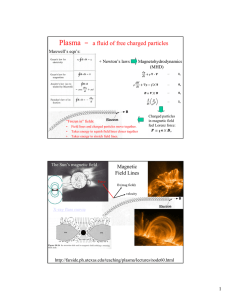
... Given two systems of N1 ≈ N2 = 1022 spins with multiplicity functions g1(N1,s1) and g2(N2,s-s1), the product g1g2 as a function of s1 is relatively sharply peaked at s1 = ŝ1. For s1 = ŝ1 + 1012, the product g1g2 is reduced by 10-174 from its peak value. Use the Gaussian approximation of the multipli ...
Uniform electric fields - Tasker Milward Physics Website
... Ek = energy gained by the particle q = charge on the particle V = accelerating voltage ...
... Ek = energy gained by the particle q = charge on the particle V = accelerating voltage ...
Marvin_Weinstein
... required, just a choice of coupling constant. Question: What do we hold fixed ? My choice is the energy of the zero momentum two-particle state. This immediately shows why this theory is trivial in four dimensions. ...
... required, just a choice of coupling constant. Question: What do we hold fixed ? My choice is the energy of the zero momentum two-particle state. This immediately shows why this theory is trivial in four dimensions. ...
Quantum Mechanics Lecture Course for 4 Semester Students by W.B. von Schlippe
... The history of optical theories shows that the scientific view has for long oscillated between a mechanical and an undulatory conception of light; however, these two views are perhaps less opposed to one another than was previously thought, and the development of quantum theory, in particular, appea ...
... The history of optical theories shows that the scientific view has for long oscillated between a mechanical and an undulatory conception of light; however, these two views are perhaps less opposed to one another than was previously thought, and the development of quantum theory, in particular, appea ...
Lecture 1
... Δx and Δp in these measurements satisfy the following relation (Heisenberg’s uncertainty relation): ...
... Δx and Δp in these measurements satisfy the following relation (Heisenberg’s uncertainty relation): ...
Geometry, Physics, and Representation Theory Traces of intertwiners for quantum affine and
... Felder-Varchenko functions Abstract. This talk concerns two approaches for studying a family of special functions occurring in the study of the q-Knizhnik-Zamolodchikov-Bernard (q-KZB) equation. The philosophy of KZ-type equations predicts that it admits solutions via (1) traces of intertwining oper ...
... Felder-Varchenko functions Abstract. This talk concerns two approaches for studying a family of special functions occurring in the study of the q-Knizhnik-Zamolodchikov-Bernard (q-KZB) equation. The philosophy of KZ-type equations predicts that it admits solutions via (1) traces of intertwining oper ...
Propagator of a Charged Particle with a Spin in Uniform Magnetic
... RICARDO CORDERO-SOTO ET AL. ...
... RICARDO CORDERO-SOTO ET AL. ...
By convention magnetic momentum of a current loop is calculated by
... particle has an electric unit charge, we can write this current to: ...
... particle has an electric unit charge, we can write this current to: ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 15) Estimate the ground state energy of a two-electron system by the variation method. PART C ( 4x 12 ½ m=50 m) ANSWER ANY FOUR QUESTIONS 16) (a) State and prove closure property for a complete set of orthonormal functions. (b) Normalize the wave function ψ(x) = e - ׀x ׀sinx. 17) Discuss the sim ...
... 15) Estimate the ground state energy of a two-electron system by the variation method. PART C ( 4x 12 ½ m=50 m) ANSWER ANY FOUR QUESTIONS 16) (a) State and prove closure property for a complete set of orthonormal functions. (b) Normalize the wave function ψ(x) = e - ׀x ׀sinx. 17) Discuss the sim ...
Transparancies for Feynman Graphs
... KG as old as QM, originally dismissed. No spin 0 particles known. Pion was only discovered in 1948. Dirac equation of 1928 described known spin ½ electron. Also described an anti-particle – Dirac boldly postulated existence of positron Discovered by Anderson in 1933 using a cloud chamber (C.Wilson) ...
... KG as old as QM, originally dismissed. No spin 0 particles known. Pion was only discovered in 1948. Dirac equation of 1928 described known spin ½ electron. Also described an anti-particle – Dirac boldly postulated existence of positron Discovered by Anderson in 1933 using a cloud chamber (C.Wilson) ...