document
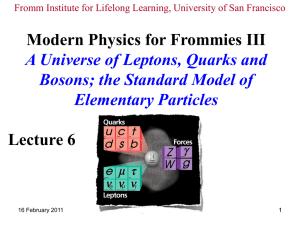
... Reinterpret Feynman diagram for e- moving through space. Direction and l → momentum vector, f → energy Absolute cannot be measured, only D s are observable. Probably universe is symmetric under global phase changes but special relativity doecn’t allow application of global symmetries. Our e- sh ...
... Reinterpret Feynman diagram for e- moving through space. Direction and l → momentum vector, f → energy Absolute cannot be measured, only D s are observable. Probably universe is symmetric under global phase changes but special relativity doecn’t allow application of global symmetries. Our e- sh ...
Strong-Disorder Fixed Point in the Dissipative Random Transverse-Field Ising Model
... of Griffiths-McCoy singularities [1,2], leading to the divergence of various quantities like the susceptibility at zero temperature even far away from a quantum critical point, has received considerable attention recently [3–7]. This quantum Griffiths behavior is characteristic for quantum phase tra ...
... of Griffiths-McCoy singularities [1,2], leading to the divergence of various quantities like the susceptibility at zero temperature even far away from a quantum critical point, has received considerable attention recently [3–7]. This quantum Griffiths behavior is characteristic for quantum phase tra ...
Shock drift acceleration
... • Profile of number of accelerated electrons shows similar features with observations. ...
... • Profile of number of accelerated electrons shows similar features with observations. ...
Glassy Chimeras Could Be Blind to Quantum Speedup:
... only occurs at zero temperature, despite the Chimera graph being nonplanar. Furthermore, the divergence of the correlation length is rather violent, with ξ ∼ T −4 for T → 0. This suggests that the phase space and correlations only build up close to T = 0 for a spin glass defined on the Chimera topol ...
... only occurs at zero temperature, despite the Chimera graph being nonplanar. Furthermore, the divergence of the correlation length is rather violent, with ξ ∼ T −4 for T → 0. This suggests that the phase space and correlations only build up close to T = 0 for a spin glass defined on the Chimera topol ...
Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms
... • Louis de Broglie said that if ____________________ can have material properties, ____________________ should exhibit wave properties. • He demonstrated that the relationship between mass and wavelength was ...
... • Louis de Broglie said that if ____________________ can have material properties, ____________________ should exhibit wave properties. • He demonstrated that the relationship between mass and wavelength was ...
Kondo Effect in Quantum Dots
... • Wick’s theorem only valid for operators, whose commutator is a c-number • Not the case for the impurity spin, obeying the standard commutation relations of angular momentum Gesa von Bornstaedt ...
... • Wick’s theorem only valid for operators, whose commutator is a c-number • Not the case for the impurity spin, obeying the standard commutation relations of angular momentum Gesa von Bornstaedt ...
The Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen Argument and the Bell Inequalities
... p ( D ) = 1, therefore p (< 1 >) = 0.05,... p (< 6 >) = 0.55. Our probabilistic model will be based on these probabilities, and it works well. It correctly describes the behavior of the system: it correctly reflects the relative frequencies, correctly predicts that the mean value of the thrown numbe ...
... p ( D ) = 1, therefore p (< 1 >) = 0.05,... p (< 6 >) = 0.55. Our probabilistic model will be based on these probabilities, and it works well. It correctly describes the behavior of the system: it correctly reflects the relative frequencies, correctly predicts that the mean value of the thrown numbe ...
Atomic Physics
... c) at the short wavelength side of the electromagnetic spectrum. d) at the low frequency side of the electromagnetic spectrum 5) In classical physics a) an electron travels with an associated deBroglie wavelength b) a particle is associated with any wave phenomenon c) the Pauli exclusion principle a ...
... c) at the short wavelength side of the electromagnetic spectrum. d) at the low frequency side of the electromagnetic spectrum 5) In classical physics a) an electron travels with an associated deBroglie wavelength b) a particle is associated with any wave phenomenon c) the Pauli exclusion principle a ...