C485 Exam I
... Glycogen synthase elongates the chain by reaction between the 4-OH of the nonreducing end of the polymer with UDP glucose to make the alpha 1,4 linkage. Branching enzyme transfers blocks of (usually) seven residues to an internal C-6 OH of the chain. Must be at least 4 residues away from an existing ...
... Glycogen synthase elongates the chain by reaction between the 4-OH of the nonreducing end of the polymer with UDP glucose to make the alpha 1,4 linkage. Branching enzyme transfers blocks of (usually) seven residues to an internal C-6 OH of the chain. Must be at least 4 residues away from an existing ...
3. Feedback mechanisms control cellular respiration
... • Not all the organic molecules of food are completely oxidized to make ATP. • Intermediaries in glycolysis and the Krebs cycle can be diverted to anabolic pathways. • For example, a human cell can synthesize about half the 20 different amino acids by modifying compounds from the Krebs cycle. ...
... • Not all the organic molecules of food are completely oxidized to make ATP. • Intermediaries in glycolysis and the Krebs cycle can be diverted to anabolic pathways. • For example, a human cell can synthesize about half the 20 different amino acids by modifying compounds from the Krebs cycle. ...
The use of the movie "Lorenzo`s Oil" as a Teaching Tool
... acids to make the VLCSFAs. In the movie, Odone used a paper clip to represent the two carbon unit and he added paper clips until he produced chains of 24 or 26 carbons (12-13 paper clips). However, the very long chain fatty acids are unusual in that they are broken down by ß-oxidation in the peroxis ...
... acids to make the VLCSFAs. In the movie, Odone used a paper clip to represent the two carbon unit and he added paper clips until he produced chains of 24 or 26 carbons (12-13 paper clips). However, the very long chain fatty acids are unusual in that they are broken down by ß-oxidation in the peroxis ...
Amino Acids
... L-Lysine: L-Lysine, an essential amino acid, is needed to support proper growth and bone development. It can also support immune function. N-Acetyl Cysteine: N-Acetyl Cysteine (NAC) is a form of the amino acid cysteine. NAC is used in the body to make glutathione peroxidase - one of the body’s most ...
... L-Lysine: L-Lysine, an essential amino acid, is needed to support proper growth and bone development. It can also support immune function. N-Acetyl Cysteine: N-Acetyl Cysteine (NAC) is a form of the amino acid cysteine. NAC is used in the body to make glutathione peroxidase - one of the body’s most ...
what the ribosome is made of tRNA – brings the amino acids to the
... • DNA codes for RNA, RNA codes for proteins ...
... • DNA codes for RNA, RNA codes for proteins ...
Document - Van Demon Fitness
... deficiency (a fat-soluble vitamin), but where then discovered to be due to lack of omega-6 fat. In humans, signs of omega-6 LA deficiency include dermatitis, poor wound healing, loss of hair, and infertility. Thankfully, all of these outcomes are reversible. ...
... deficiency (a fat-soluble vitamin), but where then discovered to be due to lack of omega-6 fat. In humans, signs of omega-6 LA deficiency include dermatitis, poor wound healing, loss of hair, and infertility. Thankfully, all of these outcomes are reversible. ...
and Medium-Chain-Length Fatty Acids
... cycles, respectively, of FAS-like extension from an i4:0 primer, as suggested by the previous observation of d8-Val incorporation into d7-i10:0 (Walters and Steffens, 1990). In accordance with this, the FAS-like extension of d9-i5:0 (d93-methylbutyric acid), which is derived from d10-Leu by transami ...
... cycles, respectively, of FAS-like extension from an i4:0 primer, as suggested by the previous observation of d8-Val incorporation into d7-i10:0 (Walters and Steffens, 1990). In accordance with this, the FAS-like extension of d9-i5:0 (d93-methylbutyric acid), which is derived from d10-Leu by transami ...
acid
... This reaction occurs under anaerobic conditions. Formation of lactate using NADH as hydrogen donor is essential for the continuation of glycolysis in rapidly contracting skeletal muscle and erythrocytes because NADH can not be oxidized by respiratory chain O2 been reduced to NADH. By reducing pyruva ...
... This reaction occurs under anaerobic conditions. Formation of lactate using NADH as hydrogen donor is essential for the continuation of glycolysis in rapidly contracting skeletal muscle and erythrocytes because NADH can not be oxidized by respiratory chain O2 been reduced to NADH. By reducing pyruva ...
Patterns of nucleotide and amino acid substitution
... are those at which any of the four nucleotides can be present in a codon for a single amino acid. In some cases there is redundancy in the first codon position, e.g, both AGA and CGA are codons for arginine. Thus, many nucleotide substitutions at third positions do not lead to amino acid substitutio ...
... are those at which any of the four nucleotides can be present in a codon for a single amino acid. In some cases there is redundancy in the first codon position, e.g, both AGA and CGA are codons for arginine. Thus, many nucleotide substitutions at third positions do not lead to amino acid substitutio ...
Which of the following statements about saliva is NOT true
... 4.Which of the following statements about the Unstirred Water Layer (UWL) is true? a. Movement through the UWL may be rate limiting for absorption of hydrophilic substances b. Rate of movement through the UWL is equivalent to the rate of movement through the membrane for hydrophobic compounds c. The ...
... 4.Which of the following statements about the Unstirred Water Layer (UWL) is true? a. Movement through the UWL may be rate limiting for absorption of hydrophilic substances b. Rate of movement through the UWL is equivalent to the rate of movement through the membrane for hydrophobic compounds c. The ...
Ch. 7.4: Cellular Respiration
... In respiration, C-H bonds of glucose are re-arranged into C-O and H-O bonds of carbon dioxide and water. These bonds store less energy. The energy difference is stored in ATP. ...
... In respiration, C-H bonds of glucose are re-arranged into C-O and H-O bonds of carbon dioxide and water. These bonds store less energy. The energy difference is stored in ATP. ...
Photosynthesis/Cell Resp Notes
... The process by which mitochondria break down glucose to make ATP Two types o Aerobic respiration: requires oxygen and carried out by plants, animals, and some bacteria o Anaerobic respiration: requires no oxygen and carried out by yeast, some bacteria, and sometimes animals Chemical equation for ...
... The process by which mitochondria break down glucose to make ATP Two types o Aerobic respiration: requires oxygen and carried out by plants, animals, and some bacteria o Anaerobic respiration: requires no oxygen and carried out by yeast, some bacteria, and sometimes animals Chemical equation for ...
Amino Acid Limitation Induces the Amino Acid
... Using qPCR (quantitative PCR, also known as realtime (RT-PCR)) relative mRNA expressions can be detected in specific samples. Experiments were designed to test whether the AAR pathway is affected in the treatment. Amino acid starvation could induce the AAR pathway in a timely dependent manner in H4I ...
... Using qPCR (quantitative PCR, also known as realtime (RT-PCR)) relative mRNA expressions can be detected in specific samples. Experiments were designed to test whether the AAR pathway is affected in the treatment. Amino acid starvation could induce the AAR pathway in a timely dependent manner in H4I ...
doc file
... resistance of the organism, influences the tone of cardiac vessels, decreases the cholesterol level in the blood. Methionine prevents from excess fat accumulation in the liver, protects liver cells from influence of toxic substances, and participates in the synthesis of phosphatidylcholine. Amino ac ...
... resistance of the organism, influences the tone of cardiac vessels, decreases the cholesterol level in the blood. Methionine prevents from excess fat accumulation in the liver, protects liver cells from influence of toxic substances, and participates in the synthesis of phosphatidylcholine. Amino ac ...
Antagonistic activities of lactic acid bacteria in food and feed
... and glycerol can also be used as alternate hydrogen acceptors [31,32]. Most species posessing heterofermentative activity also contain flavoprotein oxidases which catalyse reduction of oxygen resulting in accumulation of hydrogen peroxide [2,*]. This use of oxygen as an alternate hydrogen acceptor a ...
... and glycerol can also be used as alternate hydrogen acceptors [31,32]. Most species posessing heterofermentative activity also contain flavoprotein oxidases which catalyse reduction of oxygen resulting in accumulation of hydrogen peroxide [2,*]. This use of oxygen as an alternate hydrogen acceptor a ...
Amino acids: fed or fasted?
... Low BCAA’s in phenylacetate treated UCD pts Gln deficit due to excretion phenylacetylglutamine ...
... Low BCAA’s in phenylacetate treated UCD pts Gln deficit due to excretion phenylacetylglutamine ...
Chapter 7 - Coenzymes
... Coenzymes There are other groups that contribute to the reactivity of enzymes beside amino acid residues. These groups are called cofactors - chemicals required by apoenzymes (inactive) to become holoenzymes (active). There are two types of cofactors: 1) essential ions - metal ions -inorganic 2) coe ...
... Coenzymes There are other groups that contribute to the reactivity of enzymes beside amino acid residues. These groups are called cofactors - chemicals required by apoenzymes (inactive) to become holoenzymes (active). There are two types of cofactors: 1) essential ions - metal ions -inorganic 2) coe ...
Fate of Carbon Skeleton
... 1- Deamination of amino acids with formation of α-keto acids and ammonia 2- Transamination of most amino acids with α- ketoglutaric acid to form glutamic acid, which in turn is deaminated by glutamate dehydrogenase to form α-ketoglutarate and ammonia. 3- Glutamine in the kidney by glutaminase enzyme ...
... 1- Deamination of amino acids with formation of α-keto acids and ammonia 2- Transamination of most amino acids with α- ketoglutaric acid to form glutamic acid, which in turn is deaminated by glutamate dehydrogenase to form α-ketoglutarate and ammonia. 3- Glutamine in the kidney by glutaminase enzyme ...
AP Biology Cellular Respiration Notes 9.1
... 9.12 List the products of the citric acid cycle. Explain why it is called a cycle. ...
... 9.12 List the products of the citric acid cycle. Explain why it is called a cycle. ...
Oxidation of Glucose
... 3ATPs from oxidation of NADH of (α-ketoglutanate dehydrogenase) 3ATPs from oxidation of NADH of (malate dehydrogenase) 3ATPs from oxidation of NADH of(isocitrate dehydrogenase) *Total energy yield in aerobic phase oxidation(kreb's) : (12ATP)+(3ATP)from oxidative decarboxylation =(15ATP) ...
... 3ATPs from oxidation of NADH of (α-ketoglutanate dehydrogenase) 3ATPs from oxidation of NADH of (malate dehydrogenase) 3ATPs from oxidation of NADH of(isocitrate dehydrogenase) *Total energy yield in aerobic phase oxidation(kreb's) : (12ATP)+(3ATP)from oxidative decarboxylation =(15ATP) ...
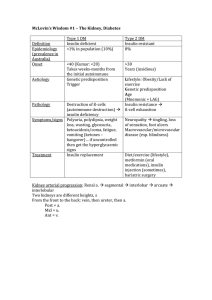
McLovin`s Wisdom #1 – The Kidney, Diabetes Type 1 DM Type 2
... At complex 4, 1/2O2 + 2H+ H2O (the H+s are reacted with oxygen to reduce it to water. Hence oxygen is needed). ATP synthase. 4H+ going through ATP synthase produce 1 ATP (3H+ go through there, and 1H+ used to transport the ATP back out into the intermembrane space – the outer mitochondrial membra ...
... At complex 4, 1/2O2 + 2H+ H2O (the H+s are reacted with oxygen to reduce it to water. Hence oxygen is needed). ATP synthase. 4H+ going through ATP synthase produce 1 ATP (3H+ go through there, and 1H+ used to transport the ATP back out into the intermembrane space – the outer mitochondrial membra ...
Solution Worksheet Respiration
... Glycolysis is the process of Glucose break-down into pyruvate. It occurs in the cytoplasm. When pyruvate is further oxidized within the cytoplasm, we call it fermentation. Since the mitochondria are not involved, it is also referred to as anaerobic fermentation or anaerobic metabolism. What are the ...
... Glycolysis is the process of Glucose break-down into pyruvate. It occurs in the cytoplasm. When pyruvate is further oxidized within the cytoplasm, we call it fermentation. Since the mitochondria are not involved, it is also referred to as anaerobic fermentation or anaerobic metabolism. What are the ...
L- Amino Acid Assay Kit (Colorimetric)
... Note: This assay is continuous (not terminated) and therefore may be measured at multiple time points to follow the reaction kinetics. 4. Read the plate with a spectrophotometric microplate reader in the 540-570 nm range. 5. Calculate the concentration of L-Amino Acids within samples by comparing th ...
... Note: This assay is continuous (not terminated) and therefore may be measured at multiple time points to follow the reaction kinetics. 4. Read the plate with a spectrophotometric microplate reader in the 540-570 nm range. 5. Calculate the concentration of L-Amino Acids within samples by comparing th ...
D-lactic acidosis: Turning sugar into acids in the gastrointestinal tract
... Quantitatively, D-lactic acid is normally a minor compound 221, it follows that when more than 25 mmoles of butyric acid are formed in the GI tract. However, if a large quantity of glucose and produced, the excess must be metabolized by other organs, excreted appropriate bacteria meet in a metabolic ...
... Quantitatively, D-lactic acid is normally a minor compound 221, it follows that when more than 25 mmoles of butyric acid are formed in the GI tract. However, if a large quantity of glucose and produced, the excess must be metabolized by other organs, excreted appropriate bacteria meet in a metabolic ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.