Close-coupling study of rotational energy transfer of CO(v=2) by
... sudden (IOS) approximation calculations using the Heijmen et al. potential. To reduce the computational expenses, the CC calculations were restricted to vibrational level v = 0 and the IOS approximation was used for v = 1 − 6. Florian et al. [17] investigated rotational relaxation in ultracold colli ...
... sudden (IOS) approximation calculations using the Heijmen et al. potential. To reduce the computational expenses, the CC calculations were restricted to vibrational level v = 0 and the IOS approximation was used for v = 1 − 6. Florian et al. [17] investigated rotational relaxation in ultracold colli ...
Metal-Ligand and Metal-Metal Bonding Core Module 4 RED
... higher energy starting orbital character). When we talk about splitting of metal ‘d-orbitals’ in crystal field theory we are ignoring the ligand character that is present in some of the ‘d-orbitals’, however it is still a good first approximation and the relative energies between d-orbitals are corr ...
... higher energy starting orbital character). When we talk about splitting of metal ‘d-orbitals’ in crystal field theory we are ignoring the ligand character that is present in some of the ‘d-orbitals’, however it is still a good first approximation and the relative energies between d-orbitals are corr ...
Плеханов В
... appears in difference of saturation vapor pressure in liquid-vapor equilibrium state. The α-factors were estimated for equilibrium evaporation of С2Н6, С2Н4, СН3ОН, С3Н8О, СН3С1, ССl4, С6Н6 [13]. Isotope-selective processes by sorption of Cu and Zn on the amorphous ferric hydroxide are studied exper ...
... appears in difference of saturation vapor pressure in liquid-vapor equilibrium state. The α-factors were estimated for equilibrium evaporation of С2Н6, С2Н4, СН3ОН, С3Н8О, СН3С1, ССl4, С6Н6 [13]. Isotope-selective processes by sorption of Cu and Zn on the amorphous ferric hydroxide are studied exper ...
Viscosity of a nucleonic fluid
... The is then related to the number density , mass of a fluid particle m , mean speed ...
... The is then related to the number density , mass of a fluid particle m , mean speed ...
Document
... Most of the time the hadrons ooze so that we will not duplicate too much of the through each other andwork fall apart (i.e.who are similarly analyzing of others no hard scattering). The outgoing various models (e.g. constituent interchange particles continue in roughly the same model, multiperiphe ...
... Most of the time the hadrons ooze so that we will not duplicate too much of the through each other andwork fall apart (i.e.who are similarly analyzing of others no hard scattering). The outgoing various models (e.g. constituent interchange particles continue in roughly the same model, multiperiphe ...
Computational Study of protonation of ozone
... In the course of research of ozonation was experimentally found anomalous change in pH from 6.7 to 18 by passing the ozone-oxygen mixture through distilled water [3, 4]. In discussing of the observed phenomena, it was hypothesized that the pH of distilled water is increased not only due to the forma ...
... In the course of research of ozonation was experimentally found anomalous change in pH from 6.7 to 18 by passing the ozone-oxygen mixture through distilled water [3, 4]. In discussing of the observed phenomena, it was hypothesized that the pH of distilled water is increased not only due to the forma ...
NorwayWN.5
... reactions within a coherent framework is an important goal. • Ab-initio methods, continuum shell model, and modern mean field theories allow for the consistent treatment of open channels, thus linking the description of bound and unbound nuclear states and direct reactions. • The battleground in thi ...
... reactions within a coherent framework is an important goal. • Ab-initio methods, continuum shell model, and modern mean field theories allow for the consistent treatment of open channels, thus linking the description of bound and unbound nuclear states and direct reactions. • The battleground in thi ...
TN156 Understanding and Interpreting Particle Siz
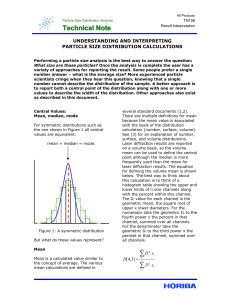
... distribution width is to normalize the standard deviation through division by the mean. This is the Coefficient of Variation (COV) (although it may also be referred to as the relative standard deviation, or RSD). Although included in HORIBA laser diffraction software this value is seldom used as oft ...
... distribution width is to normalize the standard deviation through division by the mean. This is the Coefficient of Variation (COV) (although it may also be referred to as the relative standard deviation, or RSD). Although included in HORIBA laser diffraction software this value is seldom used as oft ...
A Formal Cause Beyond Space and Time
... and is absorbed and emitted continuously by bodies. Planck, nevertheless, does not intend to question the concept of wave and the continuity of space. His law demonstrates that energy is only absorbed and emitted as discrete packets, but energy does not travel in space in the form of particles. The ...
... and is absorbed and emitted continuously by bodies. Planck, nevertheless, does not intend to question the concept of wave and the continuity of space. His law demonstrates that energy is only absorbed and emitted as discrete packets, but energy does not travel in space in the form of particles. The ...
ELECTRONIC PROPERTIES OF GaAs AND HUBBARD
... directly, the problem is cast in a way such as to make it tractable in an approximate, but in many cases surprisingly accurate way. The success of DFT is largely due to the availability of increasingly accurate approximations to the central quantity of DFT, the so-called exchange-correlation energy ...
... directly, the problem is cast in a way such as to make it tractable in an approximate, but in many cases surprisingly accurate way. The success of DFT is largely due to the availability of increasingly accurate approximations to the central quantity of DFT, the so-called exchange-correlation energy ...
COURSE NAME Chemistry for B.Sc. 1st Year PAPER TITLE
... the size of your classroom, then the nucleus would be the size of a grain of sand in the entire class. What holds an atom together? Here let me ask you a question. Have you ever wondered what holds an atom together? Let us try to answer this one. Actually the atom is held together by two fundamental ...
... the size of your classroom, then the nucleus would be the size of a grain of sand in the entire class. What holds an atom together? Here let me ask you a question. Have you ever wondered what holds an atom together? Let us try to answer this one. Actually the atom is held together by two fundamental ...
What is Reality? New Scientist
... This strange behaviour is shared by any sufficiently small piece of matter, including electrons, neutrons, photons and other elementary particles, but not just by these. Similar effects have been observed for objects that are large enough in principle to be seen under a microscope, such as buckybal ...
... This strange behaviour is shared by any sufficiently small piece of matter, including electrons, neutrons, photons and other elementary particles, but not just by these. Similar effects have been observed for objects that are large enough in principle to be seen under a microscope, such as buckybal ...
Photo-Ionization of Noble Gases: A Demonstration of Hybrid
... is the main source of available theoretical data. There have been many studies on multi-photon ionization of noble gas atoms performed using R-matrix theory, for example [12,14,15]. We recently developed a hybrid coupled channels method [16] to study photo-ionization of multi-electron systems. The m ...
... is the main source of available theoretical data. There have been many studies on multi-photon ionization of noble gas atoms performed using R-matrix theory, for example [12,14,15]. We recently developed a hybrid coupled channels method [16] to study photo-ionization of multi-electron systems. The m ...
Chapter 7 The Quantum–Mechanical Model of the Atom Chemistry
... why some elements are metals and others are nonmetals why some elements gain one electron when forming an ...
... why some elements are metals and others are nonmetals why some elements gain one electron when forming an ...
$doc.title
... interacting trapped quantum gases [4]. So far, most of the experimental results in this area can be very accurately modeled by mean-field methods and its extensions, based on the Gross-Pitaevskii (GP) equation and Bogoliubovde Gennes equations for bosonic gases [5], and on the BCS theory for fermioni ...
... interacting trapped quantum gases [4]. So far, most of the experimental results in this area can be very accurately modeled by mean-field methods and its extensions, based on the Gross-Pitaevskii (GP) equation and Bogoliubovde Gennes equations for bosonic gases [5], and on the BCS theory for fermioni ...
Electron scattering

Electron scattering occurs when electrons are deviated from their original trajectory. This is due to the electrostatic forces within matter interaction or, if an external magnetic field is present, the electron may be deflected by the Lorentz force. This scattering typically happens with solids such as metals, semiconductors and insulators; and is a limiting factor in integrated circuits and transistors.The application of electron scattering is such that it can be used as a high resolution microscope for hadronic systems, that allows the measurement of the distribution of charges for nucleons and nuclear structure. The scattering of electrons has allowed us to understand that protons and neutrons are made up of the smaller elementary subatomic particles called quarks.Electrons may be scattered through a solid in several ways:Not at all: no electron scattering occurs at all and the beam passes straight through.Single scattering: when an electron is scattered just once.Plural scattering: when electron(s) scatter several times.Multiple scattering: when electron(s) scatter very many times over.The likelihood of an electron scattering and the proliferance of the scattering is a probability function of the specimen thickness to the mean free path.