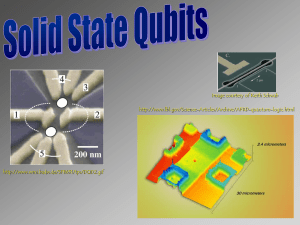
Authors:Qing Jie, Rongwei Hu, Emil Bozin, A
... spinless p-wave superconductor in one dimension, emphasizing how this model emerges from more realistic settings based on semiconductor nanowires. We show that the flux periodicity of the Josephson current provides signatures of the topological phase transition and the emergence of Majorana fermions ...
... spinless p-wave superconductor in one dimension, emphasizing how this model emerges from more realistic settings based on semiconductor nanowires. We show that the flux periodicity of the Josephson current provides signatures of the topological phase transition and the emergence of Majorana fermions ...
pptx - Harvard Condensed Matter Theory group
... Example of topologically non-trivial evolution operator and relation to Thouless topological pumping Spin ½ particle in 1d lattice. Spin down particles do not move. Spin up particles move by one lattice site per period ...
... Example of topologically non-trivial evolution operator and relation to Thouless topological pumping Spin ½ particle in 1d lattice. Spin down particles do not move. Spin up particles move by one lattice site per period ...
Quantum-mechanical aspects of magnetic resonance imaging
... A volume element of the sample is defined as a voxel. Having placed a transmitting antenna in the direction of maximum emission to the voxel in the vertical plane and changing the transmission frequency, when we emit the frequency of precession (Larmor frequency), the nuclei are able to absorb energ ...
... A volume element of the sample is defined as a voxel. Having placed a transmitting antenna in the direction of maximum emission to the voxel in the vertical plane and changing the transmission frequency, when we emit the frequency of precession (Larmor frequency), the nuclei are able to absorb energ ...
Effective Hamiltonian in the Problem of a
... introduced some time ago to describe the large superparamagnetic ”spin clusters” which are believed to exist in many disordered magnets at low temperature, such as Si : P near the metal-insulator transition [9], or ”giant magnetic polarons” [10]. Similar spin clusters exist in ”quantum spin glasses” ...
... introduced some time ago to describe the large superparamagnetic ”spin clusters” which are believed to exist in many disordered magnets at low temperature, such as Si : P near the metal-insulator transition [9], or ”giant magnetic polarons” [10]. Similar spin clusters exist in ”quantum spin glasses” ...