Safety - Wando High School
... 2. 2p² Tell what each part of this configuration represents. 3. How does energy level relate to distance? 4. Write the Noble gas configuration for Selenium. 5. Give 2 examples of atoms which will gain 2 electrons to become stable. 6. Give 2 examples of atoms which will lose 2 electrons to become sta ...
... 2. 2p² Tell what each part of this configuration represents. 3. How does energy level relate to distance? 4. Write the Noble gas configuration for Selenium. 5. Give 2 examples of atoms which will gain 2 electrons to become stable. 6. Give 2 examples of atoms which will lose 2 electrons to become sta ...
Lecture_19-Energy Levels in the Bohr model of the atom
... model in which the single hydrogen electron can only be in certain definite orbits. • In the nth allowed orbit, the electron has orbital angular momentum nh/2π (see Figure on the right). • Bohr proposed that angular momentum is quantized (this will turn out to be correct in general in quantum mechan ...
... model in which the single hydrogen electron can only be in certain definite orbits. • In the nth allowed orbit, the electron has orbital angular momentum nh/2π (see Figure on the right). • Bohr proposed that angular momentum is quantized (this will turn out to be correct in general in quantum mechan ...
In 1869, Russia`s Dmitri Mendeleev and Germany`s Lothar Meyer
... the atomic number. The atomic number is not always in the same place on every periodic table but it is ALWAYS a whole number. ...
... the atomic number. The atomic number is not always in the same place on every periodic table but it is ALWAYS a whole number. ...
Metal d orbitals in an O crystal field
... In the crystal field theory (CFT) model, the spectrochemical series is an empirical result that cannot be rationalized in terms of simple point charges. ...
... In the crystal field theory (CFT) model, the spectrochemical series is an empirical result that cannot be rationalized in terms of simple point charges. ...
CHAPTER 2: THE ATOMS AND MOLECULES OF ANCIENT EARTH
... b. Reduction of CO2 by H2 forms H2CO, which is used as a building block to form organic compounds (compounds containing at least one C–C bond). (Fig. 2.13) B. For carbon to be reduced, early atmosphere must have contained CH 4, H2, and NH3 (molecules that can give up electrons). 1. Volcanic ash is k ...
... b. Reduction of CO2 by H2 forms H2CO, which is used as a building block to form organic compounds (compounds containing at least one C–C bond). (Fig. 2.13) B. For carbon to be reduced, early atmosphere must have contained CH 4, H2, and NH3 (molecules that can give up electrons). 1. Volcanic ash is k ...
Lecture 27: Quantum Physics
... given by: En nhf n= quantum number (positive integer) f = frequency of vibration of the resonators h= Planck’s constant 6.626 x 10-34 J s • Energy is quantized. • each discrete energy value represents a different quantum state, where the quantum number n specifies the quantum state. ...
... given by: En nhf n= quantum number (positive integer) f = frequency of vibration of the resonators h= Planck’s constant 6.626 x 10-34 J s • Energy is quantized. • each discrete energy value represents a different quantum state, where the quantum number n specifies the quantum state. ...
Early Atomic Models
... metals) were tested and all produced same results. Magnetic fields deflected the rays. The rays produced some chemical reactions similar to those produced by ...
... metals) were tested and all produced same results. Magnetic fields deflected the rays. The rays produced some chemical reactions similar to those produced by ...
Unit IV: Nature of Matter
... metals) were tested and all produced same results. Magnetic fields deflected the rays. The rays produced some chemical reactions similar to those produced by ...
... metals) were tested and all produced same results. Magnetic fields deflected the rays. The rays produced some chemical reactions similar to those produced by ...
1. Which of the following statements best describes the
... Which statement is correct concerning the mass differences among subatomic particles? A. ...
... Which statement is correct concerning the mass differences among subatomic particles? A. ...
Lecture 18
... A solution was proposed by Max Planck in 1900: The atoms are all radiating, absorbing and redistributing energy between themselves. Each behaves as a harmonic oscillator with discrete modes The distribution of atomic oscillator energies leads to the black-body spectrum The oscillations within atoms ...
... A solution was proposed by Max Planck in 1900: The atoms are all radiating, absorbing and redistributing energy between themselves. Each behaves as a harmonic oscillator with discrete modes The distribution of atomic oscillator energies leads to the black-body spectrum The oscillations within atoms ...
Chapter 2 cont’
... do not turn into other elements ◦ Dalton’s Atomic Theory since the number of protons determines the kind of element, the number of protons in the atom does not change in a chemical reaction however, many reactions involve transferring electrons from one atom to another ...
... do not turn into other elements ◦ Dalton’s Atomic Theory since the number of protons determines the kind of element, the number of protons in the atom does not change in a chemical reaction however, many reactions involve transferring electrons from one atom to another ...
Unit 3 Review Questions - Unit #1-0
... 37. In the ionic compound magnesium fluoride, what is the ratio of the two elements necessary so that each element obtains its octet from the transfer of electrons? 1. ? 1 magnesium : 1 fluorine 2. ? 1 magnesium : 2 fluorine 3. ? 2 magnesium : 1 fluorine 4. ? 3 magnesium : 1 fluorine ...
... 37. In the ionic compound magnesium fluoride, what is the ratio of the two elements necessary so that each element obtains its octet from the transfer of electrons? 1. ? 1 magnesium : 1 fluorine 2. ? 1 magnesium : 2 fluorine 3. ? 2 magnesium : 1 fluorine 4. ? 3 magnesium : 1 fluorine ...
Chapter 2
... Hydrogen bonds form when a hydrogen atom that is already covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is attracted to another electronegative atom. o In cells, the electronegative partners are typically nitrogen or oxygen. o Hydrogen bonds form because a polar covalent bond leaves the hydrogen atom ...
... Hydrogen bonds form when a hydrogen atom that is already covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is attracted to another electronegative atom. o In cells, the electronegative partners are typically nitrogen or oxygen. o Hydrogen bonds form because a polar covalent bond leaves the hydrogen atom ...
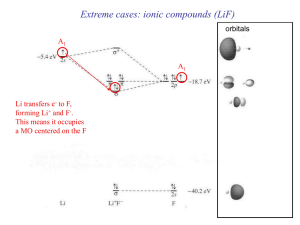
Atomic orbital
An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of either one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus. The term may also refer to the physical region or space where the electron can be calculated to be present, as defined by the particular mathematical form of the orbital.Each orbital in an atom is characterized by a unique set of values of the three quantum numbers n, ℓ, and m, which respectively correspond to the electron's energy, angular momentum, and an angular momentum vector component (the magnetic quantum number). Any orbital can be occupied by a maximum of two electrons, each with its own spin quantum number. The simple names s orbital, p orbital, d orbital and f orbital refer to orbitals with angular momentum quantum number ℓ = 0, 1, 2 and 3 respectively. These names, together with the value of n, are used to describe the electron configurations of atoms. They are derived from the description by early spectroscopists of certain series of alkali metal spectroscopic lines as sharp, principal, diffuse, and fundamental. Orbitals for ℓ > 3 continue alphabetically, omitting j (g, h, i, k, …).Atomic orbitals are the basic building blocks of the atomic orbital model (alternatively known as the electron cloud or wave mechanics model), a modern framework for visualizing the submicroscopic behavior of electrons in matter. In this model the electron cloud of a multi-electron atom may be seen as being built up (in approximation) in an electron configuration that is a product of simpler hydrogen-like atomic orbitals. The repeating periodicity of the blocks of 2, 6, 10, and 14 elements within sections of the periodic table arises naturally from the total number of electrons that occupy a complete set of s, p, d and f atomic orbitals, respectively.