1 - Chiropractic National Board Review Questions
... 60. Glutamate transanimase & alanine transaminase both require? A. Pyridoxine B. Cobalamine C. Thiamine D. Niacin 61. An increase in which of the following minerals causes a decrease in blood pressure? A. Potassium B. Na C. Chloride D. P 62. Dietary vitamin E is absorbed in the intestines by? A. Ami ...
... 60. Glutamate transanimase & alanine transaminase both require? A. Pyridoxine B. Cobalamine C. Thiamine D. Niacin 61. An increase in which of the following minerals causes a decrease in blood pressure? A. Potassium B. Na C. Chloride D. P 62. Dietary vitamin E is absorbed in the intestines by? A. Ami ...
Chemistry Of Lichens Complete
... • KC (K followed by C) - Turns yellow with usnic acid - Turns red with C- depsides and depsidones which undergo rapid hydrolysis to yield a mhydroxy phenolic moiety, e.g. alectoronic acid ...
... • KC (K followed by C) - Turns yellow with usnic acid - Turns red with C- depsides and depsidones which undergo rapid hydrolysis to yield a mhydroxy phenolic moiety, e.g. alectoronic acid ...
скачати - ua
... The process works on glucose, a 6-C, until step 4 splits the 6-C into two 3-C compounds. Glyceraldehyde phosphate (GAP, also known as phosphoglyceraldehyde, PGAL) is the more readily used of the two. Dihydroxyacetone phosphate can be converted into GAP by the enzyme Isomerase. The end of the glycoly ...
... The process works on glucose, a 6-C, until step 4 splits the 6-C into two 3-C compounds. Glyceraldehyde phosphate (GAP, also known as phosphoglyceraldehyde, PGAL) is the more readily used of the two. Dihydroxyacetone phosphate can be converted into GAP by the enzyme Isomerase. The end of the glycoly ...
Download PDF
... Biochemistry is the study of the variety of chemical structures and chemical reactions that occur in living organisms. In order to truly understand the detailed mechanisms of these diverse reactions, one must assimilate aspects of organic chemistry, inorganic chemistry, and physical chemistry and ap ...
... Biochemistry is the study of the variety of chemical structures and chemical reactions that occur in living organisms. In order to truly understand the detailed mechanisms of these diverse reactions, one must assimilate aspects of organic chemistry, inorganic chemistry, and physical chemistry and ap ...
C383 Study Guide for the Final Exam Spring 2017 Basic Information
... B. A DNA melting curve for a poly(AT) sequence and a poly(GC) sequence (indicate which is poly(AT) and which is poly(GC)) C. A plot of initial velocity versus substrate concentration for a Michaelis-Menton enzyme. D. The same plot as (B), but the enzyme is treated with a competitive inhibitor E. a p ...
... B. A DNA melting curve for a poly(AT) sequence and a poly(GC) sequence (indicate which is poly(AT) and which is poly(GC)) C. A plot of initial velocity versus substrate concentration for a Michaelis-Menton enzyme. D. The same plot as (B), but the enzyme is treated with a competitive inhibitor E. a p ...
1 - Chiropractic National Board Review Questions
... 84. What nutrients form a coenzyme which is used directly for amino acid Transamination? A. Pyroxine 85. What is catecholamine synthesized from? A. Epinephrine 86. How many essential amino acids are aromatic? A. 2 87. Thyroxime is derived from? A. Threonine B. Tyrosine C. Tyramine D. Thiamine 88. En ...
... 84. What nutrients form a coenzyme which is used directly for amino acid Transamination? A. Pyroxine 85. What is catecholamine synthesized from? A. Epinephrine 86. How many essential amino acids are aromatic? A. 2 87. Thyroxime is derived from? A. Threonine B. Tyrosine C. Tyramine D. Thiamine 88. En ...
organic chemistry ii - University of Minnesota Duluth
... (necessary to health but too much is bad for heart). • Let’s look at glycerol, fatty acids, then fats and oils. • http://www.scientificpsychic.com/fitness/fattyacids1 .html ...
... (necessary to health but too much is bad for heart). • Let’s look at glycerol, fatty acids, then fats and oils. • http://www.scientificpsychic.com/fitness/fattyacids1 .html ...
gln.val.tyr.ala lys.arg.glu.trp met.his.leu.asp cys.pro.gly.asn F-A-D
... (Explain your reasoning). ...
... (Explain your reasoning). ...
Organic Compounds
... Have no double bonds in their fatty acid chains – maximum # of H atoms Straight ...
... Have no double bonds in their fatty acid chains – maximum # of H atoms Straight ...
Water soluble Vit. Vit C: (Ascorbic Acid)
... ,,vegetable diet lack this vit.. Alcoholism is an important precipitating factor for niacin deficiency . ...
... ,,vegetable diet lack this vit.. Alcoholism is an important precipitating factor for niacin deficiency . ...
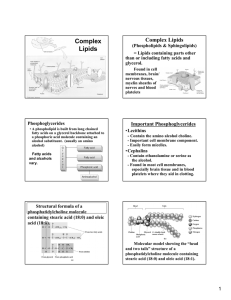
L2 - Complex Lipids
... built from long chained fatty acids attached to a sphingosine backbone rather than glycerol. •There are two types of sphingolipids: - Sphingomylins - Glycolipids ...
... built from long chained fatty acids attached to a sphingosine backbone rather than glycerol. •There are two types of sphingolipids: - Sphingomylins - Glycolipids ...
What are Vitamins?
... The energy charge can have a value ranging from 0 (all AMP) to 1(all ATP). Most cells maintain EC at a constant value with very little variation: The energy charge of most cells range from 0.8 to 0.95. As EC drops catabolic, energy producing pathways, such as Glycolysis increase in rate, while anabo ...
... The energy charge can have a value ranging from 0 (all AMP) to 1(all ATP). Most cells maintain EC at a constant value with very little variation: The energy charge of most cells range from 0.8 to 0.95. As EC drops catabolic, energy producing pathways, such as Glycolysis increase in rate, while anabo ...
Macromolecules - Georgetown ISD
... 7. Made up of smaller “building blocks” called _________________. 8. Examples of macromolecules _______________, _______________, _______________, & _______________. 9. How are macromolecules formed?_____________________ (also called _______________) 10. Polymers are formed when monomers combine by ...
... 7. Made up of smaller “building blocks” called _________________. 8. Examples of macromolecules _______________, _______________, _______________, & _______________. 9. How are macromolecules formed?_____________________ (also called _______________) 10. Polymers are formed when monomers combine by ...
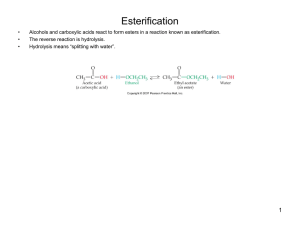
Esterification
... Prostaglandins and Pain Arachadonic acid is synthesized from an essential omega-6-fatty acid that must be obtained from diet. Arachadonic acid is used by the body to make prostaglandins. Cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes are needed for these reactions to occur. Since prostaglandin production is responsi ...
... Prostaglandins and Pain Arachadonic acid is synthesized from an essential omega-6-fatty acid that must be obtained from diet. Arachadonic acid is used by the body to make prostaglandins. Cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes are needed for these reactions to occur. Since prostaglandin production is responsi ...
2.3 Guided Notes
... Made mostly of C & H’s and are generally not soluble in water Examples are fats, oils, waxes, and steroids Functions: 1.) _____________________________________________________ 2.) _____________________________________________________ 3.) _____________________________________________________ 4.) ____ ...
... Made mostly of C & H’s and are generally not soluble in water Examples are fats, oils, waxes, and steroids Functions: 1.) _____________________________________________________ 2.) _____________________________________________________ 3.) _____________________________________________________ 4.) ____ ...
2- All essential amino acids are glucogenic. False
... 6- Carbamoyl Phosphate adds with Ornithine to form A. Citrulline √ B. Arginine C. Aspartate ...
... 6- Carbamoyl Phosphate adds with Ornithine to form A. Citrulline √ B. Arginine C. Aspartate ...
Amino acid metabolism III. Brake down of amino acids
... Coenzyme B12-dependent reactions in mammals: • methionine synthase reaction • rearrangament of L-methylmalonyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA ...
... Coenzyme B12-dependent reactions in mammals: • methionine synthase reaction • rearrangament of L-methylmalonyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA ...
fatty acid synthesis
... synthesis. Phosphorylation of ACC, for example a result of activation of PKA by stress or exercise switches on fatty acid oxidation (via phosphorylation and inhibition of ACC-2 resulting in decreased malonyl CoA levels) while switching off fatty acid synthesis (via phosphorylation and inhibition of ...
... synthesis. Phosphorylation of ACC, for example a result of activation of PKA by stress or exercise switches on fatty acid oxidation (via phosphorylation and inhibition of ACC-2 resulting in decreased malonyl CoA levels) while switching off fatty acid synthesis (via phosphorylation and inhibition of ...
Title: Molecular recognition of amino acids by using pseudopeptidic
... In the first part, the synthesis of two [2+2] pseudopeptidic macrocycles through reductive amination reaction is described. They differ in the linking positions of the central benzene ring (meta or para). In both cases, the use of anionic templates is necessary to favor the formation of the desired ...
... In the first part, the synthesis of two [2+2] pseudopeptidic macrocycles through reductive amination reaction is described. They differ in the linking positions of the central benzene ring (meta or para). In both cases, the use of anionic templates is necessary to favor the formation of the desired ...
Acids
... Why be concerned about pH? • All functional proteins are pH sensitive – Enzymes, hormones, Hb, etc • Therefore, all metabolic reactions are pH sensitive ...
... Why be concerned about pH? • All functional proteins are pH sensitive – Enzymes, hormones, Hb, etc • Therefore, all metabolic reactions are pH sensitive ...
CHE 4310 Fall 2011
... 19. When glucose labeled with a 14C at C-2 passes through glycolysis, the glyceraldehyde 3phosphate that is produced from it still contains the radioactive carbon atom. Draw the structure of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, and circle the atom(s) that would be radioactive. ...
... 19. When glucose labeled with a 14C at C-2 passes through glycolysis, the glyceraldehyde 3phosphate that is produced from it still contains the radioactive carbon atom. Draw the structure of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, and circle the atom(s) that would be radioactive. ...
MODULE 2
... 94. Fusion inhibitors are new class of antiviral that blocks the entry of viruses into host cells, which of the following drug is a synthetic 36amino acid peptide and the first representative of the fusion inhibitor? A. Lamivudine B. Enfuvirtide ...
... 94. Fusion inhibitors are new class of antiviral that blocks the entry of viruses into host cells, which of the following drug is a synthetic 36amino acid peptide and the first representative of the fusion inhibitor? A. Lamivudine B. Enfuvirtide ...
Sample exam 1
... site. Explain how this takes part in the mechanism of the cleavage. The guanidino group is shown below: ...
... site. Explain how this takes part in the mechanism of the cleavage. The guanidino group is shown below: ...
Hepoxilin

Hepoxilins (HxA3 and HxB3) are nonclassic eicosanoid hormones involved in inflammation.