Worksheet 1.1 Finding the Ionization Energy of H
... That seems pretty small (and it is!) but in fact this atom is almost entirely empty space. The best estimate of the radius of a proton is about 1.20x10–15 m, which is much, much smaller! To give you some idea, imagine that the atom were the size of the head of a pin. Put it in the middle of a footba ...
... That seems pretty small (and it is!) but in fact this atom is almost entirely empty space. The best estimate of the radius of a proton is about 1.20x10–15 m, which is much, much smaller! To give you some idea, imagine that the atom were the size of the head of a pin. Put it in the middle of a footba ...
Quantum Field Theory I, Lecture Notes
... Usually, excitations of the quantum field will be described by “particles”. In QFT the number of these particles is not conserved, they are created and annihilated when they interact. It is precisely what we observe in elementary particle physics, hence QFT has become the mathematical framework for ...
... Usually, excitations of the quantum field will be described by “particles”. In QFT the number of these particles is not conserved, they are created and annihilated when they interact. It is precisely what we observe in elementary particle physics, hence QFT has become the mathematical framework for ...
Electromagnetism and Circular Motion in a Cyclotron
... That seems pretty small (and it is!) but in fact this atom is almost entirely empty space. The best estimate of the radius of a proton is about 1.20x10–15 m, which is much, much smaller! To give you some idea, imagine that the atom were the size of the head of a pin. Put it in the middle of a footba ...
... That seems pretty small (and it is!) but in fact this atom is almost entirely empty space. The best estimate of the radius of a proton is about 1.20x10–15 m, which is much, much smaller! To give you some idea, imagine that the atom were the size of the head of a pin. Put it in the middle of a footba ...
A quantum logical and geometrical approach to the study of
... magnitude M is represented by an operator M acting over the state space. For bounded selfadjoint operators, conditions for the existence of the spectral decomposition M = 兺iai Pi = 兺iai兩ai典具ai兩 are satisfied 共along this work we will restrict the study to the finite dimensional case兲. The real number ...
... magnitude M is represented by an operator M acting over the state space. For bounded selfadjoint operators, conditions for the existence of the spectral decomposition M = 兺iai Pi = 兺iai兩ai典具ai兩 are satisfied 共along this work we will restrict the study to the finite dimensional case兲. The real number ...
The mode of deuterium uptake during Pd–D co–deposition has been... perturbation techniques. The resultant potential relaxation curves exhibit four distinct...
... higher efficiency of electrochemical charging compared with that of charging from the gas phase [3]. This poses the question as to what role, if any, the electrode potential plays in maintaining a high D/Pd atomic ratio. It is often assumed that there is little difference, apart from the usual isoto ...
... higher efficiency of electrochemical charging compared with that of charging from the gas phase [3]. This poses the question as to what role, if any, the electrode potential plays in maintaining a high D/Pd atomic ratio. It is often assumed that there is little difference, apart from the usual isoto ...
The Quantum Phases of Matter The Harvard community has made
... in the Bardeen-Cooper-Schrieffer theory, a superconductor is obtained when the electrons form pairs, and the pairs Bose condense. In this case, the ground state is typically adiabatically connected to the Bose-Einstein condensate of electron pairs, which is a simple product of single boson states. He ...
... in the Bardeen-Cooper-Schrieffer theory, a superconductor is obtained when the electrons form pairs, and the pairs Bose condense. In this case, the ground state is typically adiabatically connected to the Bose-Einstein condensate of electron pairs, which is a simple product of single boson states. He ...
Can gas hydrate structures be described using - e-Spacio
... very heavy isotopes)33,34 . These studies throw light on just how much the properties of water are affected by nuclear quantum effects. In this work we shall perform both classical and path integral simulations of the hydrate structures sI, sII and sH using the same model to determine the importanc ...
... very heavy isotopes)33,34 . These studies throw light on just how much the properties of water are affected by nuclear quantum effects. In this work we shall perform both classical and path integral simulations of the hydrate structures sI, sII and sH using the same model to determine the importanc ...
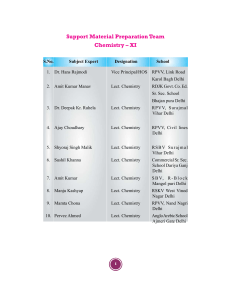
Support Material
... Law of Multiple Proportions (John Dalton) : When two elements combine to form two or more compounds, then the different masses of one element, which combine with a ®xed mass of the other, bear a simple ratio to one another. Gay Lussac’s Law : When gases combine or are produced in a chemical reac ...
... Law of Multiple Proportions (John Dalton) : When two elements combine to form two or more compounds, then the different masses of one element, which combine with a ®xed mass of the other, bear a simple ratio to one another. Gay Lussac’s Law : When gases combine or are produced in a chemical reac ...
Free Energies of Cavity and Noncavity Hydrated Electrons at the
... computed with cutoff electrostatics.1 However, this red shift is consistent with what Herbert and coworkers found when Ewald summation is used to handle electrostatics;5 therefore, the spectrum at these distances corresponds to the bulk predictions of this model. Similar to the behavior of the VBE, w ...
... computed with cutoff electrostatics.1 However, this red shift is consistent with what Herbert and coworkers found when Ewald summation is used to handle electrostatics;5 therefore, the spectrum at these distances corresponds to the bulk predictions of this model. Similar to the behavior of the VBE, w ...
Level shifts of rubidium Rydberg states due to binary interactions
... dominant contributions usually come from only 5 to 10 twoparticle states, with one or two of those often accounting for 70%⫺90% of the level shift. In our calculations, we have included single-particle basis states with principal quantum numbers over a restricted n-range and have verified that the i ...
... dominant contributions usually come from only 5 to 10 twoparticle states, with one or two of those often accounting for 70%⫺90% of the level shift. In our calculations, we have included single-particle basis states with principal quantum numbers over a restricted n-range and have verified that the i ...
Five Lecture Course on Basic Physics of
... • It is important that at such low temperatures a superconductor can be considered to be a single large quantum particle or molecule which is characterized by a single (BCS) wave function. • A huge amount of electrons is incorporated into a single quantum state. This is not possible for normal elect ...
... • It is important that at such low temperatures a superconductor can be considered to be a single large quantum particle or molecule which is characterized by a single (BCS) wave function. • A huge amount of electrons is incorporated into a single quantum state. This is not possible for normal elect ...
Interacting Cold Rydberg Atoms: a Toy Many-Body
... It is also possible to use a non dissipative atom-light interaction to produce conservative traps in which cold atoms can be stored. The principle is the following. The electric field EL of a laser at frequency ω induces an atomic dipole d = αEL . Here α is the polarizability of the atom. In the cas ...
... It is also possible to use a non dissipative atom-light interaction to produce conservative traps in which cold atoms can be stored. The principle is the following. The electric field EL of a laser at frequency ω induces an atomic dipole d = αEL . Here α is the polarizability of the atom. In the cas ...
Exercises 2013 - Oxford School on Neutron Scattering
... where Ei is the energy of the incident neutron, Ef is its energy after scattering, and ΔE is the energy transferred to the scattering system. ΔE may be positive (neutrons lose energy) or negative (neutrons gain energy). If k is the wave-number of a neutron, its energy E is related to k by E = 81.8 / ...
... where Ei is the energy of the incident neutron, Ef is its energy after scattering, and ΔE is the energy transferred to the scattering system. ΔE may be positive (neutrons lose energy) or negative (neutrons gain energy). If k is the wave-number of a neutron, its energy E is related to k by E = 81.8 / ...
Terahertz Response of Excitons in Nanorod Heterostructures Ryan d’Eon
... and each element has its own unique discrete set of electron state energies. Manipulating electron states has been a very fruitful technology path: X-ray emitters and gas lasers, for example, are important technologies that work by causing specific electron transitions in target atoms. Observational ...
... and each element has its own unique discrete set of electron state energies. Manipulating electron states has been a very fruitful technology path: X-ray emitters and gas lasers, for example, are important technologies that work by causing specific electron transitions in target atoms. Observational ...
Nature’s Queer Performativity “O 25
... Angeles Times on January 14, 1989. An online position paper entitled “Homosexuality and Natural Law”, posted on the website of the ultra-right-wing The Claremont Institute in southern California, quotes the line from the opposite the editorial page piece and finishes the thought: “To regard ‘the gen ...
... Angeles Times on January 14, 1989. An online position paper entitled “Homosexuality and Natural Law”, posted on the website of the ultra-right-wing The Claremont Institute in southern California, quotes the line from the opposite the editorial page piece and finishes the thought: “To regard ‘the gen ...
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).