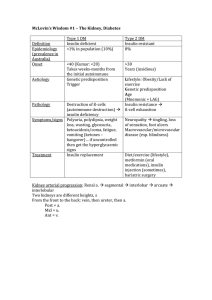
McLovin`s Wisdom #1 – The Kidney, Diabetes Type 1 DM Type 2
... 4H+ going through ATP synthase produce 1 ATP (3H+ go through there, and 1H+ used to transport the ATP back out into the intermembrane space – the outer mitochondrial membrane is just permeable to ATP) Hence because one NADH produces 10 ATP, there are 2.5 ATP produced per NADH (similarly, FADH2 produ ...
... 4H+ going through ATP synthase produce 1 ATP (3H+ go through there, and 1H+ used to transport the ATP back out into the intermembrane space – the outer mitochondrial membrane is just permeable to ATP) Hence because one NADH produces 10 ATP, there are 2.5 ATP produced per NADH (similarly, FADH2 produ ...
DESCRIPTION FUNCTIONS INDICATIONS SUGGESTED USE
... caused by toxic free radicals and reactive oxygen species (e.g., peroxides) which are produced during normal oxygen metabolism, by other chemical reactions, and by toxic agents in the environment. Free radicals, once formed, are capable of disrupting metabolic activity and cell structure. When this ...
... caused by toxic free radicals and reactive oxygen species (e.g., peroxides) which are produced during normal oxygen metabolism, by other chemical reactions, and by toxic agents in the environment. Free radicals, once formed, are capable of disrupting metabolic activity and cell structure. When this ...
METBIONET GUIDELINES FOR AMINO ACID ANALYSIS.
... E. Analytical The analytical guidelines will be reviewed following the publication of the results of the ERNDIM amino acid questionnaire. These guidelines are primarily based on the use of ion exchange chromatography for a full amino acid profile. This is currently the most widely used method but t ...
... E. Analytical The analytical guidelines will be reviewed following the publication of the results of the ERNDIM amino acid questionnaire. These guidelines are primarily based on the use of ion exchange chromatography for a full amino acid profile. This is currently the most widely used method but t ...
Exam 2 Key
... 3· (8 pts) The 6 events listed below occur during photosynthesis. List the order of events (#1 first-#6last) ...
... 3· (8 pts) The 6 events listed below occur during photosynthesis. List the order of events (#1 first-#6last) ...
PPT File
... Lipids as signals, cofactors, and pigments 1. Phosphatidylinositols and sphingosine derivatives act as intracellular signals. 2. Eicosanoids carry messages to nearby cells. 3. Steroid hormones carry messages between tissues. ...
... Lipids as signals, cofactors, and pigments 1. Phosphatidylinositols and sphingosine derivatives act as intracellular signals. 2. Eicosanoids carry messages to nearby cells. 3. Steroid hormones carry messages between tissues. ...
Amino Acids
... Amino Acids As their name indicates, amino acids are compounds that contain an amino group and a carboxylic acid group. The amino acids in proteins have the amino group bonded to the α carbon of the carboxylic acid. As a result, they are called α-amino acids. The amino group of an amino acid is suff ...
... Amino Acids As their name indicates, amino acids are compounds that contain an amino group and a carboxylic acid group. The amino acids in proteins have the amino group bonded to the α carbon of the carboxylic acid. As a result, they are called α-amino acids. The amino group of an amino acid is suff ...
Replacement of antioxidants
... penetrate skin barrier but may penetrate through follicles, sweat glands and damaged skin Produce epidermal signaling cytokines which affect dermal fibroblasts Mechanism is not elucidated ...
... penetrate skin barrier but may penetrate through follicles, sweat glands and damaged skin Produce epidermal signaling cytokines which affect dermal fibroblasts Mechanism is not elucidated ...
Case 26 The Role of Specific Amino Acids in the Peptide Hormone
... primarily on the liver where binding to specific extracellular receptors stimulates glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis with subsequent release of glucose from the liver for the benefit of other body tissues. Glucagon is counter-regulatory to insulin which is secreted by pancreatic $-cells and stimul ...
... primarily on the liver where binding to specific extracellular receptors stimulates glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis with subsequent release of glucose from the liver for the benefit of other body tissues. Glucagon is counter-regulatory to insulin which is secreted by pancreatic $-cells and stimul ...
1 - u.arizona.edu
... - base products xanthine oxidized by xanthine oxidase uric acid; xanthine oxidase also converts hypoxanthine xanthine; xanthine oxidase requires molecular oxygen and molybdenum, non-heme iron, and FAD ...
... - base products xanthine oxidized by xanthine oxidase uric acid; xanthine oxidase also converts hypoxanthine xanthine; xanthine oxidase requires molecular oxygen and molybdenum, non-heme iron, and FAD ...
Which amino acids matter? - Berkeley Cosmology Group
... - A kind of protein that help a reaction go faster. Amino acids - Are the building blocks of proteins. - There are 20 different kinds of amino acids. ...
... - A kind of protein that help a reaction go faster. Amino acids - Are the building blocks of proteins. - There are 20 different kinds of amino acids. ...
Cloning, Functional Characterization and Site
... acids into corresponding hydroxycinnamate CoA thioesters and exhibits higher activity toward p-coumaric and ferulic acids. Consequently, Pp4CL1 may primarily regulate the p-coumaric acid and ferulic acid paths to achieve biosynthesis of coumarins, mainly umbelliferone, scopoletin as well as correspo ...
... acids into corresponding hydroxycinnamate CoA thioesters and exhibits higher activity toward p-coumaric and ferulic acids. Consequently, Pp4CL1 may primarily regulate the p-coumaric acid and ferulic acid paths to achieve biosynthesis of coumarins, mainly umbelliferone, scopoletin as well as correspo ...
Lactic Acid Bacteria and Lactic Fermentations
... We will still be talking about the source of the microbes in the food, the conditions which select for their proliferation, and what happens as they proliferate. The difference is that the focus is on how to facilitate the process rather than how to minimize it. The topic of food fermentation also d ...
... We will still be talking about the source of the microbes in the food, the conditions which select for their proliferation, and what happens as they proliferate. The difference is that the focus is on how to facilitate the process rather than how to minimize it. The topic of food fermentation also d ...
CreaPrime™ Blend
... Caffeine acts as an adenosine receptor antagonist. Adenosine decreases the release of stimulatory/excitatory neurotransmitters (i.e. norepinephrine [NE]). Therefore, ...
... Caffeine acts as an adenosine receptor antagonist. Adenosine decreases the release of stimulatory/excitatory neurotransmitters (i.e. norepinephrine [NE]). Therefore, ...
Biochem09 - Amit Kessel Ph.D
... 37. Which list of fatty acids shows them in order of decreasing melting points. A. a saturated fatty acid with 20 carbons, stearate, oleate, linoleate, linolenate B. a saturated fatty acid with 20 carbons, linolenate, linoleate, oleate, stearate C. oleate, linoleate, linolenate, a saturated fatty ac ...
... 37. Which list of fatty acids shows them in order of decreasing melting points. A. a saturated fatty acid with 20 carbons, stearate, oleate, linoleate, linolenate B. a saturated fatty acid with 20 carbons, linolenate, linoleate, oleate, stearate C. oleate, linoleate, linolenate, a saturated fatty ac ...
The use of medium chain fatty acids as
... production of sows. These properties reduce the pre-weaning mortality in piglets, while improving their growth performances Conclusion With strongly increasing insights in genetic selection, today’s sows, piglets and fatteners possess an enormous genetic potential which cannot be kept up by standard ...
... production of sows. These properties reduce the pre-weaning mortality in piglets, while improving their growth performances Conclusion With strongly increasing insights in genetic selection, today’s sows, piglets and fatteners possess an enormous genetic potential which cannot be kept up by standard ...
CHAPTER 7, CELLULAR RESPIRATION In Eukaryotic Cells, the
... 8. The BULK of the Energy released by the Oxidation of Glucose still has NOT been transferred to ATP. Only FOUR Molecules of ATP - TWO from Glycolysis and TWO From the Krebs cycle. 9. 10 Molecules of NADH and the 2 FADH2 Molecules from the Krebs cycle DRIVE the Next Stage of Aerobic Respiration - Th ...
... 8. The BULK of the Energy released by the Oxidation of Glucose still has NOT been transferred to ATP. Only FOUR Molecules of ATP - TWO from Glycolysis and TWO From the Krebs cycle. 9. 10 Molecules of NADH and the 2 FADH2 Molecules from the Krebs cycle DRIVE the Next Stage of Aerobic Respiration - Th ...
Chapter 14- RESPIRATION IN PLANTS Living cells require a
... Chapter 14‐ RESPIRATION IN PLANTS Living cells require a continuous supply of energy for maintaining various life activities. This energy is obtained by oxidizing the organic food substances present in the cells. The food substances like Carbohydrates, proteins, fats which are used for oxidation dur ...
... Chapter 14‐ RESPIRATION IN PLANTS Living cells require a continuous supply of energy for maintaining various life activities. This energy is obtained by oxidizing the organic food substances present in the cells. The food substances like Carbohydrates, proteins, fats which are used for oxidation dur ...
Very long chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (VLCAD)
... VLCAD deficiency is treated by avoidance of fasting and a diet which is low in long chain fatty acids. Dietary supplementation with carnitine may be considered. Parent education is an important component of treatment, including advising parents on actions to be taken when their child develops a mino ...
... VLCAD deficiency is treated by avoidance of fasting and a diet which is low in long chain fatty acids. Dietary supplementation with carnitine may be considered. Parent education is an important component of treatment, including advising parents on actions to be taken when their child develops a mino ...
The Implausibility of Metabolic Cycles on the
... of reactants to products without itself being changed almost guarantees that a catalyst can initiate successive “cycles” of the same reaction. Metabolic cycles are different. Strictly, they are by definition restricted to biochemistry. Like catalytic cycles, they too result in repeated conversions of ...
... of reactants to products without itself being changed almost guarantees that a catalyst can initiate successive “cycles” of the same reaction. Metabolic cycles are different. Strictly, they are by definition restricted to biochemistry. Like catalytic cycles, they too result in repeated conversions of ...
carbon skeleton
... breakdown and are not needed for new protein synthesis undergo oxidative degradation. When a diet is rich in protein and the ingested amino acids exceed the body’s needs for protein synthesis, the surplus is catabolized; amino acids cannot be stored. During starvation or in uncontrolled diabetes mel ...
... breakdown and are not needed for new protein synthesis undergo oxidative degradation. When a diet is rich in protein and the ingested amino acids exceed the body’s needs for protein synthesis, the surplus is catabolized; amino acids cannot be stored. During starvation or in uncontrolled diabetes mel ...
Principles of BIOCHEMISTRY
... precursors in plants, bacteria and yeast (not animals) • Glyoxylate cycle leads from 2-carbon compounds to glucose • In animals, acetyl CoA is not a carbon source for the net formation of glucose (2 carbons of acetyl CoA enter cycle, 2 are released as 2 CO2) ...
... precursors in plants, bacteria and yeast (not animals) • Glyoxylate cycle leads from 2-carbon compounds to glucose • In animals, acetyl CoA is not a carbon source for the net formation of glucose (2 carbons of acetyl CoA enter cycle, 2 are released as 2 CO2) ...
WHY DO CARDIOMYOCYTES (HEART MUSCLE CELLS) STORE
... The "Krebs' Cycle", otherwise known as the "Citric Acid Cycle", is a well-‐known metabolic pathway. It occurs only in the mitochondrion, and is a circular metabolic route that starts and ends with oxal ...
... The "Krebs' Cycle", otherwise known as the "Citric Acid Cycle", is a well-‐known metabolic pathway. It occurs only in the mitochondrion, and is a circular metabolic route that starts and ends with oxal ...
Antihyperlipidemic Drugs
... • Bile Acid Binding Resins are not absorbed across the gut into the blood - bile and cholesterol are irreversibly bound in the gut and disposed of in the feces ...
... • Bile Acid Binding Resins are not absorbed across the gut into the blood - bile and cholesterol are irreversibly bound in the gut and disposed of in the feces ...
LIPO BC
... Reduces toxic levels of homocysteine (a contributing factor in heart disease and stroke) ...
... Reduces toxic levels of homocysteine (a contributing factor in heart disease and stroke) ...
Hepoxilin

Hepoxilins (HxA3 and HxB3) are nonclassic eicosanoid hormones involved in inflammation.























