Exam 2 Sol/81/F01
... possible. Let’s call the oscillator coordinate x. The ground state wavefunction for the harmonic oscillator is an even function of x, but the first excited state wavefunc– tion is an odd function (one node right at x = 0). But that’s OK—the dipole operator, –ex, is also an odd function of x. Thus, t ...
... possible. Let’s call the oscillator coordinate x. The ground state wavefunction for the harmonic oscillator is an even function of x, but the first excited state wavefunc– tion is an odd function (one node right at x = 0). But that’s OK—the dipole operator, –ex, is also an odd function of x. Thus, t ...
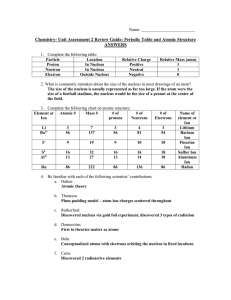
Year 11 Chemistry Balancing Equations
... • Balance the equation. (don’t change any FORMULA e.g. CO2 does not change when you ...
... • Balance the equation. (don’t change any FORMULA e.g. CO2 does not change when you ...
Questions
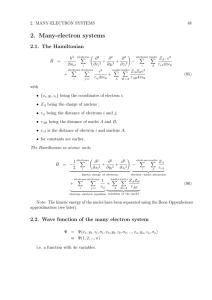
... We have seen that the spectrum of hydrogen has an “accidental” degeneracy – states with the same principle quantum number n, but different angular momentum quantum number l are degenerate. This was an artifact of the pure 1/r Coulomb potential associated . In a multielectron atom things are, of cour ...
... We have seen that the spectrum of hydrogen has an “accidental” degeneracy – states with the same principle quantum number n, but different angular momentum quantum number l are degenerate. This was an artifact of the pure 1/r Coulomb potential associated . In a multielectron atom things are, of cour ...
Electrons in Atoms
... Begin filling orbitals at the lowest energy level (Aufbau principle) Continue filling, applying Hund’s rule ...
... Begin filling orbitals at the lowest energy level (Aufbau principle) Continue filling, applying Hund’s rule ...
File
... • Orbital = region around nucleus where an electron with a given energy level will probably (90%) be found • Four kinds of orbitals s - spherical in shape, lowest orbital for every energy level p - dumbbell shaped, second orbital d - complex “flower” shape, third orbital f - very complex shape, ...
... • Orbital = region around nucleus where an electron with a given energy level will probably (90%) be found • Four kinds of orbitals s - spherical in shape, lowest orbital for every energy level p - dumbbell shaped, second orbital d - complex “flower” shape, third orbital f - very complex shape, ...
4 - College of Arts and Sciences
... Identify the GROUP of elements that corresponds to each of the following generalized electron configurations ...
... Identify the GROUP of elements that corresponds to each of the following generalized electron configurations ...
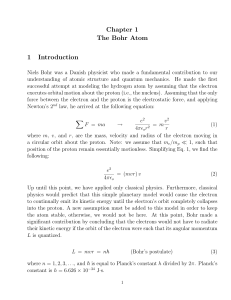
Chapter 1 The Bohr Atom 1 Introduction
... physics would predict that this simple planetary model would cause the electron to continually emit its kinetic energy until the electron’s orbit completely collapses into the proton. A new assumption must be added to this model in order to keep the atom stable, otherwise, we would not be here. At t ...
... physics would predict that this simple planetary model would cause the electron to continually emit its kinetic energy until the electron’s orbit completely collapses into the proton. A new assumption must be added to this model in order to keep the atom stable, otherwise, we would not be here. At t ...
Physical Chemistry
... • (1) Atoms can exist in stable “states” without radiating. The states have discrete energies En, n= 1, 2, 3,..., where n= 1 is the lowest energy state (the most negative, relative to the dissociated atom at zero energy), n= 2 is the next lowest energy state, etc. The number “n” is an integer, a qua ...
... • (1) Atoms can exist in stable “states” without radiating. The states have discrete energies En, n= 1, 2, 3,..., where n= 1 is the lowest energy state (the most negative, relative to the dissociated atom at zero energy), n= 2 is the next lowest energy state, etc. The number “n” is an integer, a qua ...
Quiz 8
... 3. (15 points) For each of the four quantum numbers: (1) give the name of the quantum number, (2) give the abbreviation of the quantum number, (3) give a short explanation of the physical attributes of the quantum number (energy, shape , etc.), and (4) tell the range in values for this quantum numb ...
... 3. (15 points) For each of the four quantum numbers: (1) give the name of the quantum number, (2) give the abbreviation of the quantum number, (3) give a short explanation of the physical attributes of the quantum number (energy, shape , etc.), and (4) tell the range in values for this quantum numb ...
Ch. 3
... made up off protons (+) and neutrons (0). 2) electron cloud- surrounds the nucleus and is made up of electrons (-) ...
... made up off protons (+) and neutrons (0). 2) electron cloud- surrounds the nucleus and is made up of electrons (-) ...
Ch. 4: Electron Configuration
... • Pauli exclusion principle – No two electrons in the same atom can have the same set of 4 quantum numbers. – Therefore, electrons can pair in an orbital as long as their spins are opposite. ...
... • Pauli exclusion principle – No two electrons in the same atom can have the same set of 4 quantum numbers. – Therefore, electrons can pair in an orbital as long as their spins are opposite. ...
Chemistry I Honors – Semester Exam Review – Fall 2000
... Hydrogen atoms have specific energy levels. Therefore, the atoms can only gain or lose certain amounts of energy. When atoms lose energy, they emit photons which correspond to the lines in the emission spectrum. The more energy lost, the more energy the photon has. Bohr’s model stated that electrons ...
... Hydrogen atoms have specific energy levels. Therefore, the atoms can only gain or lose certain amounts of energy. When atoms lose energy, they emit photons which correspond to the lines in the emission spectrum. The more energy lost, the more energy the photon has. Bohr’s model stated that electrons ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI-600034 M.Sc. Part-A NOVEMBER 2015
... long makes a transition from the energy level, n = 1 to n = 2. ...
... long makes a transition from the energy level, n = 1 to n = 2. ...
1. Atomic Structure
... The orbital with the lowest (n + l) value is filled first. When two or more orbitals have the same (n + l) value, the one with the lowest ‘n’ value is preferred in filling. Consider two orbitals 3d and 4s. The n + l value of 3d = 3 + 2 = 5 and of 4s = 4 + 0 = 4. Since 4s has lowest (n + l) value, it ...
... The orbital with the lowest (n + l) value is filled first. When two or more orbitals have the same (n + l) value, the one with the lowest ‘n’ value is preferred in filling. Consider two orbitals 3d and 4s. The n + l value of 3d = 3 + 2 = 5 and of 4s = 4 + 0 = 4. Since 4s has lowest (n + l) value, it ...
quantum number
... electrons. It is described by specific values of n, m and l. It can only hold 2 electrons. A sublevel includes all the similarly shaped orbitals in a particular main energy level. So for a given value of n, a sublevel consists of all orbitals with the same value of l. ...
... electrons. It is described by specific values of n, m and l. It can only hold 2 electrons. A sublevel includes all the similarly shaped orbitals in a particular main energy level. So for a given value of n, a sublevel consists of all orbitals with the same value of l. ...
Atomic Structure
... Formulated an equation that would describe the behaviour and energies of submicroscopic particles in general. Used this equation to find the probability of locating an electron in a given volume. This led to quantum mechanics or wave mechanics model. Describe the distribution of electron in an atom ...
... Formulated an equation that would describe the behaviour and energies of submicroscopic particles in general. Used this equation to find the probability of locating an electron in a given volume. This led to quantum mechanics or wave mechanics model. Describe the distribution of electron in an atom ...
Chem 1151
... (5) Titration with solutions of KBrO3 can be used to determine the concentration of As(III) in an unknown sample. What is the molarity of As(III) if 33.45 mL of 0.125M KBrO3 is needed to titrate 50.0 mL of the As(III) solution? The balanced chemical equation is H3AsO3(aq) + BrO3-(aq) Br -(aq) + 3H ...
... (5) Titration with solutions of KBrO3 can be used to determine the concentration of As(III) in an unknown sample. What is the molarity of As(III) if 33.45 mL of 0.125M KBrO3 is needed to titrate 50.0 mL of the As(III) solution? The balanced chemical equation is H3AsO3(aq) + BrO3-(aq) Br -(aq) + 3H ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.