximate this to zero. In this experiment you will gain some practical experience in the use of a solid s ...
... air to flow into the tyre and not out, the diode (ideally) allows current to flow one way only. In practice there is a very small current in the reverse direction, but for our purposes we can approximate this to zero. In this experiment you will gain some practical experience in the use of a solid s ...
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that increases the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. In this sense, an amplifier modulates the output of the power supply to make the output signal stronger than the input signal. An amplifier is effectively the opposite of an attenuator: while an amplifier provides gain, an attenuator provides loss.An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit within another device. The ability to amplify is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are extremely widely used in almost all electronic equipment. The types of amplifiers can be categorized in different ways. One is by the frequency of the electronic signal being amplified; audio amplifiers amplify signals in the audio (sound) range of less than 20 kHz, RF amplifiers amplify frequencies in the radio frequency range between 20 kHz and 300 GHz. Another is which quantity, voltage or current is being amplified; amplifiers can be divided into voltage amplifiers, current amplifiers, transconductance amplifiers, and transresistance amplifiers. A further distinction is whether the output is a linear or nonlinear representation of the input. Amplifiers can also be categorized by their physical placement in the signal chain.The first practical electronic device that amplified was the Audion (triode) vacuum tube, invented in 1906 by Lee De Forest, which led to the first amplifiers. The terms ""amplifier"" and ""amplification"" (from the Latin amplificare, 'to enlarge or expand') were first used for this new capability around 1915 when triodes became widespread. For the next 50 years, vacuum tubes were the only devices that could amplify. All amplifiers used them until the 1960s, when transistors appeared. Most amplifiers today use transistors, though tube amplifiers are still produced.