
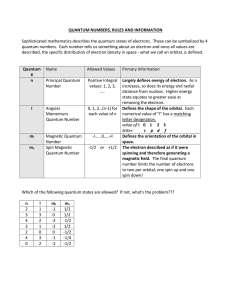
Quantum Number Table
... Sophisticated mathematics describes the quantum states of electrons. These can be symbolized by 4 quantum numbers. Each number tells us something about an electron and once all values are described, the specific distribution of electron density in space - what we call an orbital, is defined. ...
... Sophisticated mathematics describes the quantum states of electrons. These can be symbolized by 4 quantum numbers. Each number tells us something about an electron and once all values are described, the specific distribution of electron density in space - what we call an orbital, is defined. ...
PA304 QUANTUM MECHANICS
... Hamiltonian by solving the Schrödinger time-independent equation H > = E > . ...
... Hamiltonian by solving the Schrödinger time-independent equation H > = E > . ...
1.1 What has to be explained by Quantum mechanics?
... • What is: Schrödinger equation, Operator, commutator, probability function, wave function, quantum number, ...... ...
... • What is: Schrödinger equation, Operator, commutator, probability function, wave function, quantum number, ...... ...
Chapter 7 (Lecture 10) Hydrogen Atom The explanation of
... is a measure of the rotation about the z axis. ...
... is a measure of the rotation about the z axis. ...
E489: Decay of a particle with spin 0
... that the detector is placed at θ = 0 it means that one measured particle has moved up while the other has moved down. Each particle has in that case a velocity component only on the Z axis, and so the orbital angular momentum is therefore 0. Satisfaction of eq.(2) requires that the particles have op ...
... that the detector is placed at θ = 0 it means that one measured particle has moved up while the other has moved down. Each particle has in that case a velocity component only on the Z axis, and so the orbital angular momentum is therefore 0. Satisfaction of eq.(2) requires that the particles have op ...
Spin The evidence of intrinsic angular momentum or spin and its
... and therefore we expect ms to have 2s + 1 disctinct values between −s ≤ ms ≤ s. However, unlike orbital angular momentum quantum number l, the spin angular momentum quantum number can take both integer and half-integer values, s = 0, 1/2, 1, 3/2, 2, . . .. In fact, the experimental result of Stern a ...
... and therefore we expect ms to have 2s + 1 disctinct values between −s ≤ ms ≤ s. However, unlike orbital angular momentum quantum number l, the spin angular momentum quantum number can take both integer and half-integer values, s = 0, 1/2, 1, 3/2, 2, . . .. In fact, the experimental result of Stern a ...



















![ABSTRACT – Condensed Matter Physics [ORIGINAL]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/005325689_1-bd59cbe3830dc734895532d6f7679a5c-300x300.png)