1 - Técnico Lisboa - Universidade de Lisboa
... Scalar theories try to describe the gravitational field using a scalar field, which must satisfy some field equation. Newton gravitation is a scalar field theory in the way that it is completely described by the potential φ which satisfies the Poisson equation. Indeed, the first attempts to create a ...
... Scalar theories try to describe the gravitational field using a scalar field, which must satisfy some field equation. Newton gravitation is a scalar field theory in the way that it is completely described by the potential φ which satisfies the Poisson equation. Indeed, the first attempts to create a ...
Fractional topological ordered phases.
... unaffected by detrimental effects within the material such as imperfections etc., the electrons in these new materials essentially do not interact with one another – despite being charged entities and hence susceptible to repulsion (i.e., the electron-electron Coulomb interaction). In many physical ...
... unaffected by detrimental effects within the material such as imperfections etc., the electrons in these new materials essentially do not interact with one another – despite being charged entities and hence susceptible to repulsion (i.e., the electron-electron Coulomb interaction). In many physical ...
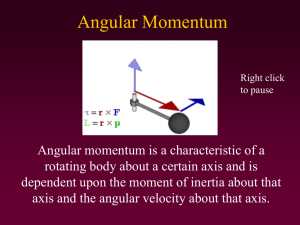
CHAPTER 9 ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS
... the forces, as well as the vector sum of all the torques, that act on the system must be zero. The figure below shows a free body diagram for the boom. Since the boom is assumed to be uniform, its weight W B is located at its center of gravity, which coincides with its geometrical center. There is a ...
... the forces, as well as the vector sum of all the torques, that act on the system must be zero. The figure below shows a free body diagram for the boom. Since the boom is assumed to be uniform, its weight W B is located at its center of gravity, which coincides with its geometrical center. There is a ...
The Identification of Particles Using Diagrams and Distributions of
... shape index distribution p( + xv) is estimated from the relationship of Gxu = dx/dy. p( Gxy) is considered to be the probability density function by which the particle dx (or dy) is measured as dy (or dx)_ (The reverse is also true.) If the particIe distribution and shape index distribution are know ...
... shape index distribution p( + xv) is estimated from the relationship of Gxu = dx/dy. p( Gxy) is considered to be the probability density function by which the particle dx (or dy) is measured as dy (or dx)_ (The reverse is also true.) If the particIe distribution and shape index distribution are know ...
Teoría Total simplificada, Revista Chilena de Ingeniería, Vol. 16, Nº1
... Electromagnetic engineering is a branch of applied physics which is developing so fast that in the near future electromagnetic engineers will be indispensable in an important emerging area, that which is now known as Wave Structure Matter (WSM). The main reason for this is the penetration capacity o ...
... Electromagnetic engineering is a branch of applied physics which is developing so fast that in the near future electromagnetic engineers will be indispensable in an important emerging area, that which is now known as Wave Structure Matter (WSM). The main reason for this is the penetration capacity o ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... Law of Conservation of Matter: Matter (mass) cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. The atoms are only re-arranged. (Antoine Lavoisier) Total mass reactants = total mass of products Chemical reaction: a process where one or more substances are converted into new substances with dif ...
... Law of Conservation of Matter: Matter (mass) cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. The atoms are only re-arranged. (Antoine Lavoisier) Total mass reactants = total mass of products Chemical reaction: a process where one or more substances are converted into new substances with dif ...
ppt - CS Technion
... more often to upper bound the error probability Amplitude amplification approach is used to overcome this issue and achieve the improved bounds ...
... more often to upper bound the error probability Amplitude amplification approach is used to overcome this issue and achieve the improved bounds ...
Producing Squeezed Input States for an Atomic Clock Using an Optical Cavity.
... the two scattering rates are equal (no information revealed) and reduces to the average scattering rate when the process occurs for only one clock state (which then gets labelled by every scattering event). For our choice of detuning, where 2/3 of the scattering is Rayleigh scattering which occurs a ...
... the two scattering rates are equal (no information revealed) and reduces to the average scattering rate when the process occurs for only one clock state (which then gets labelled by every scattering event). For our choice of detuning, where 2/3 of the scattering is Rayleigh scattering which occurs a ...
Quantum Computing with Quantum Dots
... the elementary quantum bit. According to DiVincenzo, the five requirements that must be satisfied in order to obtain a reliable QC system are: (1) a scalable system, (2) the ability to initialize qubits (3) relatively long decoherence times (longer than the gate operation times), (4) a qubit-specifi ...
... the elementary quantum bit. According to DiVincenzo, the five requirements that must be satisfied in order to obtain a reliable QC system are: (1) a scalable system, (2) the ability to initialize qubits (3) relatively long decoherence times (longer than the gate operation times), (4) a qubit-specifi ...
BARRIER PENETRATION AND INSTANTONS J. ZINN - IPhT
... been noticed that, formally, barrier penetration has a semi-classical interpretation in terms of classical particles moving in imaginary time (see the discussion at the end of section 1.1). The Euclidean formalism based on calculating the density matrix at thermal equilibrium e−βH , describes formal ...
... been noticed that, formally, barrier penetration has a semi-classical interpretation in terms of classical particles moving in imaginary time (see the discussion at the end of section 1.1). The Euclidean formalism based on calculating the density matrix at thermal equilibrium e−βH , describes formal ...