Lactic Acid : Brief History
... dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine trip hosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it wa ...
... dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine trip hosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it wa ...
File - twynham a level pe
... removal of LA relies on the buffering capacity of the blood. Quite good at this as hydrogen carbonate ions are produced by the kidneys- which absorbs hydrogen ions from the lactic acid -to form carbonic acid and eventually carbon dioxide. Breathed out! ...
... removal of LA relies on the buffering capacity of the blood. Quite good at this as hydrogen carbonate ions are produced by the kidneys- which absorbs hydrogen ions from the lactic acid -to form carbonic acid and eventually carbon dioxide. Breathed out! ...
Biochemistry –Second year, Coll
... liver and other tissues, mainly Muscles; cardiac and skeletal. Muscles used fatty acids even in the presence of glucose as a source of energy which spare the glucose for other tissues dependent on glucose. The pathway of utilization of saturated (even C2, C4,…C16,….C20….) fatty acids is the oxidati ...
... liver and other tissues, mainly Muscles; cardiac and skeletal. Muscles used fatty acids even in the presence of glucose as a source of energy which spare the glucose for other tissues dependent on glucose. The pathway of utilization of saturated (even C2, C4,…C16,….C20….) fatty acids is the oxidati ...
Lipids are biological molecules that are insoluble, or only sparingly
... Lipids are biological molecules that are insoluble or only sparingly soluble in water. These include triacylglycerols (also known as triglycerides), phospholipids, cholesterol (often in ester form), glycolipids, steroids, fat-soluble vitamins, and other compounds present in smaller amounts. These le ...
... Lipids are biological molecules that are insoluble or only sparingly soluble in water. These include triacylglycerols (also known as triglycerides), phospholipids, cholesterol (often in ester form), glycolipids, steroids, fat-soluble vitamins, and other compounds present in smaller amounts. These le ...
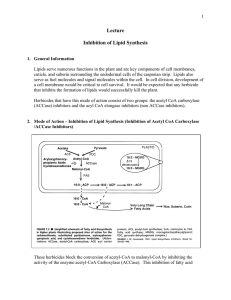
Lecture Inhibition of Lipid Synthesis
... quizalofop and fluazifop readily absorbed by foliage and translocated in symplast accumulating in meristematic regions of root and shoot; translocation is slow diclofop rapidly absorbed into roots and leaves and translocated in symplast selective – in general control grasses but not broadleafs; gram ...
... quizalofop and fluazifop readily absorbed by foliage and translocated in symplast accumulating in meristematic regions of root and shoot; translocation is slow diclofop rapidly absorbed into roots and leaves and translocated in symplast selective – in general control grasses but not broadleafs; gram ...
Word Doc - Computer Press Releases
... actually identified within Thaiboxing and any sport. The systems identified would be the ATP, ATP-CP, Lactic Acid and the Aerobic-oxidative system. An elementary understanding of methods is helpful to understand the design of the actual workouts. ATP Program ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the insta ...
... actually identified within Thaiboxing and any sport. The systems identified would be the ATP, ATP-CP, Lactic Acid and the Aerobic-oxidative system. An elementary understanding of methods is helpful to understand the design of the actual workouts. ATP Program ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the insta ...
Section 3. Antimicrobial Sulfonamides and Antibacterial Synergists
... The discovery of sulfonamides is a significant milestone event in the human chemotherapeutic history. Sulfonamides are synthetic compounds that have activity against both gram-positive and ...
... The discovery of sulfonamides is a significant milestone event in the human chemotherapeutic history. Sulfonamides are synthetic compounds that have activity against both gram-positive and ...
Amino Acids and Simple Proteins
... The ability to understand modern problems in biochemistry and use the fundamental biological performance in the sphere of professional activities (PC-1); An independent analysis of available information, the identification of the fundamental problems, setting goals and objectives of the study; the ...
... The ability to understand modern problems in biochemistry and use the fundamental biological performance in the sphere of professional activities (PC-1); An independent analysis of available information, the identification of the fundamental problems, setting goals and objectives of the study; the ...
A REVIEW ABS - International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences
... hypercholesterolemia, menstrual disorders, certain types of cancers, diabetes, allergies, weight loss, and high blood pressure for application in curing certain skin related as well as a variety of other diseases. For the normal human metabolism, the content of GLA in plasma should be about 25 mgL-1 ...
... hypercholesterolemia, menstrual disorders, certain types of cancers, diabetes, allergies, weight loss, and high blood pressure for application in curing certain skin related as well as a variety of other diseases. For the normal human metabolism, the content of GLA in plasma should be about 25 mgL-1 ...
EXAMPLES OF “STEP
... 23. Vitamin A together with specific cytoreceptors penetrates through the nuclear membranes, induces transcription processes that stimulate growth and differentiation of cells. This biological function is realized by the following form of vitamin A: A Trans-retinoic acid * B Trans-retinal C Cis-reti ...
... 23. Vitamin A together with specific cytoreceptors penetrates through the nuclear membranes, induces transcription processes that stimulate growth and differentiation of cells. This biological function is realized by the following form of vitamin A: A Trans-retinoic acid * B Trans-retinal C Cis-reti ...
Mass spectrometric analysis of tricarboxylic acid cycle
... The TCA cycle is an amphibolic metabolic pathway: it participates both in catabolic and anabolic processes. Due to this ambiguity, the cycle serves as source of energy, but also provides variety of important biosynthetic precursors. For example oxaloacetate is a starting material for gluconeogenesi ...
... The TCA cycle is an amphibolic metabolic pathway: it participates both in catabolic and anabolic processes. Due to this ambiguity, the cycle serves as source of energy, but also provides variety of important biosynthetic precursors. For example oxaloacetate is a starting material for gluconeogenesi ...
Lesson - ACS Distance Education (UK)
... If a person is running a marathon, breathing may not be supplying ample oxygen to produce ATP through this system, hence the lactic acid system may start to be used, resulting in a build up of lactic acid OR the ATP-PC system may be used resulting in a depletion of phosphocreatine in the muscles. Af ...
... If a person is running a marathon, breathing may not be supplying ample oxygen to produce ATP through this system, hence the lactic acid system may start to be used, resulting in a build up of lactic acid OR the ATP-PC system may be used resulting in a depletion of phosphocreatine in the muscles. Af ...
How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy
... 6.16 Cells use many kinds of organic molecules as fuel for cellular respiration • Polysaccharides can be hydrolyzed to monosaccharides and then converted to glucose for glycolysis • Proteins can be digested to amino acids, which are chemically altered and then used in the ...
... 6.16 Cells use many kinds of organic molecules as fuel for cellular respiration • Polysaccharides can be hydrolyzed to monosaccharides and then converted to glucose for glycolysis • Proteins can be digested to amino acids, which are chemically altered and then used in the ...
H - IS MU
... • typically appear during infancy or early childhood and can include severe brain dysfunction (encephalopathy), a weakened and enlarged heart (cardiomyopathy), confusion, vomiting, muscle weakness, and low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). All individuals with this disorder are at risk for heart failure, ...
... • typically appear during infancy or early childhood and can include severe brain dysfunction (encephalopathy), a weakened and enlarged heart (cardiomyopathy), confusion, vomiting, muscle weakness, and low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). All individuals with this disorder are at risk for heart failure, ...
normal myocardial metabolism: fueling cardiac contraction
... matching of energy generation to energetic demands and the orchestrated metabolism of multiple substrate oxidation to generate sufficient ATP under varied physiologic conditions. In the actively pumping heart, the rate of ATP hydrolysis must match the rate of ATP resynthesis. The focus in this revie ...
... matching of energy generation to energetic demands and the orchestrated metabolism of multiple substrate oxidation to generate sufficient ATP under varied physiologic conditions. In the actively pumping heart, the rate of ATP hydrolysis must match the rate of ATP resynthesis. The focus in this revie ...
Document
... Triglyceride lowering - Glycemic control first priority - Fibric acid derivative (gemfibrozil, fenofibrate) ...
... Triglyceride lowering - Glycemic control first priority - Fibric acid derivative (gemfibrozil, fenofibrate) ...
Product Information Sheet - Sigma
... benzene. Storage/Stability In dried form, hirudin was found to lose <5% of its activity in 2-3 years, when stored at –20 °C. In water with preservative added, it is stable for 6 months at room temperature. It is also stable when heated for 15 minutes at 80 °C. The heat stability decreases with incre ...
... benzene. Storage/Stability In dried form, hirudin was found to lose <5% of its activity in 2-3 years, when stored at –20 °C. In water with preservative added, it is stable for 6 months at room temperature. It is also stable when heated for 15 minutes at 80 °C. The heat stability decreases with incre ...
Glycerolipids and Glycerophospholipids
... Phosphatidic acid = the simplest glycerophospholipid -the precursor to other phospholipids and to triacylglycerols. ...
... Phosphatidic acid = the simplest glycerophospholipid -the precursor to other phospholipids and to triacylglycerols. ...
pbl – night starvation - UQMBBS-2013
... (b) State whether energy stores in these organs can be used to maintain blood glucose concentrations during fasting, and if not, explain why (3 marks) Liver glycogen can be degraded into glucose and released into the blood to maintain BGL. Muscle glycogen is broken down the glucose but cannot exit ...
... (b) State whether energy stores in these organs can be used to maintain blood glucose concentrations during fasting, and if not, explain why (3 marks) Liver glycogen can be degraded into glucose and released into the blood to maintain BGL. Muscle glycogen is broken down the glucose but cannot exit ...
Chapter 4: Amino Acids General Features of Amino Acids
... SH > OH > NH2 > COOH > CHO > CH2OH > C6H5 > CH3 > 2H > 1H ...
... SH > OH > NH2 > COOH > CHO > CH2OH > C6H5 > CH3 > 2H > 1H ...
Regulation of metabolic products and gene expression in Fusarium
... subunit 2 gene, the product of which converts citrate from the matrix of the mitochondria into cytosolic acetyl-CoA, was increased approximately 2.8-fold. The expression of the gene encoding acetyl-CoA carboxylase, which changes acetyl-CoA into malonyl-CoA, was increased approximately 7-fold. Moreov ...
... subunit 2 gene, the product of which converts citrate from the matrix of the mitochondria into cytosolic acetyl-CoA, was increased approximately 2.8-fold. The expression of the gene encoding acetyl-CoA carboxylase, which changes acetyl-CoA into malonyl-CoA, was increased approximately 7-fold. Moreov ...
0 13C labeling of the tricarboxylic acid cycle and carbon conversion
... nitrogen and stored at -80 °C for protein extraction. The lipid extractions were dried down under nitrogen for methylation, to cleave triacylglycerol (TAG) fatty acids from their glycerol backbones and to create volatile fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs). To solubilize the dried lipid extracts, 0.5 ...
... nitrogen and stored at -80 °C for protein extraction. The lipid extractions were dried down under nitrogen for methylation, to cleave triacylglycerol (TAG) fatty acids from their glycerol backbones and to create volatile fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs). To solubilize the dried lipid extracts, 0.5 ...
Exercise Physiology Study Guide-Test 1 History of Exercise
... Glycogen concentration can be greatly increased by training and diet Can be the sole source of energy during heavy exercise Disadvantages: Stored with a lot of water (reduces caloric value of storage form) Small amount of glycogen stored Accumulation of lactate with anaerobic use of glyc ...
... Glycogen concentration can be greatly increased by training and diet Can be the sole source of energy during heavy exercise Disadvantages: Stored with a lot of water (reduces caloric value of storage form) Small amount of glycogen stored Accumulation of lactate with anaerobic use of glyc ...
Chapter 14 cycles
... Ultimately, these large polymers are degraded and produce new cell mass, CO2 (which returns to the atmosphere), and contribute to the formation of a stable organic matter fraction, humus. Humus turns over slowly, at a rate of 3 to 5% per year. In addition to mineralization to CO2, a number of small ...
... Ultimately, these large polymers are degraded and produce new cell mass, CO2 (which returns to the atmosphere), and contribute to the formation of a stable organic matter fraction, humus. Humus turns over slowly, at a rate of 3 to 5% per year. In addition to mineralization to CO2, a number of small ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.