Learning Goals
... 2. Light as a Particle- why believe idea that there are particle and wave like properties to objects, role of probability in this interpretation • Write down the mathematical description of a classical electromagnetic wave, and relate the terms in the expression to the velocity, wavelength, and freq ...
... 2. Light as a Particle- why believe idea that there are particle and wave like properties to objects, role of probability in this interpretation • Write down the mathematical description of a classical electromagnetic wave, and relate the terms in the expression to the velocity, wavelength, and freq ...
File
... The electronic charge of an atom All elements in order A unit of energy Positive or negative charge on an atom or group of atoms Atoms of the same element with different atomic mass A negatively charged particle A positively charged particle An atomic particle with no charge Used Boyle’s information ...
... The electronic charge of an atom All elements in order A unit of energy Positive or negative charge on an atom or group of atoms Atoms of the same element with different atomic mass A negatively charged particle A positively charged particle An atomic particle with no charge Used Boyle’s information ...
document
... You need to keep track of how you are doing in the class and take action if you fall behind or have trouble with the material. A. Fellow students - meet others in the class. Even though you and the other student may be perplexed about a subject, you will find that talking together in the language of ...
... You need to keep track of how you are doing in the class and take action if you fall behind or have trouble with the material. A. Fellow students - meet others in the class. Even though you and the other student may be perplexed about a subject, you will find that talking together in the language of ...
o Schrödinger equation for o Two-electron atoms. o Multi
... There are two electrons => S = s1+ s2 = 0 or 1. S = 0 states are called singlets because they only have one ms value. S = 1 states are called triplets as ms = +1, 0, -1. ...
... There are two electrons => S = s1+ s2 = 0 or 1. S = 0 states are called singlets because they only have one ms value. S = 1 states are called triplets as ms = +1, 0, -1. ...
Pretest 4.3 2008
... concentrated in a nucleus and the negative charges surround the nucleus. c. According to Rutherford, the atom is a positive sphere in which the negative charges are ...
... concentrated in a nucleus and the negative charges surround the nucleus. c. According to Rutherford, the atom is a positive sphere in which the negative charges are ...
2008 Midterm Multiple Choice
... A) a mixture of elements B) a single element C) a mixture of compounds D) a single compound Based on the Selected Radioisotopes chemistry reference table, which radioisotope is best represented by the graph? A) 32P C) 222Rn B) 131I ...
... A) a mixture of elements B) a single element C) a mixture of compounds D) a single compound Based on the Selected Radioisotopes chemistry reference table, which radioisotope is best represented by the graph? A) 32P C) 222Rn B) 131I ...
Advanced electronic bonding and how these affect molecular shapes
... electrons whirling through circular orbits. • Rather, we now know we cannot pinpoint an electron’s exact location. • This is because of the Heisenberg uncertainty principle. An electron cannot be pinpointed as the photon striking it will cause it to change momentum and position, so you will never be ...
... electrons whirling through circular orbits. • Rather, we now know we cannot pinpoint an electron’s exact location. • This is because of the Heisenberg uncertainty principle. An electron cannot be pinpointed as the photon striking it will cause it to change momentum and position, so you will never be ...
A1985ANN1800001
... Historically, there have been two main approaches to a quantum-mechanical description of chemical bonding in a molecule. One, popularized ...
... Historically, there have been two main approaches to a quantum-mechanical description of chemical bonding in a molecule. One, popularized ...
Revision topic 1-3
... the wavelengths or frequencies of visible light. An absorption spectrum is produced where some colours are missing ( those that are absorbed by hydrogen). A corresponding emission line spectrum has only certain wavelegths or frequencies of visible light.The lines correspond to the light of particula ...
... the wavelengths or frequencies of visible light. An absorption spectrum is produced where some colours are missing ( those that are absorbed by hydrogen). A corresponding emission line spectrum has only certain wavelegths or frequencies of visible light.The lines correspond to the light of particula ...
Electrons and Atoms
... • All electromagnetic radiation travels at this same rate when measured in a vacuum ...
... • All electromagnetic radiation travels at this same rate when measured in a vacuum ...
16.12.2013 1 Chapter 6 The Periodic Table and Atomic Structure
... The Wave Nature of Light • Wavelength, , is the distance between two corresponding points on a wave. • Amplitude is the size or “height” of a wave. • Frequency, , is the number of cycles of the wave passing a ...
... The Wave Nature of Light • Wavelength, , is the distance between two corresponding points on a wave. • Amplitude is the size or “height” of a wave. • Frequency, , is the number of cycles of the wave passing a ...
AP Chapter 7, 8 review
... • Account for each of the following in terms of principles of atom structure, including the number, properties, and arrangements of subatomic particles. • (a) The second ionization energy of sodium is about three times greater than the second ionization energy of magnesium. • (b) The difference betw ...
... • Account for each of the following in terms of principles of atom structure, including the number, properties, and arrangements of subatomic particles. • (a) The second ionization energy of sodium is about three times greater than the second ionization energy of magnesium. • (b) The difference betw ...
Quantum Mechanics
... The number n is called principal quantum number. So the energy of the electron is quantized and this result is the consequence of Schrödinger equation. Although the energies of the hydrogen atom states can be described by the single quantum number n, the wave functions describing these states requir ...
... The number n is called principal quantum number. So the energy of the electron is quantized and this result is the consequence of Schrödinger equation. Although the energies of the hydrogen atom states can be described by the single quantum number n, the wave functions describing these states requir ...
Document
... combinations with the same energy. For hydrogen, the energy is set by n. For a given n consider all of the combinations of quantum numbers ℓ, m, and ms. Remember ℓ=0,1…n−1 and m=0,±1,±2…±2ℓ and ms=±½. How many combinations are there? A. n Before we found out about spin we determined the B. 2n number ...
... combinations with the same energy. For hydrogen, the energy is set by n. For a given n consider all of the combinations of quantum numbers ℓ, m, and ms. Remember ℓ=0,1…n−1 and m=0,±1,±2…±2ℓ and ms=±½. How many combinations are there? A. n Before we found out about spin we determined the B. 2n number ...
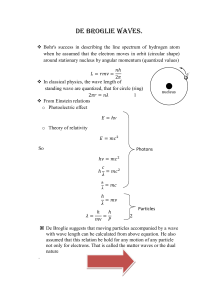
t7_photoel
... PHOTOELECTIC EFFECT PARTICLE MODEL OF LIGHT PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT EMR falling on a metal surface can eject electrons (photocurrent) Hert’z experiments – speed of radio waves (same as light) 1886-7 Hertz’s observation of the effect of a radio wave on a receiver – photoelectric effect - UV can cause el ...
... PHOTOELECTIC EFFECT PARTICLE MODEL OF LIGHT PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT EMR falling on a metal surface can eject electrons (photocurrent) Hert’z experiments – speed of radio waves (same as light) 1886-7 Hertz’s observation of the effect of a radio wave on a receiver – photoelectric effect - UV can cause el ...
Module 1 : Atomic Structure Lecture 6 : Multi-Electron Atoms
... which is being studied. Before outlining how these levels are determined, we shall describe two principles which help in understanding atomic structure. These are the Pauli exclusion principle (which is rigorously valid in all situations) and the aufbau principle (‘aufbau' means ‘building up' in Ger ...
... which is being studied. Before outlining how these levels are determined, we shall describe two principles which help in understanding atomic structure. These are the Pauli exclusion principle (which is rigorously valid in all situations) and the aufbau principle (‘aufbau' means ‘building up' in Ger ...
6.1 Organizing the Periodic Table
... • Arranged the elements into rows in order of increasing mass so that elements with similar properties were in the same column • Left empty spaces where undiscovered elements would fit ...
... • Arranged the elements into rows in order of increasing mass so that elements with similar properties were in the same column • Left empty spaces where undiscovered elements would fit ...
Atomic orbital
An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of either one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus. The term may also refer to the physical region or space where the electron can be calculated to be present, as defined by the particular mathematical form of the orbital.Each orbital in an atom is characterized by a unique set of values of the three quantum numbers n, ℓ, and m, which respectively correspond to the electron's energy, angular momentum, and an angular momentum vector component (the magnetic quantum number). Any orbital can be occupied by a maximum of two electrons, each with its own spin quantum number. The simple names s orbital, p orbital, d orbital and f orbital refer to orbitals with angular momentum quantum number ℓ = 0, 1, 2 and 3 respectively. These names, together with the value of n, are used to describe the electron configurations of atoms. They are derived from the description by early spectroscopists of certain series of alkali metal spectroscopic lines as sharp, principal, diffuse, and fundamental. Orbitals for ℓ > 3 continue alphabetically, omitting j (g, h, i, k, …).Atomic orbitals are the basic building blocks of the atomic orbital model (alternatively known as the electron cloud or wave mechanics model), a modern framework for visualizing the submicroscopic behavior of electrons in matter. In this model the electron cloud of a multi-electron atom may be seen as being built up (in approximation) in an electron configuration that is a product of simpler hydrogen-like atomic orbitals. The repeating periodicity of the blocks of 2, 6, 10, and 14 elements within sections of the periodic table arises naturally from the total number of electrons that occupy a complete set of s, p, d and f atomic orbitals, respectively.