Chapters 14 and 15 Outline
... pH meter – is a device that determines the pH of a solution by measuring the voltage between the two electrodes that are in the solution. Titration – is a controlled addition and measurement of the amount of a solution of known concentration required to react completely with a measure of a solution ...
... pH meter – is a device that determines the pH of a solution by measuring the voltage between the two electrodes that are in the solution. Titration – is a controlled addition and measurement of the amount of a solution of known concentration required to react completely with a measure of a solution ...
12. Acids and Bases
... periodic table!! The PAI’s will be given to you, except the 12 we had to memorize! ...
... periodic table!! The PAI’s will be given to you, except the 12 we had to memorize! ...
Renal Physiology 9 (Acid Base 1)
... H+ (e.g., HCO3- + H+ H2CO3). • STRONG bases – dissociate easily in H2O and quickly bind H+. • WEAK bases – accept H+ more slowly (e.g., HCO3- and NH3) Proteins in body function as weak bases as some constituent AMINO ACIDS have net negative charge and attract H+ (e.g. HAEMOGLOBIN). ...
... H+ (e.g., HCO3- + H+ H2CO3). • STRONG bases – dissociate easily in H2O and quickly bind H+. • WEAK bases – accept H+ more slowly (e.g., HCO3- and NH3) Proteins in body function as weak bases as some constituent AMINO ACIDS have net negative charge and attract H+ (e.g. HAEMOGLOBIN). ...
(Acid Base 1).
... 2. The acid in question, if we have two equally concentrated solutions of acids, the solution of a strong acid will have a lower pH than that of a weak acid, because it is more fully dissociated and therefore produces more H3O+ ions. HCl, for example, is completely dissociated. ...
... 2. The acid in question, if we have two equally concentrated solutions of acids, the solution of a strong acid will have a lower pH than that of a weak acid, because it is more fully dissociated and therefore produces more H3O+ ions. HCl, for example, is completely dissociated. ...
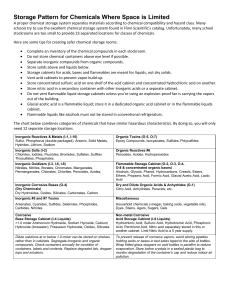
Storage Pattern for Chemicals Where Space is Limited
... Vent acid cabinets to prevent vapor build-up. Store concentrated sulfuric acid on one shelf of the acid cabinet and concentrated hydrochloric acid on another. Store nitric acid in a secondary container with other inorganic acids or a separate cabinet. Do not vent flammable liquid storage cabinets un ...
... Vent acid cabinets to prevent vapor build-up. Store concentrated sulfuric acid on one shelf of the acid cabinet and concentrated hydrochloric acid on another. Store nitric acid in a secondary container with other inorganic acids or a separate cabinet. Do not vent flammable liquid storage cabinets un ...
Acids and Bases
... Dissociation • In water all ionic compounds dissociate into its ionic parts • So NaCl in water dissociates into Na+ and Cl• So H3PO4 dissociates into 3H+ and PO4-3 • Remembers ionic compounds are formed by metals and nonmetals or by metals and polyatomic ions ...
... Dissociation • In water all ionic compounds dissociate into its ionic parts • So NaCl in water dissociates into Na+ and Cl• So H3PO4 dissociates into 3H+ and PO4-3 • Remembers ionic compounds are formed by metals and nonmetals or by metals and polyatomic ions ...
CHE 145-381 – TEST #2 SPRING 2009 CHAPTERS 6, 7, 8 NAME
... CHE 145-381 – TEST #2 SPRING 2009 CHAPTERS 6, 7, 8 NAME :________________________ DATE: ____________________________ You may use the Periodic Table. Please note that all quantities needed for the successful completion of this test have been given. Feel free to ask questions for clarification. 1. Ind ...
... CHE 145-381 – TEST #2 SPRING 2009 CHAPTERS 6, 7, 8 NAME :________________________ DATE: ____________________________ You may use the Periodic Table. Please note that all quantities needed for the successful completion of this test have been given. Feel free to ask questions for clarification. 1. Ind ...
material safety data sheet
... MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET I - IDENTIFICATION AND USE PRODUCT NAME: FLO-CLENE PRODUCT USE: LIQUID DRAIN OPENER SUPPLIER: ...
... MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET I - IDENTIFICATION AND USE PRODUCT NAME: FLO-CLENE PRODUCT USE: LIQUID DRAIN OPENER SUPPLIER: ...
7.2 Acids and Bases
... Acids Reacts with metals and carbonates Conducts electricity Turns blue litmus paper red Tastes sour pH < 7 Neutralizes bases ...
... Acids Reacts with metals and carbonates Conducts electricity Turns blue litmus paper red Tastes sour pH < 7 Neutralizes bases ...
Acid throwing

Acid throwing, also called an acid attack, a vitriol attack or vitriolage, is a form of violent assault defined as the act of throwing acid or a similarly corrosive substance onto the body of another ""with the intention to disfigure, maim, torture, or kill."" Perpetrators of these attacks throw acid at their victims, usually at their faces, burning them, and damaging skin tissue, often exposing and sometimes dissolving the bones. The most common types of acid used in these attacks are sulfuric and nitric acid. Hydrochloric acid is sometimes used, but is much less damaging. The long term consequences of these attacks may include blindness, as well as permanent scarring of the face and body, along with far-reaching social, psychological, and economic difficulties.Today, acid attacks are reported in many parts of the world. Since the 1990s, Bangladesh has been reporting the highest number of attacks and highest incidence rates for women, with 3,512 Bangladeshi people acid attacked between 1999 and 2013. Although acid attacks occur all over the world, including in Europe and the United States, this type of violence is mainly concentrated in South Asia.