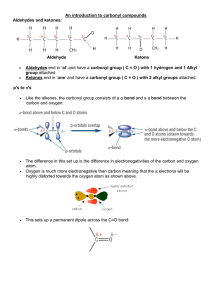
An introduction to carbonyl compounds Aldehydes and ketones
... The orange crystals from 2,4-DNPH can be filtered, recrystallised and melting point determination. Once you know whether it is an aldehyde or ketone from Tollen's reagent, look up the MPt of the derivative in a table to identify the crystals and hence the aldehyde / ...
... The orange crystals from 2,4-DNPH can be filtered, recrystallised and melting point determination. Once you know whether it is an aldehyde or ketone from Tollen's reagent, look up the MPt of the derivative in a table to identify the crystals and hence the aldehyde / ...
Phenyl Acetate Preparation ( from Phenol and
... (Table 1). Water removal via acetic acid azeotroping markedly raised this, so that preparations employing this technique and using a four mole excess of acetic acid, achieved 55-60% yields of ester based on phenol (Table 2 ) . With less efficient columns (short Vigreux and the like), equivalent yiel ...
... (Table 1). Water removal via acetic acid azeotroping markedly raised this, so that preparations employing this technique and using a four mole excess of acetic acid, achieved 55-60% yields of ester based on phenol (Table 2 ) . With less efficient columns (short Vigreux and the like), equivalent yiel ...
II. Beta oxidation of fatty acid
... _A__9. The most active enzyme involved in oxidative deamination: A. Glutamate dehydrogenase C. glutaminase B. glutamine synthetase D. L-amino acid oxidase _C__10. This amino acid does not undergo transamination: A. Valine B. Glutamine C. Lysine D. Arginine _D__11. Major means by which the brain deto ...
... _A__9. The most active enzyme involved in oxidative deamination: A. Glutamate dehydrogenase C. glutaminase B. glutamine synthetase D. L-amino acid oxidase _C__10. This amino acid does not undergo transamination: A. Valine B. Glutamine C. Lysine D. Arginine _D__11. Major means by which the brain deto ...
Microbiology Of Fermented Foods and Beverages by momina
... Lactococci were provided respiring conditions (aerobic and presence of heme)-cell growth was much better. Growth of cells extended over longer period of time. Cell densities higher as compared to cells not undergoing respiration. Viability of respiring cells extended over a longer period since pH ar ...
... Lactococci were provided respiring conditions (aerobic and presence of heme)-cell growth was much better. Growth of cells extended over longer period of time. Cell densities higher as compared to cells not undergoing respiration. Viability of respiring cells extended over a longer period since pH ar ...
chapter_6_mod_2009
... Pyruvic acid is reduced to form lactic acid. (p. 123) No carbon dioxide is released. ...
... Pyruvic acid is reduced to form lactic acid. (p. 123) No carbon dioxide is released. ...
Various University Examination Questions on Fatty acid
... 17. Write the reaction, with cofactors if any, catalyzed by Acetyl CoA carboxylase. ...
... 17. Write the reaction, with cofactors if any, catalyzed by Acetyl CoA carboxylase. ...
FALSE degradation also needs to be considered. A change in
... Synthesizes fructose-2,6-bis-phosphate Degrades fructose-2,6-bis-phosphate Stimulated by fructose-2,6-bis-phosphate Inhibited by fructose-2,6-bis-phosphate Its mRNA level is increased by glucagon Catalyzes last step in gluconeogenesis Glycolytic enzyme bypassed by 2 gluconeogenic enzymes Gluconeogen ...
... Synthesizes fructose-2,6-bis-phosphate Degrades fructose-2,6-bis-phosphate Stimulated by fructose-2,6-bis-phosphate Inhibited by fructose-2,6-bis-phosphate Its mRNA level is increased by glucagon Catalyzes last step in gluconeogenesis Glycolytic enzyme bypassed by 2 gluconeogenic enzymes Gluconeogen ...
Chapter 3 Review Questions
... a. It creates the right pH needed for the reaction. b. It decreases the amount of energy needed for the reaction. c. It provides the extra energy needed for the reaction. d. It maintains the proper temperature needed for the reaction. Examine the structural formula below. ...
... a. It creates the right pH needed for the reaction. b. It decreases the amount of energy needed for the reaction. c. It provides the extra energy needed for the reaction. d. It maintains the proper temperature needed for the reaction. Examine the structural formula below. ...
Ch.24Pt.6_000
... sequence of cycles needed to produce a C16 fatty acid from acetyl ACP. Malonyl ACP adds 2 carbons at each cycle. ...
... sequence of cycles needed to produce a C16 fatty acid from acetyl ACP. Malonyl ACP adds 2 carbons at each cycle. ...
Table S1.
... in the ER Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Protein Indirectly involved in cholesterol synthesis by ...
... in the ER Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Protein Indirectly involved in cholesterol synthesis by ...
Cellular Respiration Review
... #21. Name the 3 carbon molecule that forms when glucose is split in half during glycolysis. #22. Name the 6 carbon molecule that forms during the first step of the Krebs cycle. #23. Fermentation is said to be ________________ because it happens “NOT IN AIR” or without oxygen. 24. Compare NADH and FA ...
... #21. Name the 3 carbon molecule that forms when glucose is split in half during glycolysis. #22. Name the 6 carbon molecule that forms during the first step of the Krebs cycle. #23. Fermentation is said to be ________________ because it happens “NOT IN AIR” or without oxygen. 24. Compare NADH and FA ...
version a
... A) Leucine and isoleucine are the D and L isomers of leucine. B) The α‐helix is one possible conformation of a polypeptide. C) Peptides can adopt many conformations because of rotation about single covalent bonds. D) Unfolding or denaturation of a protein usually leads to a loss of biological act ...
... A) Leucine and isoleucine are the D and L isomers of leucine. B) The α‐helix is one possible conformation of a polypeptide. C) Peptides can adopt many conformations because of rotation about single covalent bonds. D) Unfolding or denaturation of a protein usually leads to a loss of biological act ...
Citric Acid Cycle in Anabolism
... 2) Uses NADP+ as a cofactor instead of NAD+. 3) Pyruvate carboxyl reduced to hydroxyl ...
... 2) Uses NADP+ as a cofactor instead of NAD+. 3) Pyruvate carboxyl reduced to hydroxyl ...
Wheatgrass Chlorophyllcdmcoct022012
... simpler chains of amino acids which are deposited more efficiently into the bloodstream and blood tissues. Protein is essential to build and repair tissues, and is an important building block of bones, muscles, cartlidge, skin, and blood. ...
... simpler chains of amino acids which are deposited more efficiently into the bloodstream and blood tissues. Protein is essential to build and repair tissues, and is an important building block of bones, muscles, cartlidge, skin, and blood. ...
Paper - IndiaStudyChannel.com
... 72. The cell walls of gram positive bacteria contain two modified sugars, Nacetylglucosamine (NAG) and N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM). They are covalently linked by : (A) alpha-1, 4-glycosidic bond (B) beta-1,6-glycosidic bond (C) alpha-1, 6-glycosidic bond (D) beta -1, 4-glycosidic bond 73. Many plasmi ...
... 72. The cell walls of gram positive bacteria contain two modified sugars, Nacetylglucosamine (NAG) and N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM). They are covalently linked by : (A) alpha-1, 4-glycosidic bond (B) beta-1,6-glycosidic bond (C) alpha-1, 6-glycosidic bond (D) beta -1, 4-glycosidic bond 73. Many plasmi ...
Vitamins
... giving a person more energy. This is due to the fact that these vitamins each play different roles with energy metabolism in the body. When they are present in the body, they allow energy to be used more readily by the body. Since these vitamins are water soluble, they are not stored in the body li ...
... giving a person more energy. This is due to the fact that these vitamins each play different roles with energy metabolism in the body. When they are present in the body, they allow energy to be used more readily by the body. Since these vitamins are water soluble, they are not stored in the body li ...
File - Wk 1-2
... Isomerase interconverts the 3 carbon sugars and in a test tube the reactions would reach equilibrium but in the cell, only Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate is used in glycolysis as a substrate for the enzyme in step 6. So equilibrium shifts towards the glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate, therefore the summary of ...
... Isomerase interconverts the 3 carbon sugars and in a test tube the reactions would reach equilibrium but in the cell, only Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate is used in glycolysis as a substrate for the enzyme in step 6. So equilibrium shifts towards the glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate, therefore the summary of ...
Lipids
... • 3 fatty acid molecules joined to a glycerol • Each fatty acid consists of an acid COOH group joined to a long hydrocarbon chain consisting of carbon and hydrogen • The length of the hydrocarbon chain varies but in many of the fatty acids in triglycerides there are between 14 and 16 carbon atoms ...
... • 3 fatty acid molecules joined to a glycerol • Each fatty acid consists of an acid COOH group joined to a long hydrocarbon chain consisting of carbon and hydrogen • The length of the hydrocarbon chain varies but in many of the fatty acids in triglycerides there are between 14 and 16 carbon atoms ...
Part 2
... Fermentation: Yeasts (single-celled eukaryotic fungi) and some bacteria can also do a different type of anaerobic respiration when O2 isn’t readily available. ...
... Fermentation: Yeasts (single-celled eukaryotic fungi) and some bacteria can also do a different type of anaerobic respiration when O2 isn’t readily available. ...
1. The carbon atoms of cysteine are derived from: A. Methionine B
... Glutamine is the most abundant amino acid in serum. Guutamine synthetase utilizes ATP. Glutamine donates a nitrogen to aspartate to form asparagine. Glutamine can be used as a carbon source for energy by it conversion to TCA cycle intermediates. ...
... Glutamine is the most abundant amino acid in serum. Guutamine synthetase utilizes ATP. Glutamine donates a nitrogen to aspartate to form asparagine. Glutamine can be used as a carbon source for energy by it conversion to TCA cycle intermediates. ...
9-pH and buffer_ part B 2014-2015 (1)
... buffer system in the body 2. H2PO4/ HPO4 (pKa= 6.8). 3. Plasm Proteins (20% of buffering capacity “NH2+ , COO-”) 4. Hb. (60% of buffering capacity “Histidine”) 5. Free amino acids ...
... buffer system in the body 2. H2PO4/ HPO4 (pKa= 6.8). 3. Plasm Proteins (20% of buffering capacity “NH2+ , COO-”) 4. Hb. (60% of buffering capacity “Histidine”) 5. Free amino acids ...
Title Effect of Glutamine Analogs on Glutaminase Formation in
... The formation of asparaginase of Escherichiacoli was not increased when a complex medium or an amino acid free medium were supplemented with L-asparagine (24). Only among species of Pseudomonashas there been evidence of a marked inducible formation of asparaginase by asparagine or aspartic acid (25) ...
... The formation of asparaginase of Escherichiacoli was not increased when a complex medium or an amino acid free medium were supplemented with L-asparagine (24). Only among species of Pseudomonashas there been evidence of a marked inducible formation of asparaginase by asparagine or aspartic acid (25) ...
Oregon State University, Summer 2009 Chemistry 121 Midterm
... Cl2(g) + 2KBr (aq) Æ Br2(l) + 2 KCl (aq) Which of the statements about this reaction below is CORRECT? a. Cl2 is reduced and Br- is acting as an reducing agent. b. K+ is oxidized and is acting as a reducing agent. c. Br2 is reduced, Cl- is reduced and KBr is oxidized. d. Cl2 is oxidized and Br- is a ...
... Cl2(g) + 2KBr (aq) Æ Br2(l) + 2 KCl (aq) Which of the statements about this reaction below is CORRECT? a. Cl2 is reduced and Br- is acting as an reducing agent. b. K+ is oxidized and is acting as a reducing agent. c. Br2 is reduced, Cl- is reduced and KBr is oxidized. d. Cl2 is oxidized and Br- is a ...
Types of Fermentation
... respiration, the cell first breaks glucose into smaller molecules. This releases a small amount of energy. Without oxygen cellular respiration cannot continue. Instead of entering the mitochondria, the smaller molecules stay in the cytoplasm, where fermentation occurs. There are two main types of fe ...
... respiration, the cell first breaks glucose into smaller molecules. This releases a small amount of energy. Without oxygen cellular respiration cannot continue. Instead of entering the mitochondria, the smaller molecules stay in the cytoplasm, where fermentation occurs. There are two main types of fe ...
Bioenergy basics miller
... • Can choose parameters arbitrarily or use standard values (NREL website). • Possibilities for open-ended design, multiple smaller “feeder” process units in remote locations. ...
... • Can choose parameters arbitrarily or use standard values (NREL website). • Possibilities for open-ended design, multiple smaller “feeder” process units in remote locations. ...
Hepoxilin

Hepoxilins (HxA3 and HxB3) are nonclassic eicosanoid hormones involved in inflammation.























