Slide 1 - Southwest High School
... will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students except by instructors using the accompanying text in their classes. All recipients of this work are expected to abide by these restrictions and to honor the intended ...
... will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students except by instructors using the accompanying text in their classes. All recipients of this work are expected to abide by these restrictions and to honor the intended ...
Chapter 27
... p2/2m, they cannot have the same kinetic energy. Because the kinetic energy is the only type of energy an isolated particle can have, and we have argued that the particles have different energies, Equation 27.15 tells us that the particles do not have the same ...
... p2/2m, they cannot have the same kinetic energy. Because the kinetic energy is the only type of energy an isolated particle can have, and we have argued that the particles have different energies, Equation 27.15 tells us that the particles do not have the same ...
Lecture 17: Bohr Model of the Atom
... existence of the electron in fixed energy levels could be though of as a “standing wave”. ...
... existence of the electron in fixed energy levels could be though of as a “standing wave”. ...
Electrons in Atoms
... electromagnetic radiation. Other examples include X rays, radio waves, and microwaves. All waves can be characterized by their wavelength, amplitude, frequency, and . The shortest distance between equivalent points on a continuous wave is ...
... electromagnetic radiation. Other examples include X rays, radio waves, and microwaves. All waves can be characterized by their wavelength, amplitude, frequency, and . The shortest distance between equivalent points on a continuous wave is ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿
... Results of Mass Spectrometry In atomic physics,mass spectrometers are primarily of interest as instruments for analysing the isotopic composition of chemical elements. An element often has several isotopes,for example chlorine:an isotope with mass number 35 occurs with an abundance of 75.4%;the oth ...
... Results of Mass Spectrometry In atomic physics,mass spectrometers are primarily of interest as instruments for analysing the isotopic composition of chemical elements. An element often has several isotopes,for example chlorine:an isotope with mass number 35 occurs with an abundance of 75.4%;the oth ...
Bohr Model of the Atom
... Neils Bohr thought that Rutherford’s model had merit, but needed to include some of the newly developing quantum theory to make it work (Bohr studied in Rutherford’s lab in 1912) Planck and Einstein had shown that the energy of oscillating charges must change in discrete amounts. Einstein argued tha ...
... Neils Bohr thought that Rutherford’s model had merit, but needed to include some of the newly developing quantum theory to make it work (Bohr studied in Rutherford’s lab in 1912) Planck and Einstein had shown that the energy of oscillating charges must change in discrete amounts. Einstein argued tha ...
Modern Physics Lesson 3
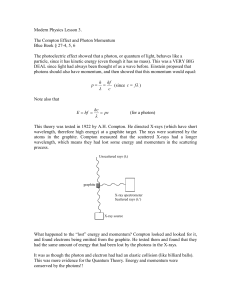
... Conclusion: A photon is a particle of light that has energy and momentum. However, photons have no mass and travel at the speed of light, c. deBroglie Wavelength Louis deBroglie proposed in 1923 that if waves behave like particles, then particles should also behave like waves! This was the beginnin ...
... Conclusion: A photon is a particle of light that has energy and momentum. However, photons have no mass and travel at the speed of light, c. deBroglie Wavelength Louis deBroglie proposed in 1923 that if waves behave like particles, then particles should also behave like waves! This was the beginnin ...
Lec-22_Strachan
... Electrons collected at C and passing through the ammeter create a current in the circuit C is maintained at a positive potential by the power supply No electrons are emitted if the incident light frequency is below some cutoff frequency that is characteristic of the material being illuminated ...
... Electrons collected at C and passing through the ammeter create a current in the circuit C is maintained at a positive potential by the power supply No electrons are emitted if the incident light frequency is below some cutoff frequency that is characteristic of the material being illuminated ...
Rdg: Electron Configuration
... The number of sublevels that an energy level can contain is equal to the principle quantum number of that level. So, for example, the second energy level would have two sublevels, and the third energy level would have three sublevels. The first sublevel is called an s sublevel. The second sublevel i ...
... The number of sublevels that an energy level can contain is equal to the principle quantum number of that level. So, for example, the second energy level would have two sublevels, and the third energy level would have three sublevels. The first sublevel is called an s sublevel. The second sublevel i ...
III. Quantum Model of the Atom
... A. Electrons as Waves • Louis de Broglie (1924) – Applied wave-particle theory to e– e- exhibit wave properties QUANTIZED WAVELENGTHS ...
... A. Electrons as Waves • Louis de Broglie (1924) – Applied wave-particle theory to e– e- exhibit wave properties QUANTIZED WAVELENGTHS ...
Structure of atoms and solids
... their atoms. We shall see how quantum theory of the atom can be extended to account for the electrical properties of solids and how this has led to the computer, mobile phones and the internet revolution now happening. The basic building blocks (computer chips, microchips, microprocessors, etc) perf ...
... their atoms. We shall see how quantum theory of the atom can be extended to account for the electrical properties of solids and how this has led to the computer, mobile phones and the internet revolution now happening. The basic building blocks (computer chips, microchips, microprocessors, etc) perf ...
File
... a. deflection of alpha particles b. atomic absorption spectra c. atomic emission spectra d. the deflection of cathode rays by an electric field e. absorption of beta particles 3. Rutherford's gold foil experiment showed that the atom is mostly empty space because a. some alpha particles were reflect ...
... a. deflection of alpha particles b. atomic absorption spectra c. atomic emission spectra d. the deflection of cathode rays by an electric field e. absorption of beta particles 3. Rutherford's gold foil experiment showed that the atom is mostly empty space because a. some alpha particles were reflect ...
Lecture 2 - Tufts University
... Properties of atoms •Atoms consist of subatomic structures. For this course, we think of atoms consisting of a nucleus (positively charged) surrounded by electrons (negatively charged) ...
... Properties of atoms •Atoms consist of subatomic structures. For this course, we think of atoms consisting of a nucleus (positively charged) surrounded by electrons (negatively charged) ...
Problem set 3
... 1. Recall that the angular momentum raising operator is L+ = ~eiφ (∂θ + i cot θ ∂φ ). Use this to find L− . 2. Use the above formulae for L± to find the coordinate representation of the angular momentum basis states Y11 , Y10 and Y1,−1 up to normalization. 3. Write out the 9 equations summarized in ...
... 1. Recall that the angular momentum raising operator is L+ = ~eiφ (∂θ + i cot θ ∂φ ). Use this to find L− . 2. Use the above formulae for L± to find the coordinate representation of the angular momentum basis states Y11 , Y10 and Y1,−1 up to normalization. 3. Write out the 9 equations summarized in ...
6.1 Coulomb interaction energy among charged particles in an atom
... Atomic orbitals of this form also occur in approximate treatments of electronic states in manyelectron atoms such as He, Li, etc, or their ions. The only difference in the latter is in the explicit expression for the radial function R; its form depends on the atom or ion under study, especially on i ...
... Atomic orbitals of this form also occur in approximate treatments of electronic states in manyelectron atoms such as He, Li, etc, or their ions. The only difference in the latter is in the explicit expression for the radial function R; its form depends on the atom or ion under study, especially on i ...
Chapter Five: Many electron atom
... would show a continuous distribution of paths. The photographic plate in the Stern-Gerlach experiment would have shown a continuous distribution of impact positions. • What was observed was quite different. The electrons were deflected either up or down by a constant amount, in roughly equal numbers ...
... would show a continuous distribution of paths. The photographic plate in the Stern-Gerlach experiment would have shown a continuous distribution of impact positions. • What was observed was quite different. The electrons were deflected either up or down by a constant amount, in roughly equal numbers ...
Physics 228 Today: Atomic Structure Bohr Model of H Atom
... atom they might form standing waves, or resonances, just like standing waves on a string: ...
... atom they might form standing waves, or resonances, just like standing waves on a string: ...
Midterm Review
... Define the law of multiple proportions and provide examples of two compounds that illustrate the concept. ...
... Define the law of multiple proportions and provide examples of two compounds that illustrate the concept. ...
Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms
... History of the Atomic Model • John Dalton (Late 1700’s) ...
... History of the Atomic Model • John Dalton (Late 1700’s) ...
Atomic orbital
An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of either one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus. The term may also refer to the physical region or space where the electron can be calculated to be present, as defined by the particular mathematical form of the orbital.Each orbital in an atom is characterized by a unique set of values of the three quantum numbers n, ℓ, and m, which respectively correspond to the electron's energy, angular momentum, and an angular momentum vector component (the magnetic quantum number). Any orbital can be occupied by a maximum of two electrons, each with its own spin quantum number. The simple names s orbital, p orbital, d orbital and f orbital refer to orbitals with angular momentum quantum number ℓ = 0, 1, 2 and 3 respectively. These names, together with the value of n, are used to describe the electron configurations of atoms. They are derived from the description by early spectroscopists of certain series of alkali metal spectroscopic lines as sharp, principal, diffuse, and fundamental. Orbitals for ℓ > 3 continue alphabetically, omitting j (g, h, i, k, …).Atomic orbitals are the basic building blocks of the atomic orbital model (alternatively known as the electron cloud or wave mechanics model), a modern framework for visualizing the submicroscopic behavior of electrons in matter. In this model the electron cloud of a multi-electron atom may be seen as being built up (in approximation) in an electron configuration that is a product of simpler hydrogen-like atomic orbitals. The repeating periodicity of the blocks of 2, 6, 10, and 14 elements within sections of the periodic table arises naturally from the total number of electrons that occupy a complete set of s, p, d and f atomic orbitals, respectively.