Bubble Chamber Work Group Presentation
... • Large Hadron Collider. Click here for further detail. What are antiparticles? • To every particle that has a non-zero value of some quantity such as electric charge, it is possible to create another particle with the opposite value – this is the antiparticle of the original one. For an example, cl ...
... • Large Hadron Collider. Click here for further detail. What are antiparticles? • To every particle that has a non-zero value of some quantity such as electric charge, it is possible to create another particle with the opposite value – this is the antiparticle of the original one. For an example, cl ...
Unit 2 Review KEY
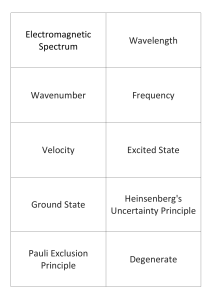
... Electromagnetic Radiation – form of energy that exhibits wavelength behavior as it travels through space. Wavelength (λ) – the distance between corresponding points on adjacent waves. Frequency (v) – number of waves that pass a given point in a specific time (1 sec) Photoelectric Effect – an emissio ...
... Electromagnetic Radiation – form of energy that exhibits wavelength behavior as it travels through space. Wavelength (λ) – the distance between corresponding points on adjacent waves. Frequency (v) – number of waves that pass a given point in a specific time (1 sec) Photoelectric Effect – an emissio ...
PhD position: Quantum information processing with single electron spins
... which are intractable with other types of computer. It is natural to use the spin of an electron as a quantum bit because spin down is ‘0’, spin up is ‘1’, and all possible superposition states can be accessed with magnetic resonance. Nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centres in diamond have isolated electrons ...
... which are intractable with other types of computer. It is natural to use the spin of an electron as a quantum bit because spin down is ‘0’, spin up is ‘1’, and all possible superposition states can be accessed with magnetic resonance. Nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centres in diamond have isolated electrons ...
Physics 2 Homework 21 2013 In 1909 British physicist
... object is that it does not “like” when we try to confine it in a small volume. As we try to „squeeze‟ it, its energy increases greatly. That is why, in spite of strong attraction force, the electron does not fall on the nucleus, but surrounds it as a small cloud. The atomic nucleus consists of posit ...
... object is that it does not “like” when we try to confine it in a small volume. As we try to „squeeze‟ it, its energy increases greatly. That is why, in spite of strong attraction force, the electron does not fall on the nucleus, but surrounds it as a small cloud. The atomic nucleus consists of posit ...
Pair Tutoring
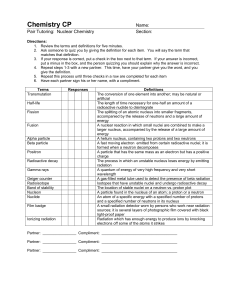
... The splitting of an atomic nucleus into smaller fragments, accompanied by the release of neutrons and a large amount of energy A nuclear reaction in which small nuclei are combined to make a larger nucleus, accompanied by the release of a large amount of energy A helium nucleus, containing two proto ...
... The splitting of an atomic nucleus into smaller fragments, accompanied by the release of neutrons and a large amount of energy A nuclear reaction in which small nuclei are combined to make a larger nucleus, accompanied by the release of a large amount of energy A helium nucleus, containing two proto ...
Quantum
... Orbital- a specific region of an atom where there is a high likeliness that an electron will actually be s orbitals are sphere like p are dumbbell like d,f, and so on have more complicated structures ...
... Orbital- a specific region of an atom where there is a high likeliness that an electron will actually be s orbitals are sphere like p are dumbbell like d,f, and so on have more complicated structures ...
Spectroscopy - Birmingham City Schools
... in his equation he used n = principle quantum number o 4 quantum numbers resulting from spectral lines: n = principle quantum number (energy level) l = orbital quantum number (shape of orbit) ml = magnetic quantum number ms = spin quantum number 1902 Einstein found the photon: Photo-electr ...
... in his equation he used n = principle quantum number o 4 quantum numbers resulting from spectral lines: n = principle quantum number (energy level) l = orbital quantum number (shape of orbit) ml = magnetic quantum number ms = spin quantum number 1902 Einstein found the photon: Photo-electr ...
Unit 1 Inorganic Flashcards
... surrounding molecules or ions by dative covalent bonds (also known as coordinate bonds). ...
... surrounding molecules or ions by dative covalent bonds (also known as coordinate bonds). ...
T3_Static_Potentials_And_Eigenstates
... • Originally postulated by de Broglie in 1924 – NO evidence at this point – He surmised that l=h/p: E=1/2 mv2=p2/2m ...
... • Originally postulated by de Broglie in 1924 – NO evidence at this point – He surmised that l=h/p: E=1/2 mv2=p2/2m ...
A1990CG38700001
... Early measurements of electron Alt for different materials appeared to cluster about a common curve September 20, 1989 when plotted versus kinetic energy This curve became known as the “universal curve” and wasa useDuring the 1960s several types of instruments be- ful guide, even though there was no ...
... Early measurements of electron Alt for different materials appeared to cluster about a common curve September 20, 1989 when plotted versus kinetic energy This curve became known as the “universal curve” and wasa useDuring the 1960s several types of instruments be- ful guide, even though there was no ...
+ + 0 - Bose Institute
... Incidentally, issue of behaviour of radiation as particle – the photon – was finally settled in 1923 by A. H. Compton. Compton found that the light scattered from a particle at rest is shifted in wavelength as given by (1 cos ) c ...
... Incidentally, issue of behaviour of radiation as particle – the photon – was finally settled in 1923 by A. H. Compton. Compton found that the light scattered from a particle at rest is shifted in wavelength as given by (1 cos ) c ...
vocab chap 6
... packed nucleus and that atoms are mostly empty space; also discovered the proton ...
... packed nucleus and that atoms are mostly empty space; also discovered the proton ...
RAD 107 HOMEWORK 4
... 5. How much kinetic energy must an electron have in order to knock a Tungsten K-shell electron out a Tungsten atom? How much to knock out a Tungsten N-shell electron? [Hint: read the first table in Problem 4.] 6. Suppose that a K-shell electron has been knocked out of a Tungsten atom due to a collis ...
... 5. How much kinetic energy must an electron have in order to knock a Tungsten K-shell electron out a Tungsten atom? How much to knock out a Tungsten N-shell electron? [Hint: read the first table in Problem 4.] 6. Suppose that a K-shell electron has been knocked out of a Tungsten atom due to a collis ...
Physics 334 Modern Physics
... the electrons. The laws of conservation of energy and momentum apply, as in any elastic collision between two particles. The momentum of a particle moving at the speed of light is: ...
... the electrons. The laws of conservation of energy and momentum apply, as in any elastic collision between two particles. The momentum of a particle moving at the speed of light is: ...
FORCE Matter
... us that “electrons repel because of the exchange of particles of light called photons” ...
... us that “electrons repel because of the exchange of particles of light called photons” ...
Inside A Particle Physicist`s Toolbox
... 1. to observe a specific particle track 2. not a random noise hit 3. passing from a specific direction or 4. with some flight time We do this by forming an trigger. A trigger is defined by a series of pulses or hits in our detectors in a restricted time interval ...
... 1. to observe a specific particle track 2. not a random noise hit 3. passing from a specific direction or 4. with some flight time We do this by forming an trigger. A trigger is defined by a series of pulses or hits in our detectors in a restricted time interval ...
Electron scattering

Electron scattering occurs when electrons are deviated from their original trajectory. This is due to the electrostatic forces within matter interaction or, if an external magnetic field is present, the electron may be deflected by the Lorentz force. This scattering typically happens with solids such as metals, semiconductors and insulators; and is a limiting factor in integrated circuits and transistors.The application of electron scattering is such that it can be used as a high resolution microscope for hadronic systems, that allows the measurement of the distribution of charges for nucleons and nuclear structure. The scattering of electrons has allowed us to understand that protons and neutrons are made up of the smaller elementary subatomic particles called quarks.Electrons may be scattered through a solid in several ways:Not at all: no electron scattering occurs at all and the beam passes straight through.Single scattering: when an electron is scattered just once.Plural scattering: when electron(s) scatter several times.Multiple scattering: when electron(s) scatter very many times over.The likelihood of an electron scattering and the proliferance of the scattering is a probability function of the specimen thickness to the mean free path.