Quantum energy distribution function of hot electrons in
... devoted to the analysis of hot electron phenomena in the presence of a magnetic field. However, only in very few of them [2] has a quantum theoretical calculation of the stationary electron distribution function (E.D.F.), in the limit of high electric and magnetic fields, been carried out without in ...
... devoted to the analysis of hot electron phenomena in the presence of a magnetic field. However, only in very few of them [2] has a quantum theoretical calculation of the stationary electron distribution function (E.D.F.), in the limit of high electric and magnetic fields, been carried out without in ...
Optomechanics Experiments
... The radiation pressure force couples the optical field to mirror motion ...
... The radiation pressure force couples the optical field to mirror motion ...
Physics 171.303: Quantum Mechanics I Fall Semester, 2014 Course
... Overview: This course is the first semester of a two-semester course providing an introduction of quantum mechanics, covering non-commuting observables, angular momentum, two-state systems, time evolution, the wave equation in one dimension, and the simple harmonic oscillator. Prerequisites: Physics ...
... Overview: This course is the first semester of a two-semester course providing an introduction of quantum mechanics, covering non-commuting observables, angular momentum, two-state systems, time evolution, the wave equation in one dimension, and the simple harmonic oscillator. Prerequisites: Physics ...
Chapter 10 Notes
... Transitions from higher energy levels to the first excited state (n = 2) result in the emission of visible photons. This series is referred to as the Balmer series. Transitions from higher levels to n = 3 result in the emission of infrared photons. This series is referred to as the Paschen serie ...
... Transitions from higher energy levels to the first excited state (n = 2) result in the emission of visible photons. This series is referred to as the Balmer series. Transitions from higher levels to n = 3 result in the emission of infrared photons. This series is referred to as the Paschen serie ...
Chapter 4 Arrangements of Electrons in Atoms
... with period 3: 1. Find the period the element in question is in. 2. Locate the closest noble gas (must have fewer electrons than the element in question). 3. Write the symbol of the noble gas in brackets (This represents ‘x’ number of electrons). 4. Continue the notation with the principal energy le ...
... with period 3: 1. Find the period the element in question is in. 2. Locate the closest noble gas (must have fewer electrons than the element in question). 3. Write the symbol of the noble gas in brackets (This represents ‘x’ number of electrons). 4. Continue the notation with the principal energy le ...
1.1.3 (a) Prove that (AB)` = BAt using components
... In the preceding review of matrices the ideas of projection operators and spectral decompositions were introduced. In this chapter we shall see how frequency spectra of physical systems are analyzed in terms of mathematical spectral decompositions. Mathematical concepts will be introduced in this an ...
... In the preceding review of matrices the ideas of projection operators and spectral decompositions were introduced. In this chapter we shall see how frequency spectra of physical systems are analyzed in terms of mathematical spectral decompositions. Mathematical concepts will be introduced in this an ...
Document
... • Symmetry properties and conservation laws to extract dependence of matrix elements inside the band on quantum numbers ...
... • Symmetry properties and conservation laws to extract dependence of matrix elements inside the band on quantum numbers ...
final1-273711-quantumdots-final-report-30-06-2013
... processor nodes (spins) connected by photons. A particularly interesting platform is a spin based semiconductor system in which photonic circuits that interconnect the nodes can be fabricated on the same semiconductor chip. Despite the appeal of semiconductor based systems the realization of spin-ph ...
... processor nodes (spins) connected by photons. A particularly interesting platform is a spin based semiconductor system in which photonic circuits that interconnect the nodes can be fabricated on the same semiconductor chip. Despite the appeal of semiconductor based systems the realization of spin-ph ...
Lecture 22 Relevant sections in text: §3.1, 3.2 Rotations in quantum mechanics
... a purely quantum mechanical possibility and has important physical consequences. Incidentally, your text book fails to allow for this phase freedom in the general definition of representation of rotations. This is a pedagogical error, and an important one at that. This error is quite ironic: the fir ...
... a purely quantum mechanical possibility and has important physical consequences. Incidentally, your text book fails to allow for this phase freedom in the general definition of representation of rotations. This is a pedagogical error, and an important one at that. This error is quite ironic: the fir ...
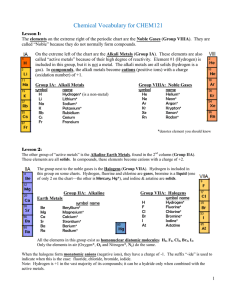
Vocabulary CHEM121
... Note the heavy stair-step line drawn between elements B & Al, etc. This line separates the metals (lower left) from the non-metals (upper right). Metals can only form cations. Non-metals form anions when combined with metals. Elements that touch the line are called metalloids (except Al, which ...
... Note the heavy stair-step line drawn between elements B & Al, etc. This line separates the metals (lower left) from the non-metals (upper right). Metals can only form cations. Non-metals form anions when combined with metals. Elements that touch the line are called metalloids (except Al, which ...
What Could You Do With A Quantum Computer?
... program to follow out...and I'm not happy with all the analyses that go with just the classical theory, because nature isn’t classical, dammit, and if you want to make a simulation of nature, you'd better make it quantum mechanical, and by golly it's a wonderful problem because it doesn't look so ea ...
... program to follow out...and I'm not happy with all the analyses that go with just the classical theory, because nature isn’t classical, dammit, and if you want to make a simulation of nature, you'd better make it quantum mechanical, and by golly it's a wonderful problem because it doesn't look so ea ...
PowerPoint - Subir Sachdev
... What is the ground state for large U/t ? Incompressible, insulating ground states, with zero superfluid density, appear at special commensurate densities ...
... What is the ground state for large U/t ? Incompressible, insulating ground states, with zero superfluid density, appear at special commensurate densities ...
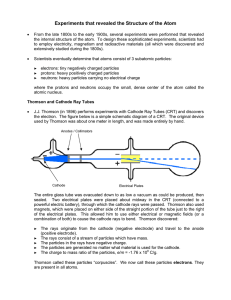
ARE THERE REALLY ELECTRONS? EXPERIMENT AND REALITY
... fundamental particle and a constituent of atoms. Bohr began with Rutherford's nuclear model of the atom, with a small, massive, positively charged nucleus orbited by electrons of mass m and charge - e. Noting that classical electrodynamics would not allow such a system to be stable, he postulated th ...
... fundamental particle and a constituent of atoms. Bohr began with Rutherford's nuclear model of the atom, with a small, massive, positively charged nucleus orbited by electrons of mass m and charge - e. Noting that classical electrodynamics would not allow such a system to be stable, he postulated th ...
Physics 125b – Problem Set 13 – Due Feb 26,... Version 1 – Feb 21, 2008
... spherical tensor states and operators; Shankar Chapter 15 and Lecture Notes 15. It is clear that the last two weeks have been very rough going for much of the class. Rotations and angular momentum are, in my experience, the toughest part of quantum mechanics because one has to deal with so many fore ...
... spherical tensor states and operators; Shankar Chapter 15 and Lecture Notes 15. It is clear that the last two weeks have been very rough going for much of the class. Rotations and angular momentum are, in my experience, the toughest part of quantum mechanics because one has to deal with so many fore ...
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).