From the Mendeleev periodic table to particle physics and back to
... by J. Chadwick in 1932. A nucleus is made of protons and neutrons, collectively denoted as nucleons. A proton has a positive electric charge, which is the opposite of the electronic charge of the electron, and the neutron has no electric charge. The discovery of a substructure for the nucleus opened ...
... by J. Chadwick in 1932. A nucleus is made of protons and neutrons, collectively denoted as nucleons. A proton has a positive electric charge, which is the opposite of the electronic charge of the electron, and the neutron has no electric charge. The discovery of a substructure for the nucleus opened ...
Superselection Rules - Philsci
... due to the existence of a conserved quantity. Well known SRs in Quantum Mechanics concern radiative transitions of atoms. For example, in case of electric dipole radiation they take the form ∆J = 0, ±1 (except J = 0 → J = 0) and ∆MJ = 0, ±1. It says that the quantum numbers J, MJ associated with the ...
... due to the existence of a conserved quantity. Well known SRs in Quantum Mechanics concern radiative transitions of atoms. For example, in case of electric dipole radiation they take the form ∆J = 0, ±1 (except J = 0 → J = 0) and ∆MJ = 0, ±1. It says that the quantum numbers J, MJ associated with the ...
Title Goes Here
... agree very well with free-pariticle calculations, but surprisingly not with more advanced calculations including many-body Coulomb interactions. The sample structure of an n-type doped GaAs quantum wire is illustrated in Fig. 1. A single T-shaped quantum wire was formed at the cross-sectional area o ...
... agree very well with free-pariticle calculations, but surprisingly not with more advanced calculations including many-body Coulomb interactions. The sample structure of an n-type doped GaAs quantum wire is illustrated in Fig. 1. A single T-shaped quantum wire was formed at the cross-sectional area o ...
Energy and Electron Transfer
... Reference: www.chem.unc.edu/undergrads/2002fall/chem145_murray/classnotes/ETtheory.pdf ...
... Reference: www.chem.unc.edu/undergrads/2002fall/chem145_murray/classnotes/ETtheory.pdf ...
READ MORE
... Ordinary bits in classical computers are in a state of 1 or 0, but quantum bits can be 1, 0 or both 1 and 0. This indefinite state is called superposition, and it is achieved in D-Wave’s quantum processor for very brief periods of time only by isolating the chip from all outside interference. Decohe ...
... Ordinary bits in classical computers are in a state of 1 or 0, but quantum bits can be 1, 0 or both 1 and 0. This indefinite state is called superposition, and it is achieved in D-Wave’s quantum processor for very brief periods of time only by isolating the chip from all outside interference. Decohe ...
Chapter 1. Introduction to Nuclear Physics
... Remember that the binding energy is a measure of the interaction among nucleons. Since nucleons are closely packed in the nucleus and the nuclear force has a very short range, each nucleon ends up interacting only with a few neighbors. This means that independently of the total number of nucleons, e ...
... Remember that the binding energy is a measure of the interaction among nucleons. Since nucleons are closely packed in the nucleus and the nuclear force has a very short range, each nucleon ends up interacting only with a few neighbors. This means that independently of the total number of nucleons, e ...
Lec5_Resonant_EM_interactions_atmospheres
... This a simple 2 atom molecule which is asymmetric so the dumbbell rotational model works. The rotational spectrum consists of approximately equally spaced rotational absorption lines spaced about 110 GHz apart. The isotopes like CO18 have very similar spectra. There will be a homework problem on thi ...
... This a simple 2 atom molecule which is asymmetric so the dumbbell rotational model works. The rotational spectrum consists of approximately equally spaced rotational absorption lines spaced about 110 GHz apart. The isotopes like CO18 have very similar spectra. There will be a homework problem on thi ...
Doppler effect and frequency
... Here π and π † are ladder operators for internal two-levels, and a and a† are the annihilation and creation operators respectively of the radiation field. The operator f(R ) arises from the dipole interaction term -eE.r. Comparing Eq. (21) with Fermi’s theory, Eqs. (15) and (16) it is straightforwar ...
... Here π and π † are ladder operators for internal two-levels, and a and a† are the annihilation and creation operators respectively of the radiation field. The operator f(R ) arises from the dipole interaction term -eE.r. Comparing Eq. (21) with Fermi’s theory, Eqs. (15) and (16) it is straightforwar ...
The development of Physics and Modern Physics
... A positively charged particle attracts a negatively charged particle, tending to accelerate one toward the other. If the medium through which the particle moves offers resistance to that motion, this may be reduced to a constant-velocity (rather than accelerated) motion, and the medium will be heate ...
... A positively charged particle attracts a negatively charged particle, tending to accelerate one toward the other. If the medium through which the particle moves offers resistance to that motion, this may be reduced to a constant-velocity (rather than accelerated) motion, and the medium will be heate ...
Transition Probability (Fidelity) and its Relatives
... The topic of the paper concerns transition probability and fidelity for general (i. e. mixed) states and some of its descendants. It belongs, metaphorically spoken, to the “skeleton” or to the “grammar” of Quantum Physics in which dynamics does not play a significant role. The needs of Quantum Infor ...
... The topic of the paper concerns transition probability and fidelity for general (i. e. mixed) states and some of its descendants. It belongs, metaphorically spoken, to the “skeleton” or to the “grammar” of Quantum Physics in which dynamics does not play a significant role. The needs of Quantum Infor ...
Joseph Henry Project Thermoelectric Battery
... 3. Free Electron Gas Model This model includes both free electron assumption and independent electron assumption. That means we assume no electron-ion and electron-electron interactions. With this simple model, the relationship between seebeck effect and temperature is sought. ...
... 3. Free Electron Gas Model This model includes both free electron assumption and independent electron assumption. That means we assume no electron-ion and electron-electron interactions. With this simple model, the relationship between seebeck effect and temperature is sought. ...
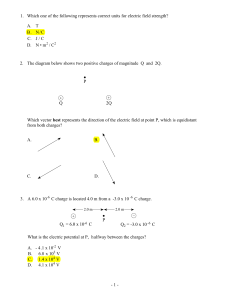
1. Which one of the following represents correct units for electric field
... 26. An object with a charge of + 4. 0 × 10 −18 C and a mass of 1.1 × 10 −15 kg is held stationary by balanced gravitational and electric forces midway between horizontal charged plates as shown. What is the applied voltage V ? ...
... 26. An object with a charge of + 4. 0 × 10 −18 C and a mass of 1.1 × 10 −15 kg is held stationary by balanced gravitational and electric forces midway between horizontal charged plates as shown. What is the applied voltage V ? ...
Modern Physics. Edition No. 2 Brochure
... physics. Beginning with a brief and focused account of the historical events leading to the formulation of modern quantum theory, later chapters delve into the underlying physics. Streamlined content, chapters on semiconductors, Dirac equation and quantum field theory, as well as a robust pedagogy a ...
... physics. Beginning with a brief and focused account of the historical events leading to the formulation of modern quantum theory, later chapters delve into the underlying physics. Streamlined content, chapters on semiconductors, Dirac equation and quantum field theory, as well as a robust pedagogy a ...
Details of Approved Courses For Mphil/Ms, Mphil Leading To Phd
... Writing data. Concept of Loops, Pretest and Post-test Loops, Initialization and updating, Event Control and C()LlJ1ter Control, Loops in C++, Other statements related to loops. Pointers: Concepts, Pointer variables, accessing variables through pointers, pointer definition and declaration, Initializ ...
... Writing data. Concept of Loops, Pretest and Post-test Loops, Initialization and updating, Event Control and C()LlJ1ter Control, Loops in C++, Other statements related to loops. Pointers: Concepts, Pointer variables, accessing variables through pointers, pointer definition and declaration, Initializ ...
Sixth lecture, 11.11.03 (BECs, lasers, superselection rules and
... measured their momenta to discern which cloud each came from. • Only after detecting an atom in such a way that it's impossible to tell which cloud it came from do the atom numbers of the two clouds become entangled, giving rise to coherence. • As soon as one atom is detected, there is some coherenc ...
... measured their momenta to discern which cloud each came from. • Only after detecting an atom in such a way that it's impossible to tell which cloud it came from do the atom numbers of the two clouds become entangled, giving rise to coherence. • As soon as one atom is detected, there is some coherenc ...
LAWS, RULES, PRINCIPLES, EFFECTS, PARADOXES, LIMITS,
... The volume of an ideal gas at constant pressure is proportional tothe thermodynamic temperature of that gas. Cherenkov radiation (P.A. Cherenkov) Radiation emitted by a massive particle which is moving fasterthan light in the medium through which it is travelling. Noparticle can travel faster than l ...
... The volume of an ideal gas at constant pressure is proportional tothe thermodynamic temperature of that gas. Cherenkov radiation (P.A. Cherenkov) Radiation emitted by a massive particle which is moving fasterthan light in the medium through which it is travelling. Noparticle can travel faster than l ...
- Natural Sciences Publishing
... relevance to the study of the nonlinear coupling between a two-level atom and the radiation field [6, 7, 8, 9, 10]. Much work has been concentrated to the theoretical study of the dissipative JC model [11, 12, 13] by considering cavities losses and atomic decay. Also, there are some experiments that ...
... relevance to the study of the nonlinear coupling between a two-level atom and the radiation field [6, 7, 8, 9, 10]. Much work has been concentrated to the theoretical study of the dissipative JC model [11, 12, 13] by considering cavities losses and atomic decay. Also, there are some experiments that ...
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).