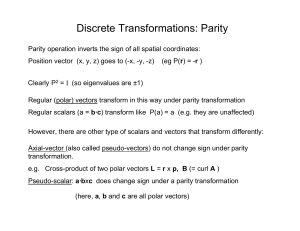
No Slide Title - WordPress.com
... we would have to magnify it to around 3,000,000,000 times its normal size ...
... we would have to magnify it to around 3,000,000,000 times its normal size ...
XXXXXX Department/Division/Office - Physics
... E951, "An R&D Program for Targetry and Capture at a Muon Collider Source": "We agree that the targeting experiment could go forward more or less as proposed subject to the suggestions made below.” [MUTAC report dated August 27, 1999] MCOG has accepted this recommendation and will endorse the carryin ...
... E951, "An R&D Program for Targetry and Capture at a Muon Collider Source": "We agree that the targeting experiment could go forward more or less as proposed subject to the suggestions made below.” [MUTAC report dated August 27, 1999] MCOG has accepted this recommendation and will endorse the carryin ...
Investigating Freezing Point Depression and Cirrus Cloud
... Homogeneous freezing and melting experiments were performed using several different concentrations of aqueous ammonium sulfate particles. The results of the experiments are shown in Figure 1. In theory, when the aerosol particles are pure water (aw = 1), they should freeze at approximately 235 K.3 Th ...
... Homogeneous freezing and melting experiments were performed using several different concentrations of aqueous ammonium sulfate particles. The results of the experiments are shown in Figure 1. In theory, when the aerosol particles are pure water (aw = 1), they should freeze at approximately 235 K.3 Th ...
Quantum Monte Carlo Methods Chapter 14
... words? I believe it is the atomic hypothesis (or atomic fact, or whatever you wish to call it) that all things are made of atoms, little particles that move around in perpetual motion, attracting each other when they are a little distance apart, but repelling upon being squeezed into one another. In ...
... words? I believe it is the atomic hypothesis (or atomic fact, or whatever you wish to call it) that all things are made of atoms, little particles that move around in perpetual motion, attracting each other when they are a little distance apart, but repelling upon being squeezed into one another. In ...
Open Structure: Ontology Repair Plan based on Atomic Modeling
... stuff represents function subject to evolution (V is stuff ). stuff ranges over a type δ of d’s (like V ranges over the type dis of distances r ’s). stuff ’s domain contains a cut-off point cop (like V ’s domain contains R). K is constant (like all other quantities remain constant throughtout V ’s e ...
... stuff represents function subject to evolution (V is stuff ). stuff ranges over a type δ of d’s (like V ranges over the type dis of distances r ’s). stuff ’s domain contains a cut-off point cop (like V ’s domain contains R). K is constant (like all other quantities remain constant throughtout V ’s e ...
surface chemistry - einstein classes
... carry the same charge while the dispersion medium has an equal but opposite charge with the result the system as a whole is electrically natural. Colloidal particles having similar charge, repel each other, and do not combine to form bigger particles and thus solution is stable and particles do not ...
... carry the same charge while the dispersion medium has an equal but opposite charge with the result the system as a whole is electrically natural. Colloidal particles having similar charge, repel each other, and do not combine to form bigger particles and thus solution is stable and particles do not ...
The Atom - Urantia Foundation
... (Note: atoms can gain or loss electrons making the element an ion. This condition will be addressed later in this paper. The number of neutrons can vary and will also be discussed later in the paper). Hydrogen (H) has 1 proton and 1 electron and can be called atom #1. Helium (He) has 2 protons and 2 ...
... (Note: atoms can gain or loss electrons making the element an ion. This condition will be addressed later in this paper. The number of neutrons can vary and will also be discussed later in the paper). Hydrogen (H) has 1 proton and 1 electron and can be called atom #1. Helium (He) has 2 protons and 2 ...
HEADING 1
... apply Newton’s Second Law to numerical and non-numerical problems including weight problems and the solution of motion problems ...
... apply Newton’s Second Law to numerical and non-numerical problems including weight problems and the solution of motion problems ...
Transport, Noise, and Conservation in the Electron Gas: Frederick Green
... distribution fk (r, t) from its steady-state ensemble average. The same external stochastic processes 3 act on the channel both at equilibrium and when it is driven by an injected current (or by a battery-generated EMF). Let ∆N ≡ kB T ∂N/∂µ be the mean-square thermal number fluctuation. Then Gauss’ ...
... distribution fk (r, t) from its steady-state ensemble average. The same external stochastic processes 3 act on the channel both at equilibrium and when it is driven by an injected current (or by a battery-generated EMF). Let ∆N ≡ kB T ∂N/∂µ be the mean-square thermal number fluctuation. Then Gauss’ ...
1 - VideoLectures.NET
... Understand the detector and the Standard Model Backgrounds Establish an excess Discover a signal compatible with supersymmetry Measure sparticle masses Measure sparticle production cross sections, branching ratios, couplings Look for more difficult sparticle signatures hidden in the data Is it rea ...
... Understand the detector and the Standard Model Backgrounds Establish an excess Discover a signal compatible with supersymmetry Measure sparticle masses Measure sparticle production cross sections, branching ratios, couplings Look for more difficult sparticle signatures hidden in the data Is it rea ...
Electron scattering

Electron scattering occurs when electrons are deviated from their original trajectory. This is due to the electrostatic forces within matter interaction or, if an external magnetic field is present, the electron may be deflected by the Lorentz force. This scattering typically happens with solids such as metals, semiconductors and insulators; and is a limiting factor in integrated circuits and transistors.The application of electron scattering is such that it can be used as a high resolution microscope for hadronic systems, that allows the measurement of the distribution of charges for nucleons and nuclear structure. The scattering of electrons has allowed us to understand that protons and neutrons are made up of the smaller elementary subatomic particles called quarks.Electrons may be scattered through a solid in several ways:Not at all: no electron scattering occurs at all and the beam passes straight through.Single scattering: when an electron is scattered just once.Plural scattering: when electron(s) scatter several times.Multiple scattering: when electron(s) scatter very many times over.The likelihood of an electron scattering and the proliferance of the scattering is a probability function of the specimen thickness to the mean free path.