Modern Physics 342
... An electron is trapped in a one-dimensional region of length 1X10-10 m. How much energy must be supplied to excite the electron from the ground state to the first excited state? In the ground state, what is the probability of finding the electron in the region from 0.09 X 10-10 m to 0.11 X 10-10 m? ...
... An electron is trapped in a one-dimensional region of length 1X10-10 m. How much energy must be supplied to excite the electron from the ground state to the first excited state? In the ground state, what is the probability of finding the electron in the region from 0.09 X 10-10 m to 0.11 X 10-10 m? ...
January 1998
... An insulated, uncharged, conducting, spherical shell of radius a is placed in a uniform electric field of magnitude E0 . Suppose the shell is cut into two hemispheres at its equator (in the plane perpendicular to the field). What force is required to keep the hemispheres from separating? ...
... An insulated, uncharged, conducting, spherical shell of radius a is placed in a uniform electric field of magnitude E0 . Suppose the shell is cut into two hemispheres at its equator (in the plane perpendicular to the field). What force is required to keep the hemispheres from separating? ...
Qualifying Exam for Graduate Students – Fall 2008
... Mechanics Consider an American football, which is usually thrown such that it spins about its long axis. (a) Sketch the principal axes of the football for rotations about the center of mass on the figure below. Label these axes {e1, e2, e3}. (b) Let i be the moment of inertia for rotations about t ...
... Mechanics Consider an American football, which is usually thrown such that it spins about its long axis. (a) Sketch the principal axes of the football for rotations about the center of mass on the figure below. Label these axes {e1, e2, e3}. (b) Let i be the moment of inertia for rotations about t ...
The relation of colour charge to electric charge (E/c) −P2 −Q2 −(mc
... This can also be done using 2x2 Pauli matrices (labelled K,L,M) because two inertial observers agree on the component of momentum Q orthogonal to the component of momentum P in the direction of a Lorentz boost. ...
... This can also be done using 2x2 Pauli matrices (labelled K,L,M) because two inertial observers agree on the component of momentum Q orthogonal to the component of momentum P in the direction of a Lorentz boost. ...
SOME STRANGE FEATURES OF THE GALILEI GROUP BARBARA GOŁUBOWSKA, VASYL
... obviously that we deal with the projective unitary representation of the group rather than with the usual representation. The status of mass is completely different than in relativistic theory, where it is a continuous eigenvalue of the Casimir invariant. In Galilei framework it is a parameter chara ...
... obviously that we deal with the projective unitary representation of the group rather than with the usual representation. The status of mass is completely different than in relativistic theory, where it is a continuous eigenvalue of the Casimir invariant. In Galilei framework it is a parameter chara ...
A critique of recent theories of spin-half quantum plasmas
... moments will dominate over quantum spin effects and Coulomb collisions imply very short meanfree paths at high densities. At low temperatures the exclusion principle makes the assumption of a unit S invalid. Furthermore, nowhere do the authors discuss the basic equilibrium state involving significan ...
... moments will dominate over quantum spin effects and Coulomb collisions imply very short meanfree paths at high densities. At low temperatures the exclusion principle makes the assumption of a unit S invalid. Furthermore, nowhere do the authors discuss the basic equilibrium state involving significan ...
Atomic Theory Study Guide - Reading Community Schools
... Equation, and identify which orbital properties are determined by each of these numbers. 2. Name orbitals given its quantum numbers, or identify quantum numbers for given orbital. 3. Sketch the relative shapes, sizes, and spatial orientations of s, p, and d orbitals of the hydrogen atom. 4. Apply th ...
... Equation, and identify which orbital properties are determined by each of these numbers. 2. Name orbitals given its quantum numbers, or identify quantum numbers for given orbital. 3. Sketch the relative shapes, sizes, and spatial orientations of s, p, and d orbitals of the hydrogen atom. 4. Apply th ...
Finding region of xy plane for which differential
... What does an xy-plane have to do with anything? I looked up the definition of unique solutions and here it is Let R be a rectangular region in the xy-planed defined by a <=x<=b, c<=y<=d that contains the ...
... What does an xy-plane have to do with anything? I looked up the definition of unique solutions and here it is Let R be a rectangular region in the xy-planed defined by a <=x<=b, c<=y<=d that contains the ...
The Infinite Square Well 6.1 Separability of Schrödinger`s Equation
... it ends up being σx2 = a12 , the first term of the quantum form. If we were to calculate the variances using a generic eigenstate, labelled by n, we would ...
... it ends up being σx2 = a12 , the first term of the quantum form. If we were to calculate the variances using a generic eigenstate, labelled by n, we would ...
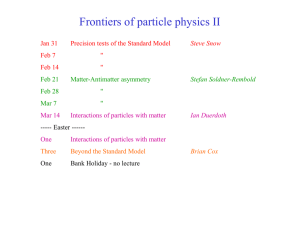
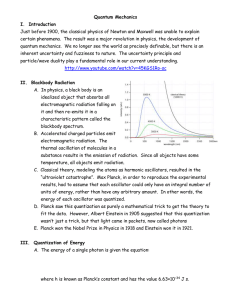
Quantum Mechanics I. Introduction Just before 1900, the classical
... C. Classical theory, modeling the atoms as harmonic oscillators, resulted in the “ultraviolet catastrophe”. Max Planck, in order to reproduce the experimental results, had to assume that each oscillator could only have an integral number of units of energy, rather than have any arbitrary amount. In ...
... C. Classical theory, modeling the atoms as harmonic oscillators, resulted in the “ultraviolet catastrophe”. Max Planck, in order to reproduce the experimental results, had to assume that each oscillator could only have an integral number of units of energy, rather than have any arbitrary amount. In ...