General and Organic Chemistry Review Primer
... For many elements, an electron configuration also reveals how many valence electrons there are. Valence electrons, the electrons in the s and p orbitals of the outermost energy level, determine the element’s chemistry (i.e., how it will react with other elements). For example, oxygen atoms with an e ...
... For many elements, an electron configuration also reveals how many valence electrons there are. Valence electrons, the electrons in the s and p orbitals of the outermost energy level, determine the element’s chemistry (i.e., how it will react with other elements). For example, oxygen atoms with an e ...
Notes for powerpoint and worksheets PDF
... The identity of an atom is determined by the number of ______________________ in the nucleus BUT, compounds form due to the interactions between ______________________ How are Electrons Involved? I. Either ________________________________________________________ Using the Periodic Table, we can ...
... The identity of an atom is determined by the number of ______________________ in the nucleus BUT, compounds form due to the interactions between ______________________ How are Electrons Involved? I. Either ________________________________________________________ Using the Periodic Table, we can ...
Tellurium
... predicted by VSEPR theory because of the lack of interactions • This anomaly for organotellurium trihalides arises because of the halide group bonded to the tellurium • As well as the lack of electronegative species on the organic group ...
... predicted by VSEPR theory because of the lack of interactions • This anomaly for organotellurium trihalides arises because of the halide group bonded to the tellurium • As well as the lack of electronegative species on the organic group ...
Wave Particle Duality
... cannot know both the position and the momentum of an electron at a given time. Rather than give exact location of an electron, the quantum model only gives the probability that an electron will be in a particular spot. The area where there is a high probability of finding an electron is called the e ...
... cannot know both the position and the momentum of an electron at a given time. Rather than give exact location of an electron, the quantum model only gives the probability that an electron will be in a particular spot. The area where there is a high probability of finding an electron is called the e ...
Chemistry 1. The Periodic Table displays the
... how to use the Periodic Table to identify the lanthanides and actinides, and transactinide elements, and know that the transuranium elements were man made how to relate the position of an element in the periodic table to its quantum electron configuration, and reactivity with other elements in the t ...
... how to use the Periodic Table to identify the lanthanides and actinides, and transactinide elements, and know that the transuranium elements were man made how to relate the position of an element in the periodic table to its quantum electron configuration, and reactivity with other elements in the t ...
Plasmons in a superlattice in a parabolic quantum well M. Sundaram
... edge mass. As E F moves up the miniband and into the minigap, nonparabolicity effects become important, m * increases, the main resonance frequency drops dramatically, strong satellite peaks appear, and the resonance is expected to depend on the number of electrons (n s ) in the well. The theorem is ...
... edge mass. As E F moves up the miniband and into the minigap, nonparabolicity effects become important, m * increases, the main resonance frequency drops dramatically, strong satellite peaks appear, and the resonance is expected to depend on the number of electrons (n s ) in the well. The theorem is ...
Physics Today
... L = nħ, with n = 1, 2, 3, . . . . Introducing that quantum constraint into classical expressions, Bohr derived the radii ρn = (n2/Z)a0 and energies En = −(Z2/2n2)(e2/a0) of the allowed orbits for a oneelectron atom. The quantity a0 = ħ2/me2 was soon christened the Bohr radius; ħ = h/2π is the reduce ...
... L = nħ, with n = 1, 2, 3, . . . . Introducing that quantum constraint into classical expressions, Bohr derived the radii ρn = (n2/Z)a0 and energies En = −(Z2/2n2)(e2/a0) of the allowed orbits for a oneelectron atom. The quantity a0 = ħ2/me2 was soon christened the Bohr radius; ħ = h/2π is the reduce ...
List Definition Chemistry - A Level / Secondary Chemistry Tuition
... in the lab, enzymes are able to selectively produce one optical isomer in the body. A transition element is a d-block element which is able to form one or more stable ions with ...
... in the lab, enzymes are able to selectively produce one optical isomer in the body. A transition element is a d-block element which is able to form one or more stable ions with ...
Ch 02.01-03: Atoms Molecules Ions
... 2. All atoms of a given element have the same mass and other properties that distinguish them from the atoms of other elements. 3. Atoms combine in simple, whole-number ratios to form compounds. 4. Atoms of one element cannot change into atoms of another element. In a chemical reaction, atoms only c ...
... 2. All atoms of a given element have the same mass and other properties that distinguish them from the atoms of other elements. 3. Atoms combine in simple, whole-number ratios to form compounds. 4. Atoms of one element cannot change into atoms of another element. In a chemical reaction, atoms only c ...
Midterm Review Teacher Answer Key December 21, 2011 `see
... State, in terms of the number of electron shells, why the radius of a strontium atom in the ground state is larger than the radius of a magnesium atom in the ground state. [1] A strontium atom in the ground state has two more electron shells than a magnesium atom in the ground state. As a result, a ...
... State, in terms of the number of electron shells, why the radius of a strontium atom in the ground state is larger than the radius of a magnesium atom in the ground state. [1] A strontium atom in the ground state has two more electron shells than a magnesium atom in the ground state. As a result, a ...
Chapter 4 The Structure of Matter
... or ions within a substance. • a. Two terms are used to specify the relative positions of atoms to each other in a compound. − (1) Bond length - gives the distance between the two nuclei of the atoms − (2) Bond angles tell how these atoms are oriented when you have three or more atoms in the compound ...
... or ions within a substance. • a. Two terms are used to specify the relative positions of atoms to each other in a compound. − (1) Bond length - gives the distance between the two nuclei of the atoms − (2) Bond angles tell how these atoms are oriented when you have three or more atoms in the compound ...
Document
... track of valence electrons. • How to write them? • Write the symbol - it represents the nucleus and inner (core) electrons • Put one dot for each valence electron (8 maximum) • They don’t pair up until they have to (Hund’s rule) ...
... track of valence electrons. • How to write them? • Write the symbol - it represents the nucleus and inner (core) electrons • Put one dot for each valence electron (8 maximum) • They don’t pair up until they have to (Hund’s rule) ...
Dr. Audrey Lugo`s AP Chemistry Course Syllabus
... Help others when they need it; ask for my help by raising your hand. We learn when we listen, take notes, and participate in all discussions and activities. Never let giving up be an option. Take joy in your accomplishments and skills more than in your grades. Honesty in your work, speech, and life ...
... Help others when they need it; ask for my help by raising your hand. We learn when we listen, take notes, and participate in all discussions and activities. Never let giving up be an option. Take joy in your accomplishments and skills more than in your grades. Honesty in your work, speech, and life ...
Wave Function Microscopy of Quasibound Atomic States
... visualizing electron standing waves corresponding to quasidiscrete electronic states of an atom. Photoionization is very different from photodetachment since photoionized electrons interact with both the electric field and the Coulomb field of the residual ion and neither field can be considered as ...
... visualizing electron standing waves corresponding to quasidiscrete electronic states of an atom. Photoionization is very different from photodetachment since photoionized electrons interact with both the electric field and the Coulomb field of the residual ion and neither field can be considered as ...
Properties of electrons - VGTU Elektronikos fakultetas
... sets of quantum numbers? 2. Find the electronic structures of Si and Ge atoms. 3. A hydrogen atom is excited from a state with n =1 to one with n = 4. Calculate and display on the energy-level diagram the different photon energies that may be emitted if the atom returns to its ground state. 4. The h ...
... sets of quantum numbers? 2. Find the electronic structures of Si and Ge atoms. 3. A hydrogen atom is excited from a state with n =1 to one with n = 4. Calculate and display on the energy-level diagram the different photon energies that may be emitted if the atom returns to its ground state. 4. The h ...
P081
... level. As a result of research upon, metal adsorption CNTs involve the charge transfer such like our previous study using Platinum atom are also interested in the study of more complex system applying for nano devices. In this study, we investigate the transport properties of (5,5) metallic single w ...
... level. As a result of research upon, metal adsorption CNTs involve the charge transfer such like our previous study using Platinum atom are also interested in the study of more complex system applying for nano devices. In this study, we investigate the transport properties of (5,5) metallic single w ...
Properties of Ionic and Covalent Substances
... Atoms will form bonds with other atoms in an attempt to obtain a stable valence electron shell. To obtain a stable valence shell atoms can either gain or lose electrons or share electrons. Ionic Compounds If an atom gains electrons it forms a negative ion (anion), and if it loses electrons it forms ...
... Atoms will form bonds with other atoms in an attempt to obtain a stable valence electron shell. To obtain a stable valence shell atoms can either gain or lose electrons or share electrons. Ionic Compounds If an atom gains electrons it forms a negative ion (anion), and if it loses electrons it forms ...
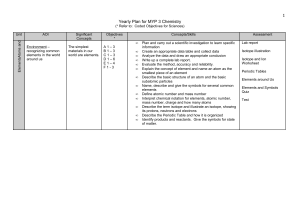
Yearly Plan for MYP 1 Science
... Analyze the data and draw an appropriate conclusion Write up a complete lab report. Evaluate the method, accuracy and reliability. Explain the concept of element and name an atom as the smallest piece of an element Describe the basic structure of an atom and the basic subatomic particles Name, descr ...
... Analyze the data and draw an appropriate conclusion Write up a complete lab report. Evaluate the method, accuracy and reliability. Explain the concept of element and name an atom as the smallest piece of an element Describe the basic structure of an atom and the basic subatomic particles Name, descr ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.