1700_QM_2_wavemech
... Zeeman effect implies “suborbits” which are affected differently by the magnetic field. • Principle (Bohr) quantum number n=1, 2, 3, 4 … • 2nd quantum number “l” where l
... Zeeman effect implies “suborbits” which are affected differently by the magnetic field. • Principle (Bohr) quantum number n=1, 2, 3, 4 … • 2nd quantum number “l” where l
THE AUFBAU PRINCIPAL, KRAMERS RELATION, SELECTION
... 2. Kramer’s Relation and the Circular State An atom which has a valance electron in an extremely high principal quantum number state is in a Rydberg state. These states are called circular states for the following reason. (We use the simpler hydrogen case due to the fact that it is not a terrible a ...
... 2. Kramer’s Relation and the Circular State An atom which has a valance electron in an extremely high principal quantum number state is in a Rydberg state. These states are called circular states for the following reason. (We use the simpler hydrogen case due to the fact that it is not a terrible a ...
Chapter 8 - Bakersfield College
... B. A spectroscope is an instrument that disperses the light emitted by an excited gas into the different frequencies the light contains. C. An emission spectrum consists of the various frequencies of light given off by an excited substance. D. A continuous spectrum consists of all frequencies of lig ...
... B. A spectroscope is an instrument that disperses the light emitted by an excited gas into the different frequencies the light contains. C. An emission spectrum consists of the various frequencies of light given off by an excited substance. D. A continuous spectrum consists of all frequencies of lig ...
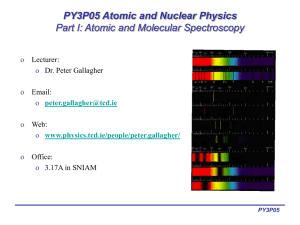
Atomic and Molecular Spectroscopy
... o Hydrogen energy levels o Fine structure o Spin-orbit coupling o Nuclear moments and hyperfine structure ...
... o Hydrogen energy levels o Fine structure o Spin-orbit coupling o Nuclear moments and hyperfine structure ...
Schrodinger equation (PPT - 7.3MB)
... observer's subjective knowledge of the system. The description of nature is essentially probabilistic, with the probability of an event related to the square of the amplitude of the wave function related to it. It is not possible to know the value of all the properties of the system at the same time ...
... observer's subjective knowledge of the system. The description of nature is essentially probabilistic, with the probability of an event related to the square of the amplitude of the wave function related to it. It is not possible to know the value of all the properties of the system at the same time ...
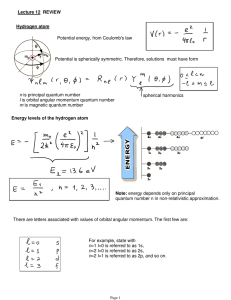
Lecture 12: Review.
... Example: hydrogen ground state J=1/2, I=1/2 (proton) F=0,1, so two levels (see picture on previous page) ...
... Example: hydrogen ground state J=1/2, I=1/2 (proton) F=0,1, so two levels (see picture on previous page) ...
Document
... combinations with the same energy. For hydrogen, the energy is set by n. For a given n consider all of the combinations of quantum numbers ℓ, m, and ms. Remember ℓ=0,1…n−1 and m=0,±1,±2…±2ℓ and ms=±½. How many combinations are there? A. n Before we found out about spin we determined the B. 2n number ...
... combinations with the same energy. For hydrogen, the energy is set by n. For a given n consider all of the combinations of quantum numbers ℓ, m, and ms. Remember ℓ=0,1…n−1 and m=0,±1,±2…±2ℓ and ms=±½. How many combinations are there? A. n Before we found out about spin we determined the B. 2n number ...
CHEMISTRY 113 EXAM 3(A)
... A. reflection of light by metal surface B. ejection of electrons by a metal when struck by light C. acceleration of electrons in vacuum by the electric field D. effect of the electric field on the emission of light 3. The frequency of electromagnetic radiation required to promote an electron from n= ...
... A. reflection of light by metal surface B. ejection of electrons by a metal when struck by light C. acceleration of electrons in vacuum by the electric field D. effect of the electric field on the emission of light 3. The frequency of electromagnetic radiation required to promote an electron from n= ...
Quantum numbers
... “Orbitals with the same potential energy get singly occupied first” • Angular momentum conservation is valid for electrons in atoms and molecules • The photon has a spin of 1 ...
... “Orbitals with the same potential energy get singly occupied first” • Angular momentum conservation is valid for electrons in atoms and molecules • The photon has a spin of 1 ...
Chapter 6: Electronic Structure of Atoms Recommended Text
... Although we cannot precisely define an electron’s orbit, we can obtain the probability of finding an electron at a given point around the nucleus. ...
... Although we cannot precisely define an electron’s orbit, we can obtain the probability of finding an electron at a given point around the nucleus. ...
Chapter 6
... Spin Quantum Number Symbolized by ms Indicates the fundamental spin states of an electron in an orbital Values are + ½ and -1/2 ...
... Spin Quantum Number Symbolized by ms Indicates the fundamental spin states of an electron in an orbital Values are + ½ and -1/2 ...
Optically polarized atoms_ch_2_old
... In classical physics, to fully specify orbital angular momentum, one needs two more parameters (e.g., to angles) in addition to the magnitude In QM, if we know projection on one axis (quantization axis), projections on other two axes are uncertain ...
... In classical physics, to fully specify orbital angular momentum, one needs two more parameters (e.g., to angles) in addition to the magnitude In QM, if we know projection on one axis (quantization axis), projections on other two axes are uncertain ...
Atomic Structure
... • When the atom gains energy, the electron leaps to a higher energy orbit. We call this an excited state. • The atom is less stable in an excited state and so it will release the extra energy to return to the ground state. – Either all at once or in several steps. ...
... • When the atom gains energy, the electron leaps to a higher energy orbit. We call this an excited state. • The atom is less stable in an excited state and so it will release the extra energy to return to the ground state. – Either all at once or in several steps. ...
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).