A semi-classical picture of quantum scattering
... the corresponding positions Xj, for j / 0, the validity of (1.6) for any ^+,^- G L 2 ^), essentially depends on the global shape of the potential V. As an example, it is valid when V(x) < 0 for x ^- 0. In such a case, the result can be extended for general ^+,^_ G ^(R^) by a simple density argument. ...
... the corresponding positions Xj, for j / 0, the validity of (1.6) for any ^+,^- G L 2 ^), essentially depends on the global shape of the potential V. As an example, it is valid when V(x) < 0 for x ^- 0. In such a case, the result can be extended for general ^+,^_ G ^(R^) by a simple density argument. ...
New Phenomena: Recent Results and Prospects from the Fermilab
... – Math, Torque, Angular Momentum, Energy again, but more sophisticated – The material will not be on the 3rd exam, but will help with the exam. It will all be on the ...
... – Math, Torque, Angular Momentum, Energy again, but more sophisticated – The material will not be on the 3rd exam, but will help with the exam. It will all be on the ...
Physics 30 - Structured Independent Learning
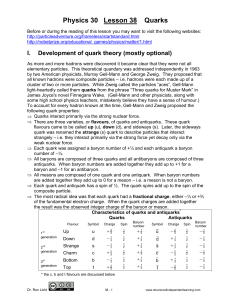
... Richter – almost simultaneously discovered a new hadron, called J by one and (psi) by the other. The J / meson was three times more massive than the proton and, remarkably, lived for 10-20 s before decaying – 1000 times longer than is normal for a hadron of that mass. The quark theory as it stoo ...
... Richter – almost simultaneously discovered a new hadron, called J by one and (psi) by the other. The J / meson was three times more massive than the proton and, remarkably, lived for 10-20 s before decaying – 1000 times longer than is normal for a hadron of that mass. The quark theory as it stoo ...
3/23/2014 1 8 Chemical Equations Chapter Outline Chemical
... produced during the reaction. Reactants: substances consumed during the reaction. Products: substances formed during the reaction. ...
... produced during the reaction. Reactants: substances consumed during the reaction. Products: substances formed during the reaction. ...
Chapter 8
... Balancing Chemical Equations Practice Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of silver nitrate with hydrogen sulfide to produce silver sulfide and nitric acid. 3. Balance the equation. a. Count the number of each atom on the reactants and products side and determine what requires bal ...
... Balancing Chemical Equations Practice Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of silver nitrate with hydrogen sulfide to produce silver sulfide and nitric acid. 3. Balance the equation. a. Count the number of each atom on the reactants and products side and determine what requires bal ...
Powerpoint
... particles will accelerate towards each other when released. Let W+ be the work done on the positive charge by the negative charge. Let W– be the work done on the negative charge by the positive charge. While the charges are moving towards each other, which of the following statements is correct? (a) ...
... particles will accelerate towards each other when released. Let W+ be the work done on the positive charge by the negative charge. Let W– be the work done on the negative charge by the positive charge. While the charges are moving towards each other, which of the following statements is correct? (a) ...
Conservation of Mass
... This equation must hold for ANY control volume, no matte what shape and size. Therefore the integrand must be equal to zero! ...
... This equation must hold for ANY control volume, no matte what shape and size. Therefore the integrand must be equal to zero! ...
Continuum Electrostatics in Molecular Modeling
... Figure 4 illustrates how a dielectric medium weakens the field due to a positive charge. The dipoles induced in the material are aligned with the inducing field. The charges at the heads and tails of the induced dipoles cancel each other except at the surface of the inducing charge. This leaves a ne ...
... Figure 4 illustrates how a dielectric medium weakens the field due to a positive charge. The dipoles induced in the material are aligned with the inducing field. The charges at the heads and tails of the induced dipoles cancel each other except at the surface of the inducing charge. This leaves a ne ...
Lecture 1: Review of Quantum Mechanics, Introduction to Statistical
... The idea is valid both for classical physics and quantum mechanics. In classical physics each particle is described by position and momentum, q̄ = {r̄i , p̄i }N i . Time average over classical microstates: ...
... The idea is valid both for classical physics and quantum mechanics. In classical physics each particle is described by position and momentum, q̄ = {r̄i , p̄i }N i . Time average over classical microstates: ...
Sources of Parallelism and Locality in Simulation
... • S&F 4. Fish alone move randomly on a square grid, with at most one fish per grid point. • S&F 5. Sharks and Fish both move randomly on a square grid, with at most one fish or shark per grid point, including rules for fish attracting sharks, eating, breeding and dying. • S&F 6. Like Sharks and Fish ...
... • S&F 4. Fish alone move randomly on a square grid, with at most one fish per grid point. • S&F 5. Sharks and Fish both move randomly on a square grid, with at most one fish or shark per grid point, including rules for fish attracting sharks, eating, breeding and dying. • S&F 6. Like Sharks and Fish ...