Unit 11 acids and bases part 1
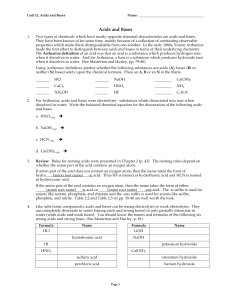
... Acidic Salts are formed from a strong acid and a weak base. Neutral salts are formed from a strong acid and strong base. Basic salts are formed from a strong base and a weak acid. Give the acid and base the following salts were formed from and label the salts as acidic, basic, or neutral. ...
... Acidic Salts are formed from a strong acid and a weak base. Neutral salts are formed from a strong acid and strong base. Basic salts are formed from a strong base and a weak acid. Give the acid and base the following salts were formed from and label the salts as acidic, basic, or neutral. ...
Journal of Molecular Catalysis A, 302
... acid derivates represents yet another approach for the synthesis of trifluoromethylbenzoic acid [19–21]. Recently, it has been shown that the carboxylation of alkenylboronic esters can be used to synthesize trifluoromethylbenzoic acid, a process which proceeds with high yields [22]. Since most of the ...
... acid derivates represents yet another approach for the synthesis of trifluoromethylbenzoic acid [19–21]. Recently, it has been shown that the carboxylation of alkenylboronic esters can be used to synthesize trifluoromethylbenzoic acid, a process which proceeds with high yields [22]. Since most of the ...
Acid - Net Texts
... An acid (from the Latin acidus/acēre meaning sour[1] ) is a substance which reacts with a base. Commonly, acids can be identified as tasting sour, reacting with metals such as calcium, and bases like sodium carbonate. Aqueous acids have a pH of less than 7, where an acid of lower pH is typically str ...
... An acid (from the Latin acidus/acēre meaning sour[1] ) is a substance which reacts with a base. Commonly, acids can be identified as tasting sour, reacting with metals such as calcium, and bases like sodium carbonate. Aqueous acids have a pH of less than 7, where an acid of lower pH is typically str ...
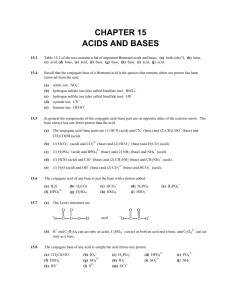
CHAPTER 15 ACIDS AND BASES
... At pH 1.00 the concentration of hydrogen ion is 0.10 M (Why only two significant figures?) This will tend to suppress the ionization of the weak acid (LeChatelier's principle, Section 14.5). The extra hydrogen ion shifts the position of equilibrium in the direction of the un-ionized acid, and to two ...
... At pH 1.00 the concentration of hydrogen ion is 0.10 M (Why only two significant figures?) This will tend to suppress the ionization of the weak acid (LeChatelier's principle, Section 14.5). The extra hydrogen ion shifts the position of equilibrium in the direction of the un-ionized acid, and to two ...
Worked solutions to textbook questions 1 Chapter 14 From organic
... Why is the sodium salt of acetylsalicylic acid more soluble than normal aspirin? A7. Sodium acetylsalicylic acid is more soluble in water than acetylsalicylic acid because it dissociates into ions (Na+ and the acetylsalicylate anion) which then attract water molecules to form solvation sheaths aroun ...
... Why is the sodium salt of acetylsalicylic acid more soluble than normal aspirin? A7. Sodium acetylsalicylic acid is more soluble in water than acetylsalicylic acid because it dissociates into ions (Na+ and the acetylsalicylate anion) which then attract water molecules to form solvation sheaths aroun ...
Structural Studies on Sulfated Glycopeptides from the Carbohydrate
... shown in Fig.2 with quantitative recovery of uronic acid. The chemical composition of each fraction is shown in Table I. The threemajor fractions (D-1, D-3, and D-4)were subjected to borate paper electrophoresis at pH 9.5. The results are illustrated in Fig. 3. D-1 and D-3 gave rise to only one majo ...
... shown in Fig.2 with quantitative recovery of uronic acid. The chemical composition of each fraction is shown in Table I. The threemajor fractions (D-1, D-3, and D-4)were subjected to borate paper electrophoresis at pH 9.5. The results are illustrated in Fig. 3. D-1 and D-3 gave rise to only one majo ...
Chapter Ten
... ► Salt solutions can be neutral, acidic, or basic, depending on the ions present, because some ions react with water to produce H+ and some ions react with water to produce OH-. ► To predict the acidity of a salt solution, it is convenient to classify salts according to the acid and base from which ...
... ► Salt solutions can be neutral, acidic, or basic, depending on the ions present, because some ions react with water to produce H+ and some ions react with water to produce OH-. ► To predict the acidity of a salt solution, it is convenient to classify salts according to the acid and base from which ...
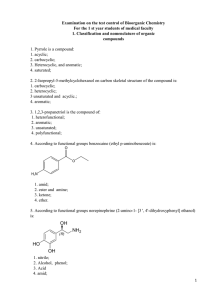
2. 2-Isopropyl-5-methylcyclohexanol on carbon skeletal
... 22. Energy of propanol-1 in the anti-conformation is less than gauche conformation, because in the anti-conformation: 1. less angular tension; 2. configuration has changed; 3. decreased Van der Waals repulsion; 4. was less torsional stress; 23. Energy of 2-chlorobutane in the eclipsed conformation m ...
... 22. Energy of propanol-1 in the anti-conformation is less than gauche conformation, because in the anti-conformation: 1. less angular tension; 2. configuration has changed; 3. decreased Van der Waals repulsion; 4. was less torsional stress; 23. Energy of 2-chlorobutane in the eclipsed conformation m ...
Buffer Solutions
... Buffer Solutions Buffers are solutions with the ability to resist the addition of strong acids or strong bases, within limits. They play an important role in chemical processes where it is essential that a fairly constant pH is maintained. In many industrial and physiological processes, specific rea ...
... Buffer Solutions Buffers are solutions with the ability to resist the addition of strong acids or strong bases, within limits. They play an important role in chemical processes where it is essential that a fairly constant pH is maintained. In many industrial and physiological processes, specific rea ...
Buffer Solutions
... Buffer Solutions Buffers are solutions with the ability to resist the addition of strong acids or strong bases, within limits. They play an important role in chemical processes where it is essential that a fairly constant pH is maintained. In many industrial and physiological processes, specific rea ...
... Buffer Solutions Buffers are solutions with the ability to resist the addition of strong acids or strong bases, within limits. They play an important role in chemical processes where it is essential that a fairly constant pH is maintained. In many industrial and physiological processes, specific rea ...
Acid‒base reaction
... or lower esophagus. Also in the digestive tract, neutralization reactions are used when food is moved from the stomach to the intestines. In order for the nutrients to be absorbed through the intestinal wall, an alkaline environment is needed, so the pancreas produce an antacid bicarbonate to cause ...
... or lower esophagus. Also in the digestive tract, neutralization reactions are used when food is moved from the stomach to the intestines. In order for the nutrients to be absorbed through the intestinal wall, an alkaline environment is needed, so the pancreas produce an antacid bicarbonate to cause ...
Chapter 17, Section 17.3
... smokestacks • “nox” from automobile exhaust see equations, page 681 ...
... smokestacks • “nox” from automobile exhaust see equations, page 681 ...
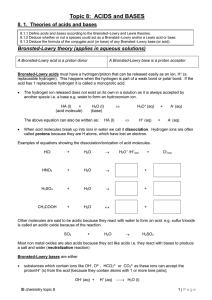
Topic 8: ACIDS and BASES
... 0.1M) will have different hydrogen concentrations - and therefore different pH’s - because of their different strengths: the pH of the hydrochloric acid will be lower than the pH of the ethanoic acid solution. Some practical procedures to distinguish between strong and weak acids and bases. Simple p ...
... 0.1M) will have different hydrogen concentrations - and therefore different pH’s - because of their different strengths: the pH of the hydrochloric acid will be lower than the pH of the ethanoic acid solution. Some practical procedures to distinguish between strong and weak acids and bases. Simple p ...
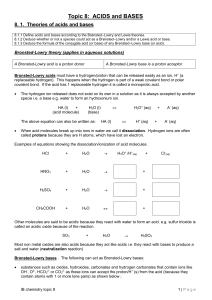
Topic 8: ACIDS and BASES
... Example: a hydrochloric acid solution and an ethanoic acid solution of the same concentration (eg 0.1M) will have different hydrogen concentrations - and therefore different pH’s - because of their different strengths: the pH of the hydrochloric acid will be lower than the pH of the ethanoic acid s ...
... Example: a hydrochloric acid solution and an ethanoic acid solution of the same concentration (eg 0.1M) will have different hydrogen concentrations - and therefore different pH’s - because of their different strengths: the pH of the hydrochloric acid will be lower than the pH of the ethanoic acid s ...
Strecker Degradation Products of Aspartic and Glutamic Acids and
... Aspartic and glutamic acids, asparagine and glutamine were oxidised with either potassium peroxodisulphate or glyoxal. Nonvolatile products were derivatised and analysed by GC/FID and GC/MS. Volatile reaction products were isolated and analysed by the same methods. It was found that the degradation ...
... Aspartic and glutamic acids, asparagine and glutamine were oxidised with either potassium peroxodisulphate or glyoxal. Nonvolatile products were derivatised and analysed by GC/FID and GC/MS. Volatile reaction products were isolated and analysed by the same methods. It was found that the degradation ...
Density functional theory and FTIR spectroscopic study of carboxyl
... cm–1. The infrared spectrum of sodium salicylate is illustrated in Fig. 2(b). Special interest is directed to the symmetric and asymmetric COO bands at 1579.4 cm–1 and 1485.9 cm–1, respectively. The shift from 1753 cm–1 (C=O) to 1579.4 cm–1 (COO) is corresponding to changing the carboxyl group into ...
... cm–1. The infrared spectrum of sodium salicylate is illustrated in Fig. 2(b). Special interest is directed to the symmetric and asymmetric COO bands at 1579.4 cm–1 and 1485.9 cm–1, respectively. The shift from 1753 cm–1 (C=O) to 1579.4 cm–1 (COO) is corresponding to changing the carboxyl group into ...
chemistry 103 - chem.uwec.edu
... The first drop of excess NaOH then reacts with the indicator that is present: HIn(aq) + OH-(aq) H2O + In-(aq) Now HIn and In- have different colors, so we can detect that the acid-base reaction is complete. ...
... The first drop of excess NaOH then reacts with the indicator that is present: HIn(aq) + OH-(aq) H2O + In-(aq) Now HIn and In- have different colors, so we can detect that the acid-base reaction is complete. ...
Thin-Layer Chromatography: Applying TLC as a
... synthesis of aspirin. For example, when using pure hexane the entire solvent has a nonpolar composition. Therefore acetylsalicylic acid, the more nonpolar compound, will be more attracted to the mobile phase and move with the hexane solvent while salicylic acid, the more polar compound, will be extr ...
... synthesis of aspirin. For example, when using pure hexane the entire solvent has a nonpolar composition. Therefore acetylsalicylic acid, the more nonpolar compound, will be more attracted to the mobile phase and move with the hexane solvent while salicylic acid, the more polar compound, will be extr ...
Introduction - Bulgarian Chemical Communications
... free energy relationships, LFER, e.g. using Taft’s ES-values. The reason for this can be traced to the nature of the GDME. Examination of a large series of the reversible cyclization of 3-(3-phenylureido) acids showed that good LFER of the Leffler type, i.e. rates against equilibria of the same reac ...
... free energy relationships, LFER, e.g. using Taft’s ES-values. The reason for this can be traced to the nature of the GDME. Examination of a large series of the reversible cyclization of 3-(3-phenylureido) acids showed that good LFER of the Leffler type, i.e. rates against equilibria of the same reac ...
Acids, Bases, and pH
... to have a low pH? How is pH measured and how does it relate to the acidity of a solution? Why is carbonated water acidic? These are all important questions and you will learn how to answer them, and more, by the end of this chapter. Not only is acid-base chemistry important in determining the acidit ...
... to have a low pH? How is pH measured and how does it relate to the acidity of a solution? Why is carbonated water acidic? These are all important questions and you will learn how to answer them, and more, by the end of this chapter. Not only is acid-base chemistry important in determining the acidit ...
Chapter 1 - TamAPChemistryHart
... that all of the dissolved CO2 is in the form of carbonic acid (H2CO3), which is produced by reaction between the CO2 and H2O: CO2(aq) + H2O(l) H2CO3(aq) What is the pH of a 0.0037 M solution of H2CO3? ...
... that all of the dissolved CO2 is in the form of carbonic acid (H2CO3), which is produced by reaction between the CO2 and H2O: CO2(aq) + H2O(l) H2CO3(aq) What is the pH of a 0.0037 M solution of H2CO3? ...
Chapter 15 Acids and Bases
... COOH group HC2H3O2, H3C6H5O7 only the first H in the formula is acidic the H is on the COOH ...
... COOH group HC2H3O2, H3C6H5O7 only the first H in the formula is acidic the H is on the COOH ...
Acid throwing

Acid throwing, also called an acid attack, a vitriol attack or vitriolage, is a form of violent assault defined as the act of throwing acid or a similarly corrosive substance onto the body of another ""with the intention to disfigure, maim, torture, or kill."" Perpetrators of these attacks throw acid at their victims, usually at their faces, burning them, and damaging skin tissue, often exposing and sometimes dissolving the bones. The most common types of acid used in these attacks are sulfuric and nitric acid. Hydrochloric acid is sometimes used, but is much less damaging. The long term consequences of these attacks may include blindness, as well as permanent scarring of the face and body, along with far-reaching social, psychological, and economic difficulties.Today, acid attacks are reported in many parts of the world. Since the 1990s, Bangladesh has been reporting the highest number of attacks and highest incidence rates for women, with 3,512 Bangladeshi people acid attacked between 1999 and 2013. Although acid attacks occur all over the world, including in Europe and the United States, this type of violence is mainly concentrated in South Asia.