Chemistry 871/671/495, Structure and Bonding
... The microscopic world at the atomic level (i.e. chemistry) is governed by quantum mechanical laws, which are quite different from classical mechanics that dictate our macroscopic world. To understand the structure of molecules and their reactivity, one has no choice but to rely on quantum mechanics. ...
... The microscopic world at the atomic level (i.e. chemistry) is governed by quantum mechanical laws, which are quite different from classical mechanics that dictate our macroscopic world. To understand the structure of molecules and their reactivity, one has no choice but to rely on quantum mechanics. ...
Chapter 7 Worksheet November 1
... Answer = 4.34 x 10-7 m or 434 nm. = Visible Light (Blueish) 16. (#70 from text) An electron in a hydrogen atom relaxes to the n = 4 level, emitting light of 114 THz. What is the value of n for the level in which the electron originated? ...
... Answer = 4.34 x 10-7 m or 434 nm. = Visible Light (Blueish) 16. (#70 from text) An electron in a hydrogen atom relaxes to the n = 4 level, emitting light of 114 THz. What is the value of n for the level in which the electron originated? ...
科目名 Course Title Extreme Laser Physics [極限レーザー物理E] 講義
... Interactions between optical field and atomic, molecular, and materials system have been providing interesting issues in physics. This course covers the basics of ultrafast optics and atomic physics, necessary to understand rapidly growing research field in atomic, molecular, and optical physics, wi ...
... Interactions between optical field and atomic, molecular, and materials system have been providing interesting issues in physics. This course covers the basics of ultrafast optics and atomic physics, necessary to understand rapidly growing research field in atomic, molecular, and optical physics, wi ...
Notes - Photons, the Photoelectric Effect and the Compton Effect (ppt)
... Group Think! – Whiteboards – 10 minutes! In a group of 2 or 3 come up with answers to the following: ...
... Group Think! – Whiteboards – 10 minutes! In a group of 2 or 3 come up with answers to the following: ...
Document
... 1. Lower-energy orbitals fill before higher-energy orbitals. 2. An orbital can only hold two electrons, which must have opposite spins (Pauli exclusion principle). 3. If two or more degenerate orbitals are available, follow Hund’s rule. Hund’s Rule: If two or more orbitals with the same energy are a ...
... 1. Lower-energy orbitals fill before higher-energy orbitals. 2. An orbital can only hold two electrons, which must have opposite spins (Pauli exclusion principle). 3. If two or more degenerate orbitals are available, follow Hund’s rule. Hund’s Rule: If two or more orbitals with the same energy are a ...
Measuring and Calculating
... Round – 1st decimal place <2 round down, >8 round up and in-between multiply by a constant o 4th write the formula by using the whole numbers as the subscripts To determine the molecular formula from the empirical formula – divide the molar mass of the molecular formula by the molar mass of the ...
... Round – 1st decimal place <2 round down, >8 round up and in-between multiply by a constant o 4th write the formula by using the whole numbers as the subscripts To determine the molecular formula from the empirical formula – divide the molar mass of the molecular formula by the molar mass of the ...
File
... a. deflection of alpha particles b. atomic absorption spectra c. atomic emission spectra d. the deflection of cathode rays by an electric field e. absorption of beta particles 3. Rutherford's gold foil experiment showed that the atom is mostly empty space because a. some alpha particles were reflect ...
... a. deflection of alpha particles b. atomic absorption spectra c. atomic emission spectra d. the deflection of cathode rays by an electric field e. absorption of beta particles 3. Rutherford's gold foil experiment showed that the atom is mostly empty space because a. some alpha particles were reflect ...
Physics 1020 Ch 10-12 Practice Exam (2).
... a. Increasing wavelength of incident light. b. Going from a Blue to Red light source. c. Increasing frequency of incident light. d. All of the above are possible methods to increase the energy of a light source. 5. True/False: The emission-line and continuous spectra is associated with each atom, wh ...
... a. Increasing wavelength of incident light. b. Going from a Blue to Red light source. c. Increasing frequency of incident light. d. All of the above are possible methods to increase the energy of a light source. 5. True/False: The emission-line and continuous spectra is associated with each atom, wh ...
Quantum Numbers, Orbitals, and Probability Patterns
... atom, and the results agreed perfectly with the known energy levels for hydrogen. Furthermore, the equation could be applied to more complicated atoms. It was found that Schrodinger’s equation gave a correct description of an electron’s behavior in almost every case. In spite of the overwhelming suc ...
... atom, and the results agreed perfectly with the known energy levels for hydrogen. Furthermore, the equation could be applied to more complicated atoms. It was found that Schrodinger’s equation gave a correct description of an electron’s behavior in almost every case. In spite of the overwhelming suc ...
File
... 3. noble gas configuration – abbreviates the electron configuration by using the prior noble gas ([Ar]3d54s1) ...
... 3. noble gas configuration – abbreviates the electron configuration by using the prior noble gas ([Ar]3d54s1) ...
The Behavior of Electrons in Atoms Spectrum of the Hydrogen Atom
... looking at the energies of photons emitted when an excited atom relaxes. These excited atoms can be generated by placing the atom in the very large electric field within a gas discharge tube (think neon light) or in the heat of a Bunsen burner flame. Photons are particles of light that carry energy. ...
... looking at the energies of photons emitted when an excited atom relaxes. These excited atoms can be generated by placing the atom in the very large electric field within a gas discharge tube (think neon light) or in the heat of a Bunsen burner flame. Photons are particles of light that carry energy. ...
chemistry 101 spring 2002 part 1
... (4) Bubble in OPTION A on the scanning sheet IF you want your grade posted. (5) When finished, put the free response answers in the envelope with the scanning sheet. You can keep the multiple choice part - the answers will be given to you as you leave. (6) There are a total of 29 questions (17 actua ...
... (4) Bubble in OPTION A on the scanning sheet IF you want your grade posted. (5) When finished, put the free response answers in the envelope with the scanning sheet. You can keep the multiple choice part - the answers will be given to you as you leave. (6) There are a total of 29 questions (17 actua ...
The concepts of an atom and chemical bond in physics and chemistry
... into adjacent regions where every region contains in principle only one maximum (atomic core). As a result of such partitioning, we are able to assign uniquely a part of physical space to individual atoms and restore the concept of atom in molecule or crystal (of course such „atoms” do not have sphe ...
... into adjacent regions where every region contains in principle only one maximum (atomic core). As a result of such partitioning, we are able to assign uniquely a part of physical space to individual atoms and restore the concept of atom in molecule or crystal (of course such „atoms” do not have sphe ...
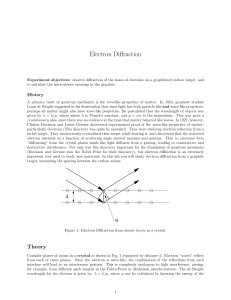
Electron Diffraction
... A primary tenet of quantum mechanics is the wavelike properties of matter. In 1924, graduate student Louis de Broglie suggested in his dissertation that since light has both particle-like and wave-like properties, perhaps all matter might also have wave-like properties. He postulated that the wavele ...
... A primary tenet of quantum mechanics is the wavelike properties of matter. In 1924, graduate student Louis de Broglie suggested in his dissertation that since light has both particle-like and wave-like properties, perhaps all matter might also have wave-like properties. He postulated that the wavele ...
The Atomic Theory
... spread very far apart and move quickly. This is why a gas has no definite shape of volume. ...
... spread very far apart and move quickly. This is why a gas has no definite shape of volume. ...
Ionic Bonding
... When a positive ion is formed from an atom, electrons are always lost first from the subshell with the largest principle quantum number A transition metal always loses electrons first from the higher 's' subshell, before losing from the underlying 'd' subshell. Iron will not have a noble gas core (i ...
... When a positive ion is formed from an atom, electrons are always lost first from the subshell with the largest principle quantum number A transition metal always loses electrons first from the higher 's' subshell, before losing from the underlying 'd' subshell. Iron will not have a noble gas core (i ...
Spectroscopy
... The constant R is called the Rydberg constant. Planck’s constant is h; the speed of light is c. In the Bohr Model, the Rydberg constant is predicted to be R 1.0975 x10 7 m 1 . We shall determine R experimentally by observing the emission spectrum of Hydrogen. The four bright spectral lines in the ...
... The constant R is called the Rydberg constant. Planck’s constant is h; the speed of light is c. In the Bohr Model, the Rydberg constant is predicted to be R 1.0975 x10 7 m 1 . We shall determine R experimentally by observing the emission spectrum of Hydrogen. The four bright spectral lines in the ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.

![科目名 Course Title Extreme Laser Physics [極限レーザー物理E] 講義](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003538965_1-4c9ae3641327c1116053c260a01760fe-300x300.png)