Artificial atoms
... In a natural atom one has little control over the spectrum of energies for adding or removing electrons. There the electrons interact with the fixed potential of the nucleus and with each other, and these two kinds of interaction determine the spectrum. In an artificial atom, however, one can change ...
... In a natural atom one has little control over the spectrum of energies for adding or removing electrons. There the electrons interact with the fixed potential of the nucleus and with each other, and these two kinds of interaction determine the spectrum. In an artificial atom, however, one can change ...
2010 Spring - Jonathan Whitmore
... An electron is emitted from the wire with velocity v0 ≈ c in the (cylindrical) radial direction. Neglecting radiation and image charge effects in the grounded wire, find the maximum distance R that the electron travels from the wire before returning. Assume the motion can be treated with classical m ...
... An electron is emitted from the wire with velocity v0 ≈ c in the (cylindrical) radial direction. Neglecting radiation and image charge effects in the grounded wire, find the maximum distance R that the electron travels from the wire before returning. Assume the motion can be treated with classical m ...
Ultracold Hydrogen—D. Kleppner, T. J. Greytak
... magnet by collisions with a buffer gas of 3He. The buffer gas is confined in a cell at a temperature of about 300 mK. Thermalization with the buffer gas causes the atoms to be trapped in the quadrupole, which forms a magnetic trap with a depth of about 2.8 K. A valve is then opened allowing the 3He ...
... magnet by collisions with a buffer gas of 3He. The buffer gas is confined in a cell at a temperature of about 300 mK. Thermalization with the buffer gas causes the atoms to be trapped in the quadrupole, which forms a magnetic trap with a depth of about 2.8 K. A valve is then opened allowing the 3He ...
$doc.title
... a particle of mass m M which comes under the graviational influence of a mass M . Assume the particle approaches from infinity with the velocity V and an impact parameter b . a. Find the ...
... a particle of mass m M which comes under the graviational influence of a mass M . Assume the particle approaches from infinity with the velocity V and an impact parameter b . a. Find the ...
Study Guide Summative Exam The following represent the
... The following represent the performance indicators around which I will create your test questions. You should expect to demonstrate your knowledge through free response questions. Chapter 3 spi 3221 1.1 Compare and contrast the major models of the atom (eg. Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr, and the ...
... The following represent the performance indicators around which I will create your test questions. You should expect to demonstrate your knowledge through free response questions. Chapter 3 spi 3221 1.1 Compare and contrast the major models of the atom (eg. Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr, and the ...
Chemistry I Review - BarbaraElam-Rice
... 30) An atom has 2 electrons in its valence shell. To what group does the atom belong? Will the atom for an anion or a cation? What will be the oxidation number of the ion? 31) An intermolecular force that holds ionic compounds together is called electrostatic attraction. 32) Describe the 3 intermole ...
... 30) An atom has 2 electrons in its valence shell. To what group does the atom belong? Will the atom for an anion or a cation? What will be the oxidation number of the ion? 31) An intermolecular force that holds ionic compounds together is called electrostatic attraction. 32) Describe the 3 intermole ...
Presentation Lesson 27 Quantum Physics
... frequency, and carries away energy from the electron – Electron predicted to continually lose energy – The electron would eventually spiral into the nucleus ...
... frequency, and carries away energy from the electron – Electron predicted to continually lose energy – The electron would eventually spiral into the nucleus ...
Q.25. Draw a plot of binding energy per nucleon (BE/A) vs. mass
... All questions are compulsory. There are 30 questions in total. Questions 1 to 8 carry one marks each, questions 9 to 18 carry two marks each, questions 19 to 27 carry three marks each and questions 28 to 30 carry five marks each. There is no overall choice. However, an interval choice has been provi ...
... All questions are compulsory. There are 30 questions in total. Questions 1 to 8 carry one marks each, questions 9 to 18 carry two marks each, questions 19 to 27 carry three marks each and questions 28 to 30 carry five marks each. There is no overall choice. However, an interval choice has been provi ...
Optical Pumping of Rubidium Vapor
... gF = 0.342 ± .0001 and Bearth = 0.421 ± .002. We also looked for evidence of power broadening and compared our lineshapes to Guassian, Lorentzian and Voigt profiles. The technique of optical pumping which we used was discovered in a series of work by Alfred Kastler in the 1940s, for which he would w ...
... gF = 0.342 ± .0001 and Bearth = 0.421 ± .002. We also looked for evidence of power broadening and compared our lineshapes to Guassian, Lorentzian and Voigt profiles. The technique of optical pumping which we used was discovered in a series of work by Alfred Kastler in the 1940s, for which he would w ...
Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms
... (d).νλ = c 44. In the Bohr model of the atom, __________. (a). electrons travel in circular paths called orbitals (b). electrons can have any energy (c). electron energies are quantized (d). electron paths are controlled by probability 45. According to the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle, it is imp ...
... (d).νλ = c 44. In the Bohr model of the atom, __________. (a). electrons travel in circular paths called orbitals (b). electrons can have any energy (c). electron energies are quantized (d). electron paths are controlled by probability 45. According to the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle, it is imp ...
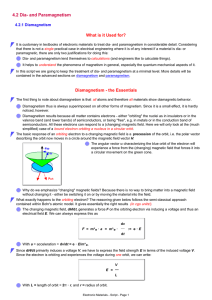
Flexbook - The Bohr Model of the Atom
... hypothesis also made predictions about emissions that had not yet been observed (the infrared light emissions). Predicted observations such as these provide an opportunity to test the hypothesis through experimentation. When these predictions were found to be correct, they provided evidence in suppo ...
... hypothesis also made predictions about emissions that had not yet been observed (the infrared light emissions). Predicted observations such as these provide an opportunity to test the hypothesis through experimentation. When these predictions were found to be correct, they provided evidence in suppo ...
Final Exam Study Guide Chapters 1-12
... ____ 48. Across a period, ionization energies of d-block elements generally a. increase. c. remain constant. b. decrease. d. drop to zero. ____ 49. The first electrons to be removed when d-block elements form ions are the a. d electrons. c. s electrons. b. p electrons. d. f electrons. ____ 50. The c ...
... ____ 48. Across a period, ionization energies of d-block elements generally a. increase. c. remain constant. b. decrease. d. drop to zero. ____ 49. The first electrons to be removed when d-block elements form ions are the a. d electrons. c. s electrons. b. p electrons. d. f electrons. ____ 50. The c ...
x - Piazza
... “down the drain” into a blind alley from which nobody has yet escaped. Nobody knows how it can be like that. - Richard Feynman Those who are not shocked when they first come across quantum mechanics cannot possibly have understood it. Richard Feynman (1918-1988) ...
... “down the drain” into a blind alley from which nobody has yet escaped. Nobody knows how it can be like that. - Richard Feynman Those who are not shocked when they first come across quantum mechanics cannot possibly have understood it. Richard Feynman (1918-1988) ...
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).