lagrangian formulation of classical
... • If you take the derivative of the action with respect to q, the result is p, such that p and q are conjugate variables • Your generalized coordinates (the q’s) can be transformed into “canonically conjugate variables” by the Hamilton-Jacobi equations. • For now this is just a fun fact, but will be ...
... • If you take the derivative of the action with respect to q, the result is p, such that p and q are conjugate variables • Your generalized coordinates (the q’s) can be transformed into “canonically conjugate variables” by the Hamilton-Jacobi equations. • For now this is just a fun fact, but will be ...
Landau Levels
... ü Code: Verify that the wavefunctions defined above are indeed eigenfunctions of H ...
... ü Code: Verify that the wavefunctions defined above are indeed eigenfunctions of H ...
PHYS632_C12_32_Maxwe..
... has units kg.m2/s. µ has units of A.m2 - current times area Recall for a current loop, the magnetic dipole moment = current times area of loop In the quantum field theory of the electron, S can not be measured. Only it’s component along the z axis can be measured. In quantum physics, there are only ...
... has units kg.m2/s. µ has units of A.m2 - current times area Recall for a current loop, the magnetic dipole moment = current times area of loop In the quantum field theory of the electron, S can not be measured. Only it’s component along the z axis can be measured. In quantum physics, there are only ...
Relativistic Electrodynamics
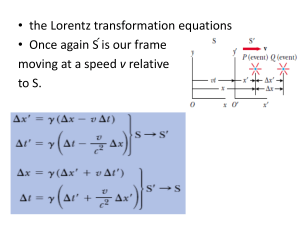
... The first postulate was known for classical mechanics a long time ago and its validity for electromagnetic was the objective of the previous experiments. Einstein generalized it for all physical laws. It means that if two observers performed an experiment in 2 different reference frames moving with ...
... The first postulate was known for classical mechanics a long time ago and its validity for electromagnetic was the objective of the previous experiments. Einstein generalized it for all physical laws. It means that if two observers performed an experiment in 2 different reference frames moving with ...
File
... 19. What is the name of the process in which the nucleus of an atom of one element is changed into the nucleus of an atom of a different element? A) decomposition C) substitution ...
... 19. What is the name of the process in which the nucleus of an atom of one element is changed into the nucleus of an atom of a different element? A) decomposition C) substitution ...
CHAPTER 4
... 4. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined or rearranged. Atoms of one element are never changed into atoms of another element as a result of a chemical reaction. ...
... 4. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined or rearranged. Atoms of one element are never changed into atoms of another element as a result of a chemical reaction. ...
Accelerate This! - University of Houston
... The force on charged particle q is due to the charge Q of another nearby particle; ...
... The force on charged particle q is due to the charge Q of another nearby particle; ...
Standard Model - UTA High Energy Physics page.
... • Quantum Mechanics and development of Charge cloud mode of atom ...
... • Quantum Mechanics and development of Charge cloud mode of atom ...
Crystal Field Theory
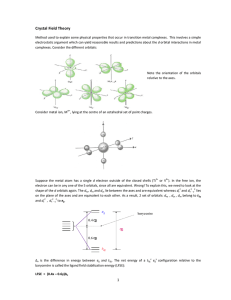
... Crystal Field Theory Method used to explain some physical properties that occur in transition metal complexes. This involves a simple electrostatic argument which can yield reasonable results and predictions about the d orbital interactions in metal complexes. Consider the different orbitals: ...
... Crystal Field Theory Method used to explain some physical properties that occur in transition metal complexes. This involves a simple electrostatic argument which can yield reasonable results and predictions about the d orbital interactions in metal complexes. Consider the different orbitals: ...
Historical pseudo simplified solution of the Dirac
... in a paper[9] published in Physical Review 22 years ago is a pseudo solution. For the said secondorder Dirac-Coulomb equations in which two equations were written in the same form by using sign “±”, two eigenvalues set should be given and they are actually different. It is well known that two differ ...
... in a paper[9] published in Physical Review 22 years ago is a pseudo solution. For the said secondorder Dirac-Coulomb equations in which two equations were written in the same form by using sign “±”, two eigenvalues set should be given and they are actually different. It is well known that two differ ...