Quantum Field Theory
... second one is dropped, and we simply call it “Field Theory”). Initially, field theory was applied mainly, but with great success, to the theory of photons and electrons, “Quantum Electrodynamics” (QED), but during the third quarter of the century this was extended to the weak and strong interactions ...
... second one is dropped, and we simply call it “Field Theory”). Initially, field theory was applied mainly, but with great success, to the theory of photons and electrons, “Quantum Electrodynamics” (QED), but during the third quarter of the century this was extended to the weak and strong interactions ...
Problems in Quantum Mechanics
... moment of a silver atom (a so-called “spin- 12 ” system), which has two basis states. Another system with two basis states is polarized light. I did not use this system mainly because photons are less familiar than atoms. This chapter develops the quantum mechanics of photon polarization much as the ...
... moment of a silver atom (a so-called “spin- 12 ” system), which has two basis states. Another system with two basis states is polarized light. I did not use this system mainly because photons are less familiar than atoms. This chapter develops the quantum mechanics of photon polarization much as the ...
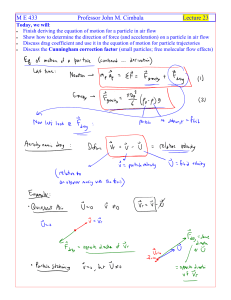
Lecture 23
... To do: Which is the correct direction of the drag force on the particle? Text your answer as “a”, “b”, or “c”, without the quotes. ...
... To do: Which is the correct direction of the drag force on the particle? Text your answer as “a”, “b”, or “c”, without the quotes. ...
Quantum mechanics
... forward in time (hence the name ‘propagator’). In non-relativistic quantum mechanics, the range of q′′ is infinite, so that the wave can propagate at any speed; in relativistic quantum mechanics, this is rectified by restricting the propagation to the forward light cone. ...
... forward in time (hence the name ‘propagator’). In non-relativistic quantum mechanics, the range of q′′ is infinite, so that the wave can propagate at any speed; in relativistic quantum mechanics, this is rectified by restricting the propagation to the forward light cone. ...
Physics 106a/196a – Problem Set 7 – Due Dec 1,...
... is independent of distance from the earth’s surface – g is only used to obviate G and Mearth in the result.) Hint: Use conservation of energy and conservation of angular momentum when you know they are conserved, and use the fact that you know exactly how they change when the thrust is applied. 4. ( ...
... is independent of distance from the earth’s surface – g is only used to obviate G and Mearth in the result.) Hint: Use conservation of energy and conservation of angular momentum when you know they are conserved, and use the fact that you know exactly how they change when the thrust is applied. 4. ( ...
Angular Momentum
... is known then the other two components remain undetermined. This situation is represented by the following diagram: ...
... is known then the other two components remain undetermined. This situation is represented by the following diagram: ...
Higgs Field and Quantum Entanglement
... The gravitational attractive force is basically a magnetic force. The same electric charges can attract one another by the magnetic force if they are moving parallel in the same direction. Since the electrically neutral matter is composed of negative and positive charges they need 2 photons to media ...
... The gravitational attractive force is basically a magnetic force. The same electric charges can attract one another by the magnetic force if they are moving parallel in the same direction. Since the electrically neutral matter is composed of negative and positive charges they need 2 photons to media ...
16.3. PROBLEM SET III 211 Answers: Problem set III Advanced
... a result, the ML of the atom can take one of seven possible values, ML = ±3, ±2, ±1, 0. As a result, we can deduce that L = 3 is the only possibility. The shell is less than half full, so Hund’s third rule requires J = |L − S| = 0, i.e. 7 F0 . 3. The 3 P0 notation signifies the total angular momentu ...
... a result, the ML of the atom can take one of seven possible values, ML = ±3, ±2, ±1, 0. As a result, we can deduce that L = 3 is the only possibility. The shell is less than half full, so Hund’s third rule requires J = |L − S| = 0, i.e. 7 F0 . 3. The 3 P0 notation signifies the total angular momentu ...
rutherfords model
... – A new quantum number, m ℓ, called the orbital magnetic quantum number, had to be introduced • m ℓ can vary from - ℓ to + ℓ in integer steps • High resolution spectrometers show that spectral lines are, in fact, two very closely spaced lines, even in the absence of a magnetic field – This splitting ...
... – A new quantum number, m ℓ, called the orbital magnetic quantum number, had to be introduced • m ℓ can vary from - ℓ to + ℓ in integer steps • High resolution spectrometers show that spectral lines are, in fact, two very closely spaced lines, even in the absence of a magnetic field – This splitting ...
Probing the Orbital Energy of an Electron in an Atom
... interaction of matter with electromagnetic radiation. This has been known for more than a century. It is well beyond time to abandon classical models of the nano-world and teach our students atomic and molecular structure from the quantum mechanical perspective. Richard Feynman made this point forci ...
... interaction of matter with electromagnetic radiation. This has been known for more than a century. It is well beyond time to abandon classical models of the nano-world and teach our students atomic and molecular structure from the quantum mechanical perspective. Richard Feynman made this point forci ...
ppt - UCSB Physics
... • Can consistently assign direction to dimers pointing from A ! B on any bipartite lattice • Dimer constraint ) Gauss’ Law • Spin fluctuations, like polarization fluctuations in a dielectric, have power-law dipolar form reflecting charge conservation ...
... • Can consistently assign direction to dimers pointing from A ! B on any bipartite lattice • Dimer constraint ) Gauss’ Law • Spin fluctuations, like polarization fluctuations in a dielectric, have power-law dipolar form reflecting charge conservation ...
Degeneracy Breaking in Some Frustrated Magnets
... • Can consistently assign direction to dimers pointing from A → B on any bipartite lattice • Dimer constraint ) Gauss’ Law • Spin fluctuations, like polarization fluctuations in a dielectric, have power-law dipolar form reflecting charge conservation ...
... • Can consistently assign direction to dimers pointing from A → B on any bipartite lattice • Dimer constraint ) Gauss’ Law • Spin fluctuations, like polarization fluctuations in a dielectric, have power-law dipolar form reflecting charge conservation ...
Advanced Chemical Physics
... momenta) is small. It is called the jj coupling approximation and it is useful only in the case of heavy atoms. 2. Coupling between the all orbital angular momenta of the electrons is strong and between the spins is also appreciable. This is the Russel-Suanders coupling approximation and is the most ...
... momenta) is small. It is called the jj coupling approximation and it is useful only in the case of heavy atoms. 2. Coupling between the all orbital angular momenta of the electrons is strong and between the spins is also appreciable. This is the Russel-Suanders coupling approximation and is the most ...